Tomcat由多个组件组成,那么Tomcat是怎么对他们的生命周期进行管理的么,这里将从Tomcat源码去分析其生命周期的实现;
Bootstrape类为Tomcat的入口,所有的组件够通过实现Lifecycle接口来管理生命周期,Tomcat启动的时候只需调用Server容器的start(),然后父容器依序启动他所包含的子容器,关闭也是如此。
通过阅读源码可知一个Server里包含一个或多个Service,一个Service里包含一个Container,一个或多个Connector、Container又包含了Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper四个容器;
Tomcat的组件启动顺序为:
StandardServer.start()——》StandardServer.startInternal() ——》StandardService().start()——StandardService.startInternal() ——>》StandardEngine().start() ——》StandardEngine.startInternal()—》StandardEngine中启动其他组件,组件关闭也是如此;
现在我们通过Demo简单模拟Tomcat的启动
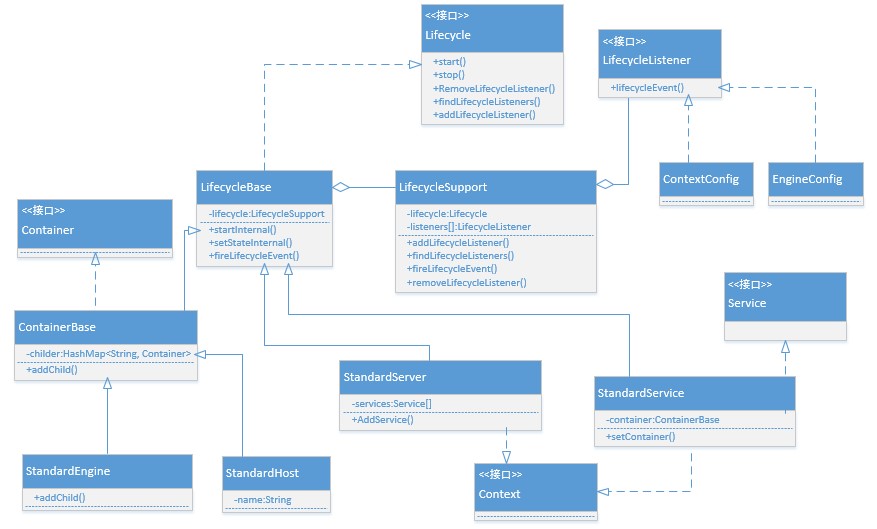
模拟Demo UML类图
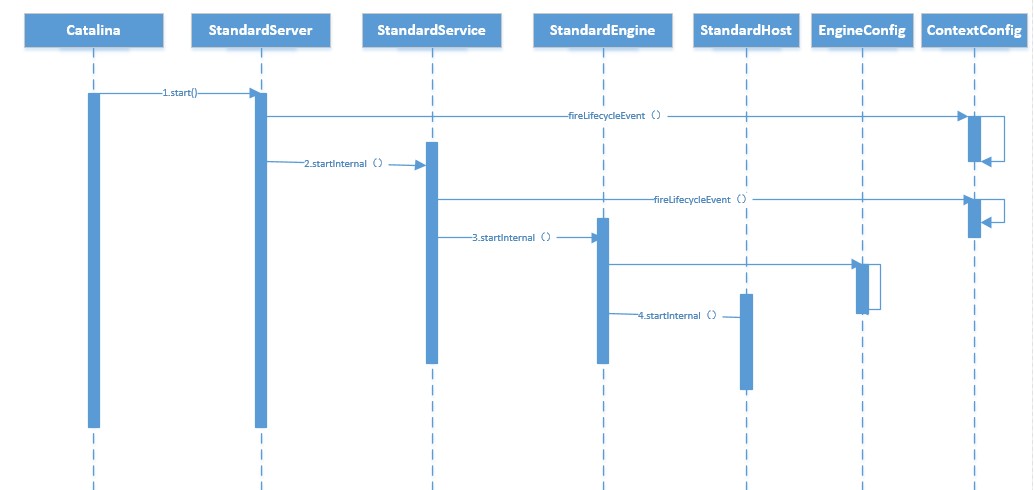
模拟Demo时序图
主要代码段如下:
Catalina类:
package co.solinx.Pattern.Observer;
/**
* Created by LX on 2014/11/26.
*/
public class Catalina {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Tomcat为多个组件组成的server为最外围最大的一个
StandardServer server = new StandardServer();
//为server添加监听器
server.addLifecycleListener(new ContextConfig());
//添加一个service
StandardService service = new StandardService();
server.AddService(service);
//为service添加监听器
service.addLifecycleListener(new ContextConfig());
//添加一个engine
StandardEngine standardEngine = new StandardEngine();
//为engine添加监听器
standardEngine.addLifecycleListener(new EngineConfig());
StandardHost standardHost = new StandardHost("localhost");
// StandardHost testHost = new StandardHost("test");
// standardHost.addLifecycleListener(new EngineConfig());
standardEngine.addChild("localhost", standardHost);
// standardEngine.addChild("test", testHost);
//往service添加engine容器
service.setContainer(standardEngine);
try {
server.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
StandardServer类
package co.solinx.Pattern.Observer;
/**
* Created by LX on 2014/11/26.
*/
public class StandardServer extends LifecycleBase implements Context {
Service services[] = new Service[0];
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].start();
}
System.out.println("StandardServer start");
}
public void AddService(Service service) {
Service result[] = new Service[services.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(services, 0, result, 0, services.length);
result[services.length] = service;
services = result;
}
}
StandardService类:
package co.solinx.Pattern.Observer;
/**
* Created by LX on 2014/11/26.
*/
public class StandardService extends LifecycleBase implements Service, Context {
protected ContainerBase container = null;
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
container.start();
System.out.println("StandardService start");
}
public void setContainer(ContainerBase container) {
this.container = container;
}
}
StandardEngine类:
package co.solinx.Pattern.Observer;
/**
* Created by LX on 2014/11/26.
*/
public class StandardEngine extends ContainerBase {
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.startInternal();
System.out.println("StandardEngine start");
}
protected void addChild(String key, Container container) {
super.addChild(key, container);
}
}
LifecycleSupport类:
package co.solinx.Pattern.Observer;
/**
* Created by LX on 2014/11/26.
* 代理了具体监听者
*/
public class LifecycleSupport {
public LifecycleSupport(Lifecycle lifecycle) {
super();
this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
}
private Lifecycle lifecycle = null;
private LifecycleListener listeners[] = new LifecycleListener[0];
private final Object listenersLock = new Object(); // Lock object for changes to listeners
public void addLifecycleListener(LifecycleListener listener) {
synchronized (listenersLock) {
LifecycleListener results[] =
new LifecycleListener[listeners.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++)
results[i] = listeners[i];
results[listeners.length] = listener;
listeners = results;
}
}
public LifecycleListener[] findLifecycleListeners() {
return listeners;
}
public void fireLifecycleEvent(String type, Object data) {
LifecycleEvent event = new LifecycleEvent(lifecycle, type, data);
LifecycleListener interested[] = listeners;
for (int i = 0; i < interested.length; i++)
interested[i].lifecycleEvent(event);
}
public void removeLifecycleListener(LifecycleListener listener) {
synchronized (listenersLock) {
int n = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
if (listeners[i] == listener) {
n = i;
break;
}
}
if (n < 0)
return;
LifecycleListener results[] =
new LifecycleListener[listeners.length - 1];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
if (i != n)
results[j++] = listeners[i];
}
listeners = results;
}
}
}
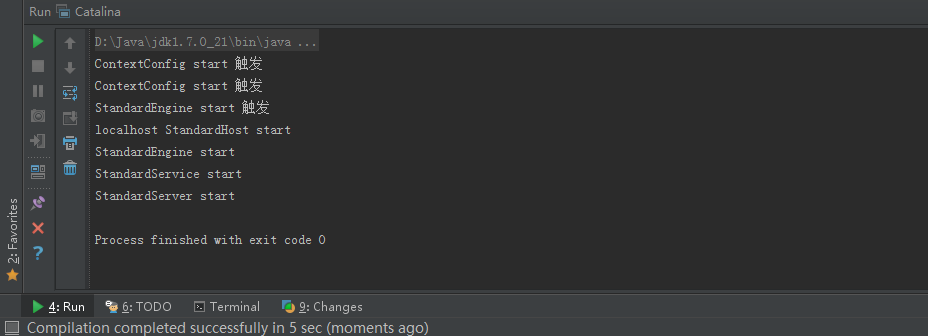
模拟程序运行结果:
文章首发地址:Solinx
http://www.solinx.co/archives/86