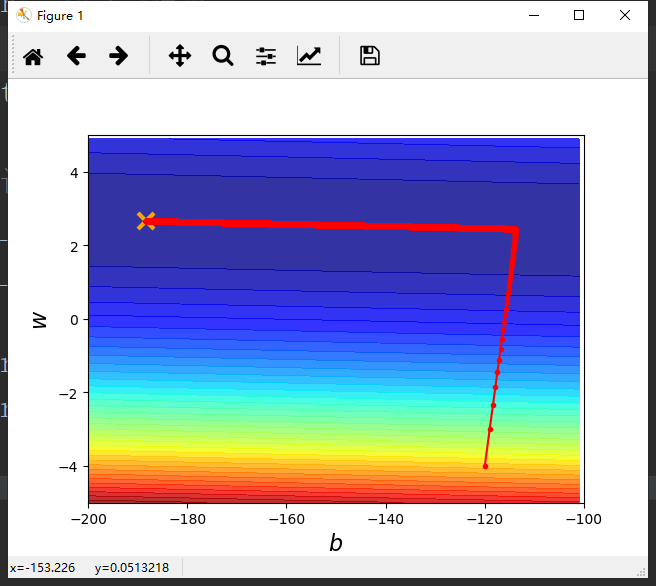
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 4 x_data = [338,333,328,207,226,25,179,60,208,606] 5 y_data = [640,633,619,393,428,27,193,66,226,1591] 6 7 8 #生成从-200到-100的数,不包括-100 9 #x轴 10 x = np.arange(-200,-100,1) 11 #y轴 12 y = np.arange(-5,5,0.1) 13 #存储对应的误差 14 Z = np.zeros((len(x),len(y))) 15 #x横向平铺给X,y纵向平铺给Y 16 #X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) 17 for i in range(len(x)): 18 for j in range(len(y)): 19 b = x[i] 20 w = y[j] 21 #按行进行计算误差 22 Z[j][i] = 0 23 #误差和 24 for n in range(len(x_data)): 25 Z[j][i] = Z[j][i] + (y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])**2 26 #归一化 27 Z[j][i] = Z[j][i]/len(x_data) 28 29 30 #y = b + w * x 31 b = -120 32 w = -4 33 #lr = 0.0000001 34 lr = 0.000001#学习速率 35 # lr = 0.00001 36 iteration = 100000 37 38 #记录每次求得的b和w 39 b_history = [b] 40 w_history = [w] 41 42 for i in range(iteration): 43 b_grad = 0.0 44 w_grad = 0.0 45 46 for n in range(len(x_data)): 47 b_grad = b_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*1.0 48 w_grad = w_grad - 2.0 * (y_data[n] - b - w * x_data[n]) * x_data[n] 49 b = b - lr * b_grad 50 w = w - lr * w_grad 51 52 b_history.append(b) 53 w_history.append(w) 54 55 #五十种颜色 透明度:0.8 56 plt.contourf(x, y, Z, 50, alpha=0.8, cmap=plt.get_cmap('jet')) 57 #画出最优解的位置 58 plt.plot([-188.4],[2.67],'x',ms=12,markeredgewidth=3,color='orange') 59 plt.plot(b_history,w_history,'o-',ms = 3,lw = 1.5,color = 'red') 60 #绘制坐标轴 61 plt.xlim(-200,-100) 62 plt.ylim(-5,5) 63 #给坐标轴命名 64 plt.xlabel(r'$b$',fontsize=16) 65 plt.ylabel(r'$w$',fontsize=16) 66 plt.show()
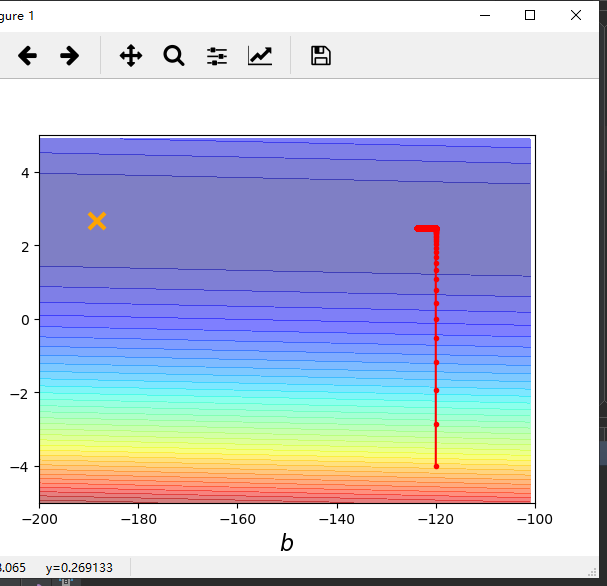
动态调整学习速率
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 4 x_data = [338,333,328,207,226,25,179,60,208,606] 5 y_data = [640,633,619,393,428,27,193,66,226,1591] 6 7 8 #生成从-200到-100的数,不包括-100 9 #x轴 10 x = np.arange(-200,-100,1) 11 #y轴 12 y = np.arange(-5,5,0.1) 13 #存储对应的误差 14 Z = np.zeros((len(x),len(y))) 15 #x横向平铺给X,y纵向平铺给Y 16 #X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) 17 for i in range(len(x)): 18 for j in range(len(y)): 19 b = x[i] 20 w = y[j] 21 #按行进行计算误差 22 Z[j][i] = 0 23 #误差和 24 for n in range(len(x_data)): 25 Z[j][i] = Z[j][i] + (y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])**2 26 #归一化 27 Z[j][i] = Z[j][i]/len(x_data) 28 29 30 #y = b + w * x 31 b = -120 32 w = -4 33 #lr = 0.0000001 34 lr = 1#学习速率 35 # lr = 0.00001 36 iteration = 100000 37 38 #记录每次求得的b和w 39 b_history = [b] 40 w_history = [w] 41 42 lr_b = 0 43 lr_w = 0 44 45 46 for i in range(iteration): 47 b_grad = 0.0 48 w_grad = 0.0 49 50 for n in range(len(x_data)): 51 b_grad = b_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*1.0 52 w_grad = w_grad - 2.0 * (y_data[n] - b - w * x_data[n]) * x_data[n] 53 54 lr_b = lr_b + b_grad ** 2 55 lr_w = lr_w + w_grad ** 2 56 # b = b - lr * b_grad 57 # w = w - lr * w_grad 58 #动态调整学习速率 59 b = b - lr/np.sqrt(lr_b) * b_grad 60 w = w - lr/np.sqrt(lr_w) * w_grad 61 62 b_history.append(b) 63 w_history.append(w) 64 65 #五十种颜色 透明度:0.8 66 plt.contourf(x, y, Z, 50, alpha=0.8, cmap=plt.get_cmap('jet')) 67 #画出最优解的位置 68 plt.plot([-188.4],[2.67],'x',ms=12,markeredgewidth=3,color='orange') 69 plt.plot(b_history,w_history,'o-',ms = 3,lw = 1.5,color = 'red') 70 #绘制坐标轴 71 plt.xlim(-200,-100) 72 plt.ylim(-5,5) 73 #给坐标轴命名 74 plt.xlabel(r'$b$',fontsize=16) 75 plt.ylabel(r'$w$',fontsize=16) 76 plt.show()