Rooted Trees
A graph G = (V, E) is a data structure where V is a finite set of vertices and E is a binary relation on Vrepresented by a set of edges. Fig. 1 illustrates an example of a graph (or graphs).
Fig. 1
A free tree is a connnected, acyclic, undirected graph. A rooted tree is a free tree in which one of the vertices is distinguished from the others. A vertex of a rooted tree is called "node."
Your task is to write a program which reports the following information for each node u of a given rooted tree T:
- node ID of u
- parent of u
- depth of u
- node type (root, internal node or leaf)
- a list of chidlren of u
If the last edge on the path from the root r of a tree T to a node x is (p, x), then p is the parent of x, and xis a child of p. The root is the only node in T with no parent.
A node with no children is an external node or leaf. A nonleaf node is an internal node
The number of children of a node x in a rooted tree T is called the degree of x.
The length of the path from the root r to a node x is the depth of x in T.
Here, the given tree consists of n nodes and evey node has a unique ID from 0 to n-1.
Fig. 2 shows an example of rooted trees where ID of each node is indicated by a number in a circle (node). The example corresponds to the first sample input.
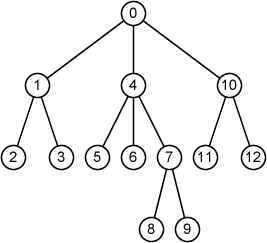
Fig. 2
Input
The first line of the input includes an integer n, the number of nodes of the tree.
In the next n lines, the information of each node u is given in the following format:
id k c1 c2 ... ck
where id is the node ID of u, k is the degree of u, c1 ... ck are node IDs of 1st, ... kth child of u. If the node does not have a child, the k is 0.
Output
Print the information of each node in the following format ordered by IDs:
node id: parent = p , depth = d, type, [c1...ck]
p is ID of its parent. If the node does not have a parent, print -1.
d is depth of the node.
type is a type of nodes represented by a string (root, internal node or leaf). If the root can be considered as a leaf or an internal node, print root.
c1...ck is the list of children as a ordered tree.
Please follow the format presented in a sample output below.
Constraints
- 1 ≤ n ≤ 100000
Sample Input 1
13 0 3 1 4 10 1 2 2 3 2 0 3 0 4 3 5 6 7 5 0 6 0 7 2 8 9 8 0 9 0 10 2 11 12 11 0 12 0
Sample Output 1
node 0: parent = -1, depth = 0, root, [1, 4, 10] node 1: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [2, 3] node 2: parent = 1, depth = 2, leaf, [] node 3: parent = 1, depth = 2, leaf, [] node 4: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [5, 6, 7] node 5: parent = 4, depth = 2, leaf, [] node 6: parent = 4, depth = 2, leaf, [] node 7: parent = 4, depth = 2, internal node, [8, 9] node 8: parent = 7, depth = 3, leaf, [] node 9: parent = 7, depth = 3, leaf, [] node 10: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [11, 12] node 11: parent = 10, depth = 2, leaf, [] node 12: parent = 10, depth = 2, leaf, []
Sample Input 2
4 1 3 3 2 0 0 0 3 0 2 0
Sample Output 2
node 0: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, [] node 1: parent = -1, depth = 0, root, [3, 2, 0] node 2: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, [] node 3: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, []
Note
You can use a left-child, right-sibling representation to implement a tree which has the following data:
- the parent of u
- the leftmost child of u
- the immediate right sibling of u
Reference
Introduction to Algorithms, Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. The MIT Press.
有根树的存储, 根据数据看出不是二叉树, 故用孩子兄弟表示法存储(左孩子, 右兄弟)
利用递归求树的深度时, 若是左孩子则深度加一, 右孩子(兄弟节点)还是当前深度
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100005
#define NIL -1
struct Node {
int parent;
int left;
int right;
};
Node T[MAX];
int n, D[MAX];
void print(int u)
{
int i, c;
cout << "node " << u << ": ";
cout << "parent = " << T[u].parent << ", ";
cout << "depth = " << D[u] << ", ";
if(T[u].parent == NIL)
{
cout << "root, ";
}
else if(T[u].left == NIL)
{
cout << "leaf, ";
}
else
{
cout << "internal node, ";
}
cout << "[";
for(i = 0, c = T[u].left; c != NIL; ++ i, c = T[c].right)
{
if(i) cout << ", ";
cout << c;
}
cout << "]" << endl;
}
// 递归求深度
void rec(int u, int p)
{
D[u] = p;
if(T[u].right != NIL)
{
rec(T[u].right, p);
}
if(T[u].left != NIL)
{
rec(T[u].left, p + 1);
}
}
int main()
{
int i, j, d, v, c, l, r;
cin >> n;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
T[i].parent = T[i].left = T[i].right = NIL;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
cin >> v >> d;
for(j = 0; j < d; ++ j)
{
cin >> c;
if(j == 0)
{
T[v].left = c; // 父节点的左孩子为c
}
else
{
T[l].right = c; // 当前兄弟节点为c
}
l = c; // 记录前一个兄弟节点
T[c].parent = v;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
if(T[i].parent == NIL)
{
r = i;
}
}
rec(r, 0);
for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
print(i);
}
return 0;
}
/*
13
0 3 1 4 10
1 2 2 3
2 0
3 0
4 3 5 6 7
5 0
6 0
7 2 8 9
8 0
9 0
10 2 11 12
11 0
12 0
*/