设计模式 - 开闭原则
即 对立与统一原则
什么是开闭原则
软件实体应该对扩展开放,对修改关闭,即实体应当通过扩展实现变化,而不是修改代码实现变化
什么是软件实体,项目或软件中按照一定逻辑规划划分的模块
抽象 类
方法
书店销售书籍
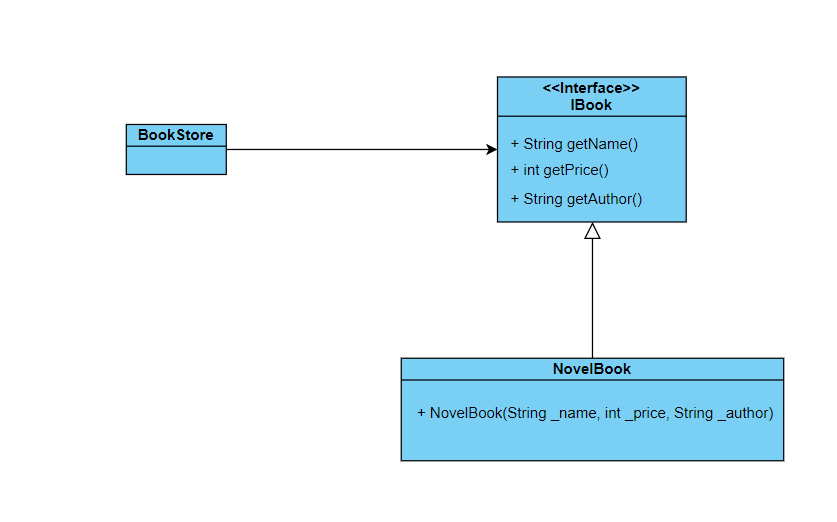
然后书写代码如下
// 书籍接口
public interface Ibook{
// 名称
public String getName();
// 售价
public int getPrice();
// 作者
public String getAuthor();
}
书店出售小说类书籍,书写代码
public class NoveIBook implements IBook {
// 名称
private String name;
// 价格
private int price;
// 作者
private String author;
// 构造函数
public NoveIBook(String _name, int _price, String _author){
this.name = _name;
this.price = _price;
this.author = _author;
}
// 获得作者
public String getAuthor(){
return this.author;
}
// 价格
public String getPrice(){
return this.price;
}
// 名字
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
}
其中,价格定义为int,不是错误,非金融类项目,取两位精度,运算过程中,扩大100倍,展示时缩小100倍。
售书
public class BookStore {
private final static ArrayList bookList = new ArrayList();
// 下发的内容,是放置在持久层,即保存到硬盘中的
// java的三层架构为视图层,服务层,持久层。
// view 层 用于接收用户提交的请求代码
// service 系统的业务逻辑
// dao 持久层,操作数据库代码
// 上下层,通过接口联系
static{
bookList.add(new NoveIBook("", 3200, ""));
}
// 买书
public static void main(String[] args){
// 大数格式化
NumberFormat formatter = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
formatter.setMaximumFractionDigits(2);
for(IBook book:bookList){
System.out.println(book.getName() + book.getPrice() + book.getAuthor());
}
}
}
然后,发生打折。
修改接口
接口不应该修改,因为接口是持久的
修改实现类
修改getPrice()方法达到打折的目的。
但是,因为采购书籍的人,要看到实现的价格。所以不修改
扩展实现
再增加一个子类,如下
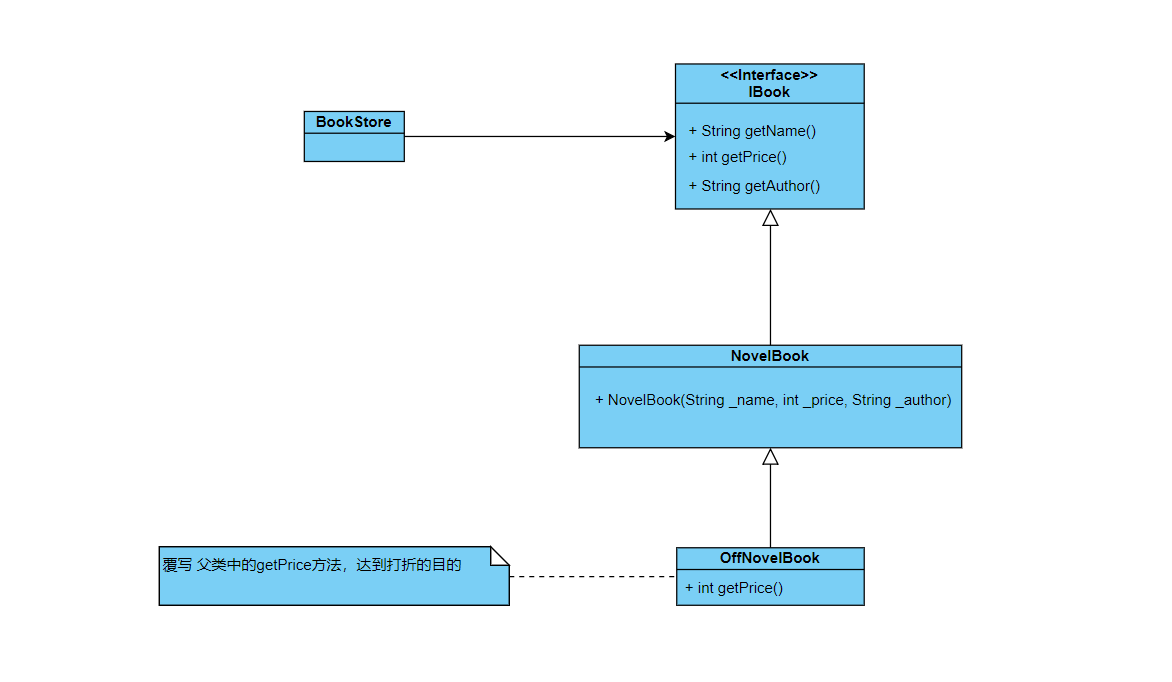
代码如下
// 打折销售的小说
public class OffNovelBook extends NoveIBook {
public OffNoveIBook(String _name, int _price, String _author){
super(_name, _price, _author);
}
// 覆盖销售
@Override
public int getPrice(){
return super.getPrice()*90 / 100;
}
}
接着修改main里面的内容即可。
变化
变化分为逻辑变化,子模块变化,可见视图变化。
使用开闭原则
抽象约束
抽象约束对一组事物的描述。
当商店增加了一个计算机书籍的销售。但是计算机书籍还有很多种,有编程语言,数据库等。
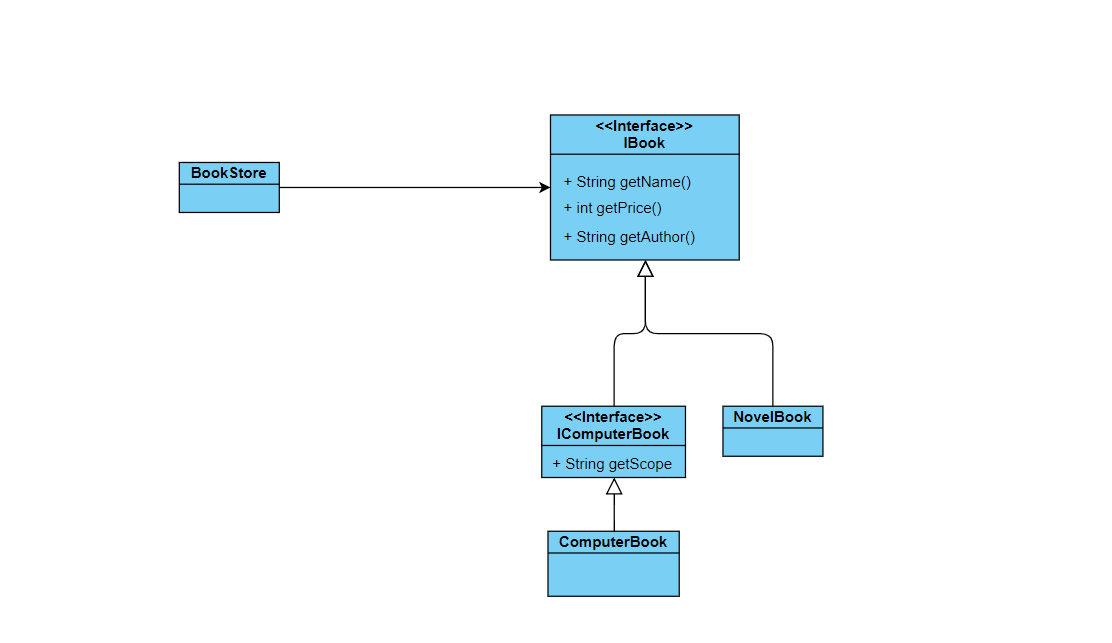
// 增加计算机书籍接口
public interface IComputerBook extends IBook{
// 计算机书籍
public String getScope(); // 计算机书籍的范围
}
同样的,书写计算机书籍类
public class ComputerBook implements IComputerBook{
private String name;
private String scope;
private String author;
public ComputerBook(String _name, int _price, String _author, String _scope){
this.name = _name;
this.price = _price;
this.author = _author;
this.scope = _scope;
}
public String getScope(){
return this.scope;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public int getPrice(){
return this.price;
}
}
直接在main中添加即可。
总结 ; 对扩展开放,前提对抽象约束。
元数据控制模块
即,使用配置参数,控制模块行为。
原则总结
单一职责
类的职责要单一
里氏替换
里氏替换原则不能破坏继承
即,子类对象,可以代替超类。
依赖倒置
面向接口。
即,每个接口只负责干一件事。
接口隔离
每个接口只干一件事
迪米特法则
通信通过类之间通信。两者之间耦合度越少越好。
开闭原则
对扩展开放,对修改关闭
www.iming.info