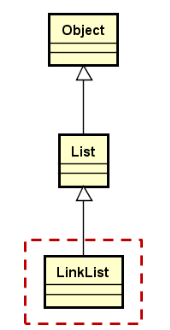
1. Linklist设计要点
- 类模板,通过头结点访问后继节点
- 定义内部节点类型Node,用于描述数据域和指针域
- 实现线性表关键操作如增、减、查等
2、Linklist的定义

3.代码
#ifndef LINKLIST_H
#define LINKLIST_H
#include "List.h"
namespace DataStructureLib
{
template <typename T>
class LinkList:public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node{
T value;
Node* next;
};
mutable Node m_header;//头结点 、mutable为了让get函数中的const属性导致的&m_header(编译器认为是要修改成员变量)mutable就允许const成员函数取地址
int m_length;//链表的长度
Node* position(int i) const//返回第i和元素的指针
{
Node* ret=&m_header;
for(int p=0;p<i;p++)
{
ret=ret->next;
}
return ret;//元素地址保存在该节点的next指针域中
}
public:
LinkList()
{
m_header.next=NULL;
m_length=0;
}
bool insert(int index, const T& elem)//思路:1.找到index位置处的元素;2.在该元素尾部insert新元素
{
bool ret=(index<=m_length)&&(index>=0);
Node* NewNode=new Node ;
if (ret)
{
if (NULL!=NewNode)
{
NewNode->value=elem;
Node* indexNode=position(index);
NewNode->next=indexNode->next;
indexNode->next=NewNode;
m_length++;
}
else{
throw("has Not enougth memory to insert new element ...");
}
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int index)
{
bool ret=((index<=m_length)&&(index>=0));
if (ret)
{
Node* CurrentNode=position(index);
Node* toDelNode=CurrentNode->next;
CurrentNode->next=toDelNode->next;
delete toDelNode ;
m_length--;
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int index,const T& e)
{
bool ret=((0<=index)&&(index<=m_length));
if (ret)
{
Node* CurrentNode=position(index);
CurrentNode->next->value=e;
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int index, T& elem) const
{
bool ret=((index<=m_length)&&(index>=0));
if (ret)
{
Node* CurrentNode=position(index);
elem= CurrentNode->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
T get(int index)
{
T ret;
if((index<m_length)&&(0<=index))
{
Node* CurrentNode=position(index);
ret= CurrentNode->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
int getlength() const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
while (m_header.next)
{
Node* toDelNode=m_header.next;
m_header.next=toDelNode->next;
delete toDelNode;
}
m_length=0;
}
//寻找e元素所在的位置,
//返回值 失败:-1 成功:e元素所在的位置的id
int find(T& e)
{
int ret = -1;
for (int i=0;i<m_length;i++)
{
if (e==get(i))
{
ret=i;
}
}
return ret;
}
~LinkList()
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif
测试
#include<iostream>
#include "object.h"
#include "SeqList.h"
#include "LinkList.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DataStructureLib;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
LinkList<int> linklist;
for (int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
linklist.insert(0,i);
}
for (int i=0;i<linklist.getlength();i++)
{
int tmp;
linklist.get(i,tmp);
cout<<tmp<<'
';
}
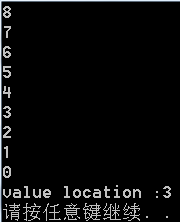
int value=5;
cout<<"value location :"<<linklist.find(value)<<'
';
linklist.clear();//清空链表中的数据
for (int i=0;i<linklist.getlength();i++)
{
int tmp;
linklist.get(i,tmp);
cout<<tmp<<'
';
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
小结
(1)通过类模板实现链表,包括头结点成员和长度成员
(2)定义结点类型,并通过堆中的结点对象构成链式存储
(3)插入和删除操作需要保证链表的完整性