原型链、继承--Mr.Ember
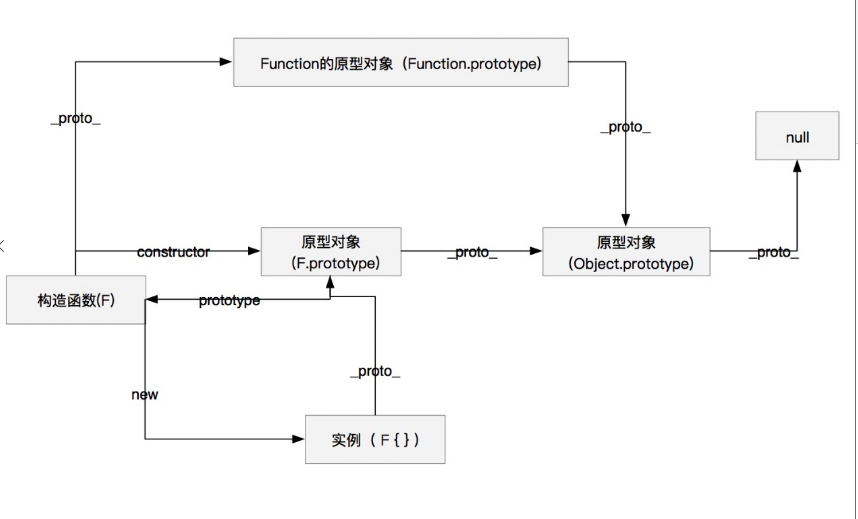
构造函数、原型对象和实例之间的关系
functionF(){}; var f = new F(); // 构造器 F.prototype.constructor === F; // true F.__proto__ === Function.prototype; // true Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype; // true Object.prototype.__proto__ === null; // true // 实例 f.__proto__ === F.prototype; // true F.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype; // true Object.prototype.__proto__ === null; // true
图示表示如下
ES6 extends继承做了什么操作
class Parent{ constructor(name) { this.name = name; } static sayHello() { console.log('hello') } sayName() { console.log('name is' + this.name) return this.name } } class Child extends Parent{ constructor(name, age) { super(name) this.age = age; } sayAge() { console.log('age is' + this.age) return this.age } } let parent = new Parent('Parent1'); let child = new Child('Child1', 18); console.log('parent:' + parent); //parent:[object Object] Parent.sayHello(); //hello parent.sayName(); //name is Parent1 console.log('child:' + child); //child:[object Object] Child.sayHello(); //hello child.sayName(); //name is Child1 child.sayAge(); //age is 18
代码中有两条原型链
// 1、构造器原型链 Child.__proto__ === Parent; // true Parent.__proto__ === Function.prototype; // true Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype; // true Object.prototype.__proto__ === null; // true // 2、实例原型链 child.__proto__ === Child.prototype; // true Child.prototype.__proto__ === Parent.prototype; // true Parent.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype; // true Object.prototype.__proto__ === null; // true
此时两条链如下图所示关系

结合代码知道,ES6extends继承,主要是:
1. 把子类构造函数(Child)的原型(__proto__)指向了父类构造函数(Parent)
2. 把子类实例child的原型对象(Child.prototype)的原型(__proto__)指向了父类parent的原型对象(Parent.prototype)
3. 子类构造函数Child继承了父类的构造函数Parent的属性。使用super调用的(es5则用call或者apply调用传参)
设置proto
new、Object.create和Object.setPrototypeof可以设置__proto__
__proto__是浏览器厂商自己实现的
new出来的实例的__proto__指向构造函数的prototype,这就是new做的事
new做了什么
(1)创建一个全新的对象
(2)这个对象会被执行[[prototype]](也就是__proto__)链接
(3)生成的新的对象会绑定到函数调用this
(4)通过new创建的新对象将最终被[[Prototype]]链接到这个函数的prototype对象上
(5)如果函数没有返回对象类型Object(包含Function,Array,Date,RegExg,Error),那么new表达式中的函数
会自动返回这个新的对象。
Object.create: ES5提供的
Object.create(proto,[propertiesObject])方法创建一个新对象,使用现有的对象来提供新创建的对象的__proto__
它接受两个参数,不过第二个可选参数是属性描述符(不常用,默认undefined)。对于不支持ES5的浏览器可以使用ployfill方案: MDN Object.create()
//简版:应用new会设置__proto__链接的原理 兼容ES5以前版本 if(typeof Object.create !=='function') { Object.create = function(proto) { function F() {} F.prototype = proto; return new F(); } }
Object.setPropertyOf: ES6提供的
Object.setPropertyOf() 方法设置一个指定的对象原型(即内部[[Prototype]]属性)到另一个对象或null:Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, prototype)
// 仅适用于Chrome和FireFox,在IE中不工作: Object.setPrototypeOf = Object.setPrototypeOf || function(obj, proto) { obj.__proto__ = proto; return obj; }
extends的ES5版本实现
知道了ES6
extends继承做了什么操作和设置 __proto__的知识点后,把上面 ES6例子的用 ES5就比较容易实现了,也就是说实现寄生组合式继承,简版代码就是:function Parent(name) { this.name = name; } Parent.sayHello = function() { console.log('hello') } Parent.prototype.sayName = function() { console.log('name is' + this.name); return this.name; } function Child(name, age) { // 相当于super Parent.call(this, name); //绑定this 继承Parent的属性 this.age = age; } //new function object() { //兼容es5的new新对象问题 function F() {} F.prototype = proto; return new F(); } function _inherits(Child, Parent) { //object.create Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype); //__proto__ //Child.prototype.__proto__ = Parent.prototype; Child.prototype.constructor = Child; //ES6 //Object.setPrototypeof(Child, Parent); //__proto__ Child.__proto__ = Parent; } _inherits(Child, Parent) Child.prototype.sayAge = function() { console.log('age is' + this.age) return this.age; } var parent = new Parent('parent2') var child = new Child('Child2', 18)
寄生组合式继承是开发者使用较多的继承方式。