Basic theory
(i) Supervised learning (parametric/non-parametric algorithms, support vector machines, kernels, neural networks, ) regression, classification.
(ii) Unsupervised learning (clustering, dimensionality reduction, recommender systems, deep learning)
Others:
Reinforcement learning, recommender systems
SSE(和方差、误差平方和):The sum of squares due to error
MSE(均方差、方差):Mean squared error
RMSE(均方根、标准差):Root mean squared error
|
Linear regression
|
cost function:
 % correspoding code to compute gradient decent
h = X * theta;
theta = theta - alpha/m * (X' * (h - y));
 Gradient Descent vs Normal Equation
time complexity for Gradient Decent is O(kn2)
|
|
Locally weighted regression: 只考虑待预测点附件的training data
 |
|
Logistic regression
|
|
a classfication algorithm
  Cost function:
  
其中偏导数的推导如下:
  |
|
Newton's method: much faster than Gradient Decent.
 上图是求f(θ)=0时候的θ, 如果对f(θ)积分的最大值或者最小值
Newton’s method gives a way of getting to f(θ) = 0. What if we want to use it to maximize some function ℓ? The maxima of ℓ correspond to points where its first derivative ℓ ′ (θ) is zero. So, by letting f(θ) = ℓ ′ (θ), we can use the same algorithm to maximize ℓ, and we obtain update rule:
θ := θ − ℓ ′(θ) / ℓ ′′(θ)
|
|
在python里,
 |
Logistic Regression (Classification) decision boundary:
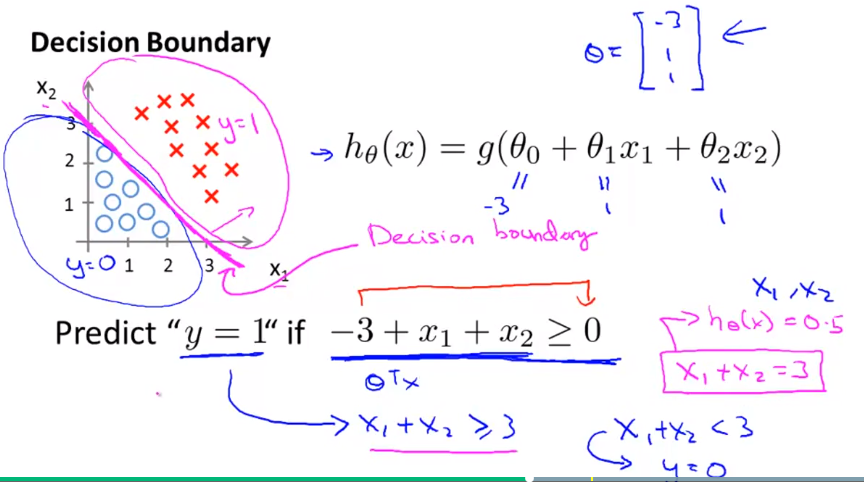
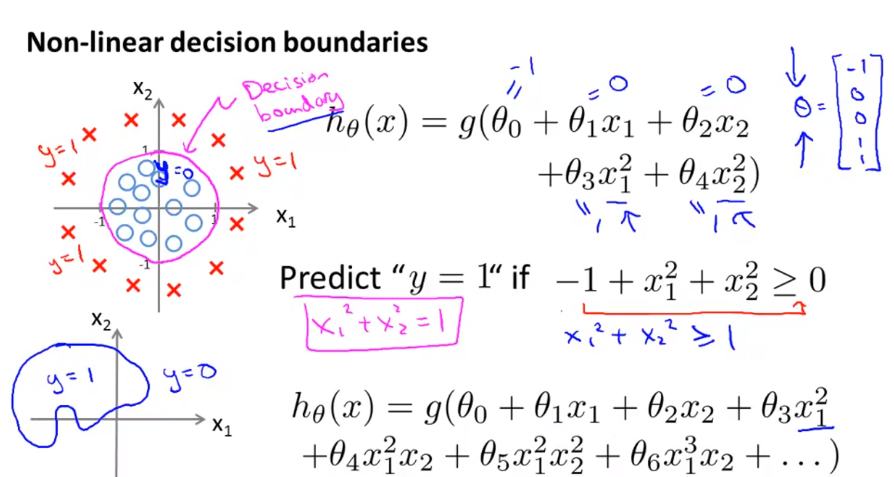
|
Neural Network
|
|
cost function:
 |
|
back propagation algorithm:
   |
|
|
Diagnostic
|
|
Diagnostic 用来分析学习算法是不是正常工作,如果不正常工作,进一步找出原因
|
|
怎么来评估learning algorithm 是否工作呢?
可以评估hypothesis 函数, 具体可以把所以input数据分成一部分training set, 另一部分作为test set 来验证,Andrew 建议 70%/30% 这个比例来划分,然后看用training set 得到的hypothesis 在 test set 上是否工作
 |
high bias:
high variance: (high gap)
|
Unsupervised Learning
Generative learning algo
Q&A
What is overfitting problem?
- How to reduce overfitting problem?
- reduce the number of features
- regularization. Keep all the features, but reduce the magnitude of parameters θ j
- besises Gradient Decent, what other algorithms we can use ?
- besides Gradient Decent, there are some optimization algorithms like Conjugate gradient, BFGS, L-BFGS.
- These 3 optimization algorithms don't need maually pick
 , and they are often faster than Gradient Decent, but more
, and they are often faster than Gradient Decent, but more
Reference:
Terms:
'parametric' learning algo
- which has fixed set of parameters Theta, like linear regression
'non-parameter' learning algo
- in which no. of parameters grow with m.
- one specific algo is Locally weighted regression (Loess, or LWR), 这个算法不需要我们自己选feature,原理是只拟合待预测点附近的点的曲线
Discriminative algo: 对y建模 p(y|x)
Generative algo: 对x建模p(x|y)
GDA - Gaussian Discriminant Analysis,x 连续,y 不连续
Naive Bayes - 比如垃圾邮件分类器,x 是不连续的,y 也是不连续的



