一,MySQL-Python插件
Python里操作MySQL数据库,需要Python下安装访问MySQL数据库接口API包即插件,从而使得Python2.7能访问操作MySQL数据库。MySQL软件可以去官网下载:http://www.mysql.com/; MySQLdb插件下载:http://sourceforge.net/projects/mysql-python/files/latest/download
二,访问MySQL数据库
1,连接数据库mysql
基本格式:connect ([host=]'ip',[user=]'user',[passwd=]'password',[db=]'dbname')
2,数据库的基本操作
1)create创建表

1 import MySQLdb 2 #connect to a database 'test' 3 conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost',user='root',passwd='zbc123',db='test') 4 cursor=conn.cursor() 5 #create a table 6 cursor.execute('create table 7 test(ID int primary key auto_increment,Name char(25))') 8 #Closing database 9 cursor.close() 10 conn.close()
2)fetchall访问:

1 import MySQLdb 2 #connect to a database 'test' 3 conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost',user='root',passwd='zbc123',db='test') 4 cursor=conn.cursor() 5 #fetch datas 6 n=cursor.execute('select * from test;') 7 r=cursor.fetchall() 8 print n,r 9 #Closing database 10 cursor.close() 11 conn.close() 12 13 >>> ================================ RESTART ================================ 14 >>> 15 3 ((4L, 'zhangbc'), (5L, 'lis08'), (6L, 'wangw')) 16 >>>
在Mysql5.6环境下运行:
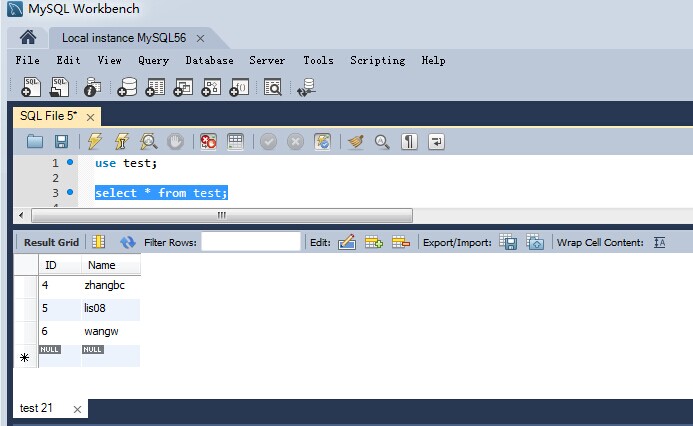
3)insert向表中插入数据:

1 import MySQLdb 2 #connect to a database 'test' 3 conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost',user='root',passwd='zbc123',db='test') 4 cursor=conn.cursor() 5 #insert data into table 'test' 6 mysql='''insert into test(id,sname) values(4,'zhanghua')''' 7 cursor.execute(mysql) 8 conn.commit()#below mysql5.0 needed 9 #fetch datas 10 n=cursor.execute('select * from test;') 11 r=cursor.fetchall() 12 print n,r 13 #Closing database 14 cursor.close() 15 conn.close() 16 17 >>> ================================ RESTART ================================ 18 >>> 19 4 ((1L, 'zhangbc'), (2L, 'lis'), (3L, 'wangw'), (4L, 'zhanghua'))
注意:一定要写上conn.commit();事物不提交,将回滚。比较:
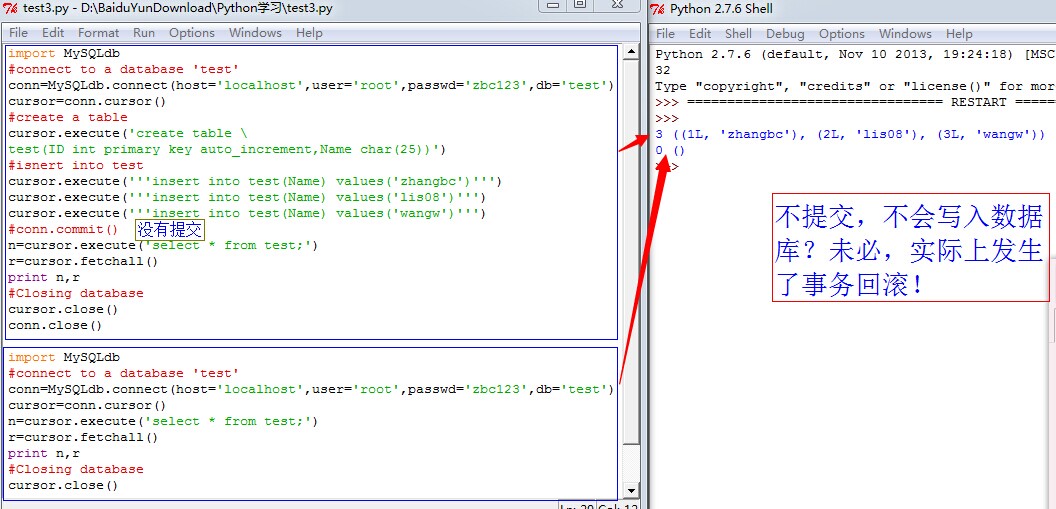
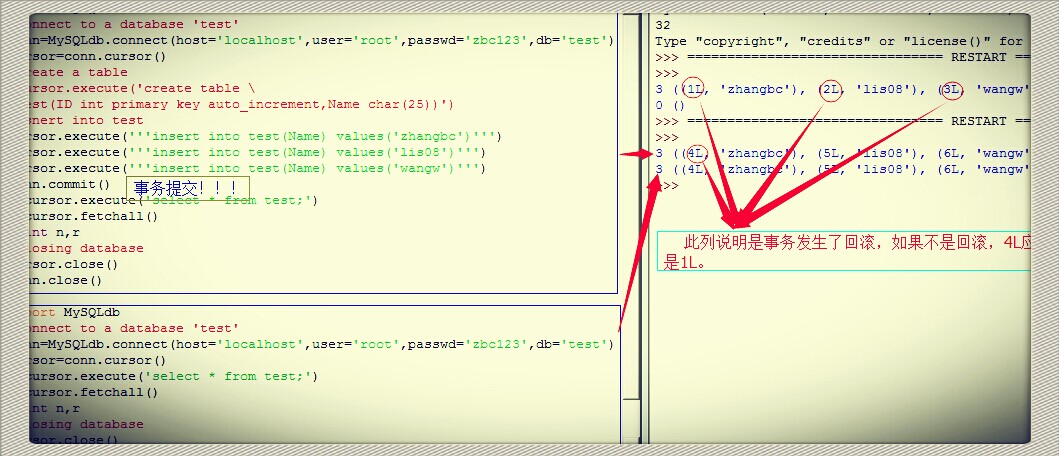
4)update修改表中数据:

1 import MySQLdb 2 #connect to a database 'test' 3 conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost',user='root',passwd='zbc123',db='test') 4 cursor=conn.cursor() 5 #update data of the table 'test' 6 mysql='''update test set sname='Lisi08' where id=2''' 7 cursor.execute(mysql) 8 conn.commit()#below mysql5.0 needed 9 #fetch datas 10 n=cursor.execute('select * from test;') 11 r=cursor.fetchall() 12 print n,r 13 #Closing database 14 cursor.close() 15 conn.close() 16 17 >>> ================================ RESTART ================================ 18 >>> 19 4 ((1L, 'zhangbc'), (2L, 'Lisi08'), (3L, 'wangw'), (4L, 'zhanghua'))
5)delete删除表中数据:

1 import MySQLdb 2 #connect to a database 'test' 3 conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost',user='root',passwd='zbc123',db='test') 4 cursor=conn.cursor() 5 #delete data of the table 'test' 6 mysql='''delete from test where id=4''' 7 cursor.execute(mysql) 8 conn.commit()#below mysql5.0 needed 9 #fetch datas 10 n=cursor.execute('select * from test;') 11 r=cursor.fetchall() 12 print n,r 13 #Closing database 14 cursor.close() 15 conn.close() 16 17 >>> ================================ RESTART ================================ 18 >>> 19 3 ((1L, 'zhangbc'), (2L, 'Lisi08'), (3L, 'wangw'))
6)关于select及其遍历:
i)使用元组tuple与fetchone结合

1 import MySQLdb 2 #connect to a database 'test' 3 conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost',user='root',passwd='zbc123',db='test') 4 cursor=conn.cursor() 5 #fetch datas 6 cursor.execute('select * from test;') 7 #获得结果集的记录 8 numrows=int(cursor.rowcount) 9 #循环,取行数据 10 for i in range(numrows): 11 row=cursor.fetchone() 12 print row[0],row[1] 13 #Closing database 14 cursor.close() 15 conn.close() 16 17 >>> ================================ RESTART ================================ 18 >>> 19 4 zhangbc 20 5 lis08 21 6 wangw
ii)使用字典cursor

1 #-*- coding:UTF-8 -*- 2 import MySQLdb as mdb 3 #connect to a database 'test' 4 conn=mdb.connect(host='localhost',user='root',passwd='zbc123',db='test') 5 with conn: 6 #获取连接上的字典cursor,每一个cursor其实都是cursor的子类 7 cur=conn.cursor(mdb.cursors.DictCursor) 8 #fetch datas 9 cur.execute('select * from test;') 10 #获得结果集 11 rows=cur.fetchall() 12 #循环,取行数据 13 for row in rows: 14 print '%s %s'%(row['ID'],row['Name']) 15 #Closing database 16 cur.close() 17 conn.close() 18 19 >>> ================================ RESTART ================================ 20 >>> 21 4 zhangbc 22 5 lis08 23 6 wangw
iii)获取单个表的字段名及其信息

1 #-*- coding:UTF-8 -*- 2 import MySQLdb as mdb 3 #connect to a database 'test' 4 conn=mdb.connect(host='localhost',user='root',passwd='zbc123',db='test') 5 with conn: 6 #获取连接上的字典cursor,每一个cursor其实都是cursor的子类 7 cur=conn.cursor() 8 #fetch datas 9 cur.execute('select * from test;') 10 #获得结果集 11 rows=cur.fetchall() 12 #获得链接对象的描述信息 13 desc=cur.description 14 print 'cur.description:',desc 15 #打印表头 16 print '%2s %3s'%(desc[0][0],desc[1][0]) 17 #循环,取行数据 18 for row in rows: 19 print '%2s %3s'%row 20 #Closing database 21 cur.close() 22 conn.close() 23 24 >>> ================================ RESTART ================================ 25 >>> 26 cur.description: (('ID', 3, 1, 11, 11, 0, 0), ('Name', 254, 7, 25, 25, 0, 1)) 27 ID Name 28 4 zhangbc 29 5 lis08 30 6 wangw
三,小结
本文主要介绍了Python下如何访问并操数据库的基本知识,如:如何连接数据库,如何执行执行SQL语句等等。
