一、hashmap底层原理:
hashmap调用默认构造方法会产生一个默认底层是长度为16的Entry数组,首先调用key的hasCode()方法来得到一个整数, int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
这个整数就是哈希码,然后把哈希码作为参数传递到hash()函数中来进行运算,即散列运算,得到一个int类型的散列值 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); (transient Entry[] table;) 把散列值和数组的长度来进行运算,最终得到Entry对象要存放到数组的位置(下标)。 hashmap内部的结构是数组加单向链表结构,因为不同的key有可能计算出相同的散列值,根据散列值计算出来的存放到数组的下标会冲突(同一个下标值),此时, 如果键相同,散列值也一样,说明是同一个对象,此时会将键所对应的旧值用新的键值覆盖掉, 如果散列值一样,键名不一样,说明是不同的对象,此时会把键值对封装成entry对象放到那个散列值对应的下标位置处, 原来那个entry对象会以链表形式链接在新创建的entry对象后面
二、hashmap常用方法:
存值:public V put(K key, V value)
取值:public V get(Object key)
获取所有的键:public Set<K> keySet()
获取所有的值: public Collection<V> values() Returns a {@link Collection} view of the values contained in this map.
取键值对的set集合:public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
map集合大小:public int size()
判断map是否非空:public boolean isEmpty()
三、示例:
1 package com.iotek.map; 2 3 import java.util.Collection; 4 import java.util.HashMap; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 import java.util.Map.Entry; 7 import java.util.Set; 8 9 public class HashMapDemo1 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); // 接口的引用变量指向实现类的对象 12 // 创建HashMap对象,也就是创建一个Map容器 13 map.put(null, "张三"); // 添加键值对元素 14 map.put(null, "李四"); // 有相同的键时,后面添加的键对应的值会覆盖掉之前键对应的值 15 map.put("john", "李四"); 16 map.put("rose", "玫瑰"); 17 map.put("mary", "小红"); 18 System.out.println("1" + map); 19 20 // 获取map中所有键,返回的是一个Set容器,可以用迭代器对象或者foreach来进行输出 21 Set<String> keys = map.keySet(); 22 System.out.println("******输出map容器中所有的键:"); 23 for (String key : keys) { 24 System.out.print(key + " "); // 用String类型的变量key来遍历keys容器 25 } 26 27 // 获取map中所有的值:使用map接口中的values方法,返回Collection接口的实现类 28 Collection<String> values = map.values(); 29 System.out.println(" ******输出map容器中所有的值:"); 30 for (String value : values) { 31 System.out.print(value + " "); // 用String类型的变量value来遍历values容器 32 } 33 34 // 得到key的同时,得到key所对应的值 35 System.out.println(" ******用获取的键来得到对应的值并输出:"); 36 for (String key : keys) { 37 System.out.print(key + "--" + map.get(key)); // 用String类型的变量key来遍历keys容器 38 } 39 System.out.println(" map容器中键值对的个数是:" + map.size()); 40 System.out.println("判断map容器中是否为空:" + map.isEmpty()); 41 42 // map.entrySet()返回的是一个set容器,其中放的是map.Entry内部接口 43 /* 44 * 当我们调用put(key,value)方法时,首先会把key和value封装到Entry这个静态内部类中, 45 * 再把Entry对象添加到数组中(哈希表),所以我们想要获取map中的所有键值对,只需要获取 46 * 数组汇总所有的Entry,接下来调用Entry对象中的getKey 和getValue方法就能获取键值对 47 * 以后想输出HashMap容器中所有的键值对,都可以调用HashMap的 entrySet()方法就可以了!!! 48 */ 49 Set<Entry<String, String>> entrys = map.entrySet(); 50 System.out.println("使用map接口的entrySet()方法获取map容器中所有的键值对:"); 51 for (Entry<String, String> entry : entrys) { 52 System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "-" + entry.getValue()); 53 } 54 map.clear(); 55 System.out.println("判断map容器中是否为空:" + map.isEmpty()); 56 57 } 58 59 }

map中键是对象时,需要重写对象的hash和equals方法:
1 package com.iotek.map; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 6 public class HashMapDemo2 { 7 8 /** 9 * @param args 10 */ 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 Map<Student, String> map = new HashMap<Student, String>(); 13 map.put(new Student("jay", 20), "张三"); // 1 14 map.put(new Student("lisi", 30), "李四");// 2 15 map.put(new Student("rose", 20), "玫瑰");// 3 16 map.put(new Student("lisi", 30), "陈飞");// 4 17 System.out.println(map.size()); 18 System.out.println(map.toString()); 19 20 /* 21 * Student类中不重写hashCode() and 22 * equals()方法,此处map.size()值是4,即map中有4个封装了键值对的Entry对象 23 * 重写了hashCode()和equals()方法后,2和4语句里的学生对象将被判断为同一个键名,因此2位置处的键值会被替换掉 24 * 这正是我们需要的,对象相同,应该判定为是同一个键,因此,这就是需要重写hashCode()和equals()方法的原因 25 */ 26 } 27 } 28 29 class Student { 30 private String name; 31 private int age; 32 33 @Override 34 public int hashCode() { 35 final int prime = 31; 36 int result = 1; 37 result = prime * result + age; 38 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); 39 return result; 40 } 41 /* 42 * 用source中的 Generate hashCode() and equals() 来 生成重写的hashCode()方法和equals()方法 43 * 只要姓名和年龄相同的学生,那么这个学生对象产生的hashCode值和equals方法的值也是一样的, 44 * 此时就可以认为是hashmap里放的是同一个对象,那么这两个相同的Student对象作为键时, 45 * 后面添加的Student对象对应的键值应该要覆盖掉前面添加的键值 46 */ 47 48 @Override 49 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 50 if (this == obj) 51 return true; 52 if (obj == null) 53 return false; 54 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 55 return false; 56 Student other = (Student) obj; 57 if (age != other.age) 58 return false; 59 if (name == null) { 60 if (other.name != null) 61 return false; 62 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 63 return false; 64 return true; // 只有当姓名和年龄都一样时,才返回一个true,表示是同一个对象 65 } 66 67 public Student(String name, int age) { 68 super(); 69 this.name = name; 70 this.age = age; 71 } 72 73 public String getName() { 74 return name; 75 } 76 77 public void setName(String name) { 78 this.name = name; 79 } 80 81 public int getAge() { 82 return age; 83 } 84 85 public void setAge(int age) { 86 this.age = age; 87 } 88 89 @Override 90 public String toString() { 91 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 92 } 93 94 }
结果:

使用hashmap判断数组中字符串出现的次数:
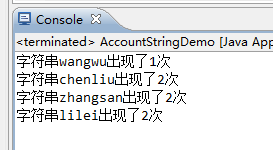
1 package com.iotek.map; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 import java.util.Map.Entry; 6 import java.util.Set; 7 /** 8 * 使用hashmap判断数组中字符串出现的次数 9 * @author Administrator 10 * 11 */ 12 public class AccountStringDemo { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 String[] strs = {"zhangsan","zhangsan","wangwu","chenliu","chenliu","lilei","lilei"}; 16 Map<String,Integer> data = AccountUtil.account(strs); 17 AccountUtil.printData(data); 18 } 19 20 } 21 22 class AccountUtil { 23 public static Map<String,Integer> account(String [] strs) { 24 Map<String,Integer> data = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); 25 for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) { 26 String str = strs[i]; 27 if(data.get(str) == null) { 28 data.put(str, 1); 29 //如果第一次统计到该字符串,将该字符串作为键名,其出现的次数作为键值,保存在map容器中 30 } else { 31 //如果不是第一次捕获到该字符串,则data.get(str)!=null,那么将键值加1,表示第二次读取到该字符串 32 data.put(str, data.get(str)+1); 33 } 34 } 35 return data; //将最终的hashmap容器,也就是data返回 36 } 37 38 public static void printData(Map<String,Integer> data) { 39 //使用HashMap的EntrySet()方法,返回map容器:data中的所有键值对(全部封装在Entry中),然后进行打印 40 Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrys = data.entrySet(); 41 for(Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrys) { 42 System.out.println("字符串" + entry.getKey() + "出现了" + entry.getValue() + "次"); 43 } 44 } 45 46 }