
第一题就是一个很简单的dp,这么想就很好想出dp方程了
前面的序列是有1到(i - 1)组成,将i插在最前面,将会增加i - 1个逆序对
如果插在第一个数的后面,将会增加i - 2个逆序对。。。以此类推
于是得到了dp方程:
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][max(j - i + 1, 0)] + f[i - 1][max(j - i + 1, 0) + 1] + ... + f[i - 1][min((i - 1) * (i - 2) / 2, j)];
有一点长,也可以用f[i][j - 1]来状态转移,这样方程很简单得多,
但是要注意“分类讨论”
但我用的是第一种方程,如果直接这么做的话,时间复杂度大概是O(n2k)
这样数据是过不完的,所以要加一个前缀和优化,就直接看代码了吧。。
Code
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<cctype> 6 #include<cstdlib> 7 #include<map> 8 #include<set> 9 #include<queue> 10 #include<stack> 11 using namespace std; 12 typedef bool boolean; 13 #define smin(a, b) (a) = min((a), (b)) 14 #define smax(a, b) (a) = max((a), (b)) 15 template<typename T> 16 inline void readInteger(T& u){ 17 char x; 18 while(!isdigit((x = getchar()))); 19 for(u = x - '0'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - '0'); 20 ungetc(x, stdin); 21 } 22 23 template<typename T>class Matrix{ 24 public: 25 T* p; 26 int rows; 27 int lines; 28 Matrix():p(NULL), rows(0), lines(0){} 29 Matrix(int rows, int lines):rows(rows), lines(lines){ 30 p = new T[rows * lines]; 31 } 32 T* operator [](int pos){ 33 return p + lines * pos; 34 } 35 }; 36 37 #define matset(m, i, s) memset((m).p, i, s * (m).rows * (m).lines) 38 39 int T; 40 Matrix<int> f; 41 Matrix<int> s; 42 int n, k; 43 44 #define limit(i) (((i) * (i - 1)) >> 1) 45 46 int adder(int a, int b){ 47 return (a + b) % 10000; 48 } 49 50 inline void dp(){ 51 f[1][0] = 1; 52 s[1][0] = 1; 53 for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){ 54 f[i][0] = 1; 55 s[i][0] = 1; 56 for(int j = 1; j <= limit(i) && j <= k; j++){ 57 if(j - i + 1 <= 0){ 58 f[i][j] = s[i - 1][min(limit(i - 1), j)]; 59 }else{ 60 f[i][j] = (s[i - 1][min(limit(i - 1), j)] - s[i - 1][j - i] + 10000) % 10000; 61 } 62 s[i][j] = adder(s[i][j - 1], f[i][j]); 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 inline void solve(){ 68 readInteger(T); 69 while(T--){ 70 readInteger(n); 71 readInteger(k); 72 if(k > n * (n - 1) / 2){ 73 printf("0 "); 74 continue; 75 } 76 f = Matrix<int>(n + 1, k + 1); 77 s = Matrix<int>(n + 1, k + 1); 78 dp(); 79 printf("%d ", f[n][k]); 80 delete f.p; 81 delete s.p; 82 } 83 } 84 85 int main(){ 86 freopen("permut.in", "r", stdin); 87 freopen("permut.out", "w", stdout); 88 solve(); 89 return 0; 90 }

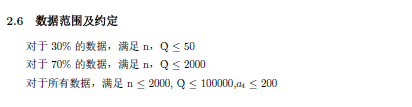
抛开中位数什么的不说,就是一道区间最大值的裸题,倍增,RMQ,线段树都可以解决
至于求中位数嘛。。你可以把它从(i + 1)至右扫一遍,记录每个地方它所需要的比ai大(或小)的个数
(重复了话,直接覆盖,反正你要的是最长的区间),再从i往左扫一遍,能够补上的就用算出长度,更新
就行了
Code
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<cctype> 6 #include<cstdlib> 7 #include<map> 8 #include<set> 9 #include<queue> 10 #include<stack> 11 using namespace std; 12 typedef bool boolean; 13 #define smin(a, b) (a) = min((a), (b)) 14 #define smax(a, b) (a) = max((a), (b)) 15 template<typename T> 16 inline void readInteger(T& u){ 17 char x; 18 while(!isdigit((x = getchar()))); 19 for(u = x - '0'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - '0'); 20 ungetc(x, stdin); 21 } 22 23 template<typename T>class Matrix{ 24 public: 25 T* p; 26 int rows; 27 int lines; 28 Matrix():p(NULL), rows(0), lines(0){} 29 Matrix(int rows, int lines):rows(rows), lines(lines){ 30 p = new T[rows * lines]; 31 } 32 T* operator [](int pos){ 33 return p + lines * pos; 34 } 35 }; 36 37 #define matset(m, i, s) memset((m).p, i, s * (m).rows * (m).lines) 38 39 int n, q; 40 int* buti; 41 int* list; 42 //int power[12] = {1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048}; 43 Matrix<int> upper; 44 Matrix<int> maxer; 45 46 inline void init(){ 47 readInteger(n); 48 list = new int[(const int)(n + 1)]; 49 buti = new int[(const int)(n + 1)]; 50 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 51 readInteger(list[i]); 52 } 53 } 54 55 inline int calc(int less, int more){ 56 return (less < more) ? (n - less + more) : (less - more); 57 } 58 59 int* buffer; 60 inline void getButi(){ 61 buffer = new int[(const int)(2 * n + 1)]; 62 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 63 int len = 1; 64 int less = 0; 65 int more = 0; 66 memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(int) * (2 * n + 1)); 67 buffer[0] = i; 68 for(int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++){ 69 if(list[j] >= list[i]) more++; 70 else less++; 71 buffer[calc(less, more)] = j; 72 } 73 less = more = 0; 74 for(int j = i; j >= 1; j--){ 75 if(list[j] > list[i]) more++; 76 else if(i != j) less++; 77 if(buffer[calc(more, less)]){ 78 smax(len, buffer[calc(more, less)] - j + 1); 79 } 80 } 81 buti[i] = len; 82 } 83 } 84 85 inline void init_bz(){ 86 upper = Matrix<int>(n + 1, 13); 87 maxer = Matrix<int>(n + 1, 13); 88 matset(upper, 0, sizeof(int)); 89 matset(maxer, 0, sizeof(int)); 90 buti[0] = 0; 91 for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){ 92 maxer[i][0] = max(buti[i], buti[i + 1]); 93 upper[i][0] = i + 1; 94 } 95 maxer[n][0] = buti[n]; 96 for(int j = 1; j <= 11; j++){ 97 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 98 upper[i][j] = upper[upper[i][j - 1]][j - 1]; 99 maxer[i][j] = max(maxer[i][j - 1], maxer[upper[i][j - 1]][j - 1]); 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 104 inline void solve(){ 105 readInteger(q); 106 for(int i = 1, l, r; i <= q; i++){ 107 readInteger(l); 108 readInteger(r); 109 int ct = r - l; 110 if(ct == 0){ 111 printf("%d ", buti[l]); 112 }else{ 113 int result = buti[l]; 114 for(int j = 0; j <= 11 && ct; j++){ 115 if(ct & 1){ 116 smax(result, maxer[l][j]); 117 l = upper[l][j]; 118 } 119 ct >>= 1; 120 } 121 printf("%d ", result); 122 } 123 } 124 } 125 126 int main(){ 127 freopen("beautiful.in", "r", stdin); 128 freopen("beautiful.out", "w", stdout); 129 init(); 130 getButi(); 131 init_bz(); 132 solve(); 133 return 0; 134 }

这道题呢,可以用一个s[216]数组来存,把每个数及其“子集”(就是and的时候如果s某一二进制
位上是1,但是a的这一位为0,虽然仍然and完了这一位是0,但是计算的时候你需要把这些情况都计
算一下,再通俗一点就是这个and 原数不变),这样的话,删除和插入的时间复杂度是O(216),但查
询的时间复杂度是O(1)。
这样做的话,如果遇到那种极不平衡的数据就死翘翘了[滑稽]
所以可以把s数组分成2部分s[pre][suf],表示一个数的高八位为pre,低8位是suf的“子集”,
插入和删除只需要考虑低八位,而查询就枚举高八位and s,这样时间复杂度就很平衡了,都是O(28)
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<cstdio> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<cctype> 7 #include<cstdlib> 8 #include<map> 9 #include<set> 10 #include<queue> 11 #include<stack> 12 using namespace std; 13 typedef bool boolean; 14 #define smin(a, b) (a) = min((a), (b)) 15 #define smax(a, b) (a) = max((a), (b)) 16 template<typename T> 17 inline void readInteger(T& u){ 18 char x; 19 while(!isdigit((x = getchar()))); 20 for(u = x - '0'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - '0'); 21 ungetc(x, stdin); 22 } 23 24 const int limit = 255; 25 26 int n; 27 char cmd[10]; 28 int s[limit + 1][limit + 1]; 29 30 inline void update(int x, int value){ 31 int pre = x >> 8, suf = x & limit, comp = suf ^ limit; 32 s[pre][suf] += value; 33 for(int i = comp; i != 0; i = (i - 1) & comp){ 34 s[pre][suf | i] += value; 35 } 36 } 37 38 inline int query(int x){ 39 int suf = x & limit, result = s[0][suf], pre = x >> 8; 40 for(int i = pre; i != 0; i = (i - 1) & pre){ 41 result += s[i][suf]; 42 } 43 return result; 44 } 45 46 inline void solve(){ 47 readInteger(n); 48 for(int i = 1, x; i <= n; i++){ 49 getchar(); 50 scanf("%s", cmd); 51 readInteger(x); 52 if(cmd[0] == 'a' || cmd[0] == 'd'){ 53 update(x, ((cmd[0] == 'a') ? (1) : (-1))); 54 }else{ 55 printf("%d ", query(x)); 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 60 int main(){ 61 freopen("subset.in", "r", stdin); 62 freopen("subset.out", "w", stdout); 63 solve(); 64 return 0; 65 }