题目链接:https://www.oj.swust.edu.cn/problem/show/1745
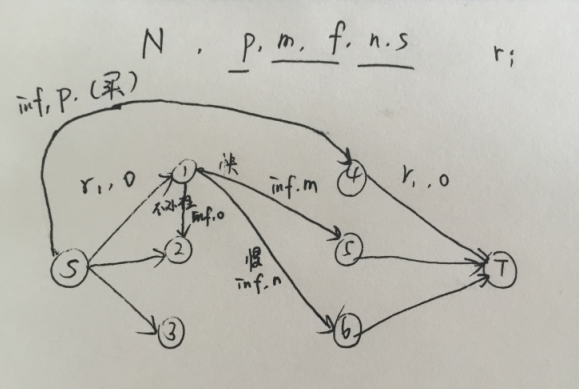
这题比较抽象,信息量也比较大。但是仔细想一下就会发现,按照天来作为节点,可以有三种操作:
当天使用的毛巾可以:1买,2从前几天中的洗完获得,洗有两种,快洗和慢洗。
当天使用完的毛巾可以:1留到后一天处理,2洗,洗有两种,同上。
将日期的节点拆成两个,一个用来表示脏的(不能直接用的)毛巾总量状态,一个表示干净的(能使用)毛巾总量状态。
建图方式如图,可以知道能量是守恒的,因为毛巾总量是一定的,并且符合要求。
毛巾需求量是一定的,所以从源点到脏的集合里建边,容量为需求量,费用为0。
同理汇点。
洗毛巾可以快洗慢洗(花费是总价,而不是单价,所以很方便),那么洗完了就是干净的,所以从脏的点集里延期n天或者m天连接到干净的点集里,容量为inf,费用为n或m。
脏毛巾可以屯一天到后面,不过直接相邻的传递就行,因为下一天会仍然有一条边传递到下下天,所以在脏的点集里建边,容量为inf,费用为0,
新买的是干净的,所以直接插到干净的点集里,从源点到干净点集建边,容量为inf,费用为p。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 typedef long long LL; 5 typedef struct Node { 6 int u, v, next; 7 LL c, w; 8 }Node; 9 const int maxn = 10010; 10 const int maxm = maxn << 5; 11 const LL mod = 0x3f3f3f3fLL; 12 const LL inf = (1LL<<55); 13 int tot, head[maxn]; 14 LL dist[maxn]; 15 LL cost, flow; 16 Node e[maxm]; 17 int pre[maxn]; 18 bool visit[maxn]; 19 queue<int> Q; 20 int S, T, N; 21 22 void init() { 23 S = T = N = 0; 24 memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); 25 tot = 0; 26 } 27 28 void adde(int u, int v, LL c, LL w) { 29 e[tot].u = u; e[tot].v = v; e[tot].c = c; e[tot].w = w; e[tot].next = head[u]; head[u] = tot++; 30 e[tot].u = v; e[tot].v = u; e[tot].c = 0; e[tot].w = -w; e[tot].next = head[v]; head[v] = tot++; 31 } 32 bool spfa(int s, int t, int n) { 33 int i; 34 for(i = 0; i <= n; i++) { 35 dist[i] = inf; 36 visit[i] = 0; 37 pre[i] = -1; 38 } 39 while(!Q.empty()) Q.pop(); 40 Q.push(s); 41 visit[s] = true; 42 dist[s] = 0; 43 pre[s] = -1; 44 while(!Q.empty()) { 45 int u = Q.front(); 46 visit[u] = false; 47 Q.pop(); 48 for(int j = head[u]; j != -1; j = e[j].next) { 49 if(e[j].c > 0 && dist[u] + e[j].w < dist[e[j].v]) { 50 dist[e[j].v] = dist[u] + e[j].w; 51 pre[e[j].v] = j; 52 if(!visit[e[j].v]) { 53 Q.push(e[j].v); 54 visit[e[j].v] = true; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 if(dist[t] == inf) return false; 60 else return true; 61 } 62 LL ChangeFlow(int t) { 63 LL det = mod; 64 int u = t; 65 while(~pre[u]) { 66 u = pre[u]; 67 det = min(det, e[u].c); 68 u = e[u].u; 69 } 70 u = t; 71 while(~pre[u]) { 72 u = pre[u]; 73 e[u].c -= det; 74 e[u ^ 1].c += det; 75 u = e[u].u; 76 } 77 return det; 78 } 79 LL MinCostFlow(int s, int t, int n) { 80 LL mincost, maxflow; 81 mincost = maxflow = 0; 82 while(spfa(s, t, n)) { 83 LL det = ChangeFlow(t); 84 mincost += det * dist[t]; 85 maxflow += det; 86 } 87 cost = mincost; 88 flow = maxflow; 89 return mincost; 90 } 91 92 int day,p,m,f,n,s; 93 int j, need[maxn]; 94 95 int main() { 96 // freopen("in", "r", stdin); 97 while(~scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d",&day,&p,&m,&f,&n,&s)) { 98 init(); 99 S = 0, T = day * 2 + 1, N = T + 1; 100 for(int i = 1; i <= day; i++) scanf("%d", &need[i]); 101 102 for(int i = 1; i < day; i++) adde(i, i+1, inf, 0LL); 103 104 for(int i = 1; i <= day; i++) adde(S, i, (LL)need[i], 0LL); 105 for(int i = 1; i <= day; i++) adde(day+i, T, (LL)need[i], 0LL); 106 107 for(int i = 1; i <= day; i++) adde(S, day+i, inf, (LL)p); 108 109 for(int i = 1; i <= day; i++) { 110 j = i + m; if(j <= day) adde(i, day+j, inf, (LL)f); 111 j = i + n; if(j <= day) adde(i, day+j, inf, (LL)s); 112 } 113 114 cout << MinCostFlow(S, T, N) << endl; 115 } 116 return 0; 117 }