Java语言内置了多线程支持。当Java程序启动的时候,实际上是启动了一个JVM进程,然后,JVM启动主线程来执行main()方法。在main()方法中,我们又可以启动其他线程。
Java 提供了三种创建线程的方法:
- 通过实现 Runnable 接口;
- 通过继承 Thread 类本身;
- 通过 Callable 和 Future 创建线程。
通过实现 Runnable 接口来创建线程

class RunnableDemo implements Runnable { private Thread t; private String threadName; RunnableDemo( String name) { threadName = name; System.out.println("Creating " + threadName ); } public void run() { System.out.println("Running " + threadName ); try { for(int i = 4; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Thread: " + threadName + ", " + i); // 让线程睡眠一会 Thread.sleep(50); } }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " interrupted."); } System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " exiting."); } public void start () { System.out.println("Starting " + threadName ); if (t == null) { t = new Thread (this, threadName); t.start (); } } } public class TestThread { public static void main(String args[]) { RunnableDemo R1 = new RunnableDemo( "Thread-1"); R1.start(); RunnableDemo R2 = new RunnableDemo( "Thread-2"); R2.start(); } }
通过继承Thread来创建线程

class ThreadDemo extends Thread { private Thread t; private String threadName; ThreadDemo( String name) { threadName = name; System.out.println("Creating " + threadName ); } public void run() { System.out.println("Running " + threadName ); try { for(int i = 4; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Thread: " + threadName + ", " + i); // 让线程睡眠一会 Thread.sleep(50); } }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " interrupted."); } System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " exiting."); } public void start () { System.out.println("Starting " + threadName ); if (t == null) { t = new Thread (this, threadName); t.start (); } } } public class TestThread { public static void main(String args[]) { ThreadDemo T1 = new ThreadDemo( "Thread-1"); T1.start(); ThreadDemo T2 = new ThreadDemo( "Thread-2"); T2.start(); } }
Thread类方法
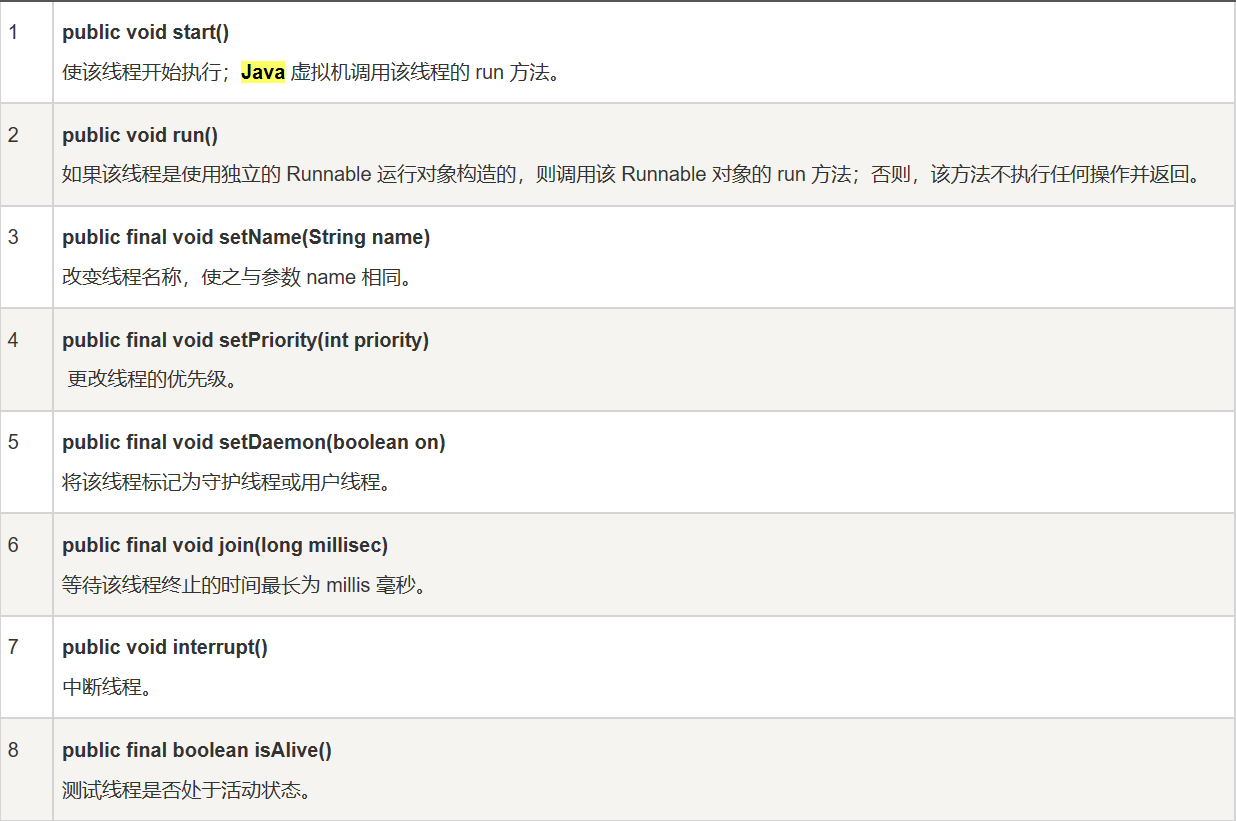
Thread类静态方法

