原型模式
定义
原型模式,用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
动机
-
资源优化场景
类初始化需要消化非常多的资源,这个资源包括数据、硬件资源等。
-
性能和安全要求的场景
通过new产生一个对象需要非常繁琐的数据准备或访问权限,则可以使用原型模式。
-
一个对象多个修改者的场景
一个对象需要提供给其他对象访问,而且各个调用者可能都需要修改其值时,可以考虑使用原型模式拷贝多个对象供调用者使用。
UML类图
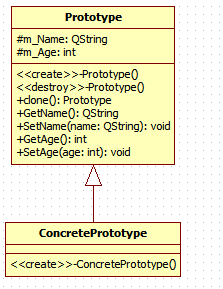
-
原型模式基类 Prototype
- 具体原型模式类 ConcretePrototype
里面的关键方法就是clone()方法。
源码实现
- prototype.h
#ifndef PROTOTYPE_H
#define PROTOTYPE_H
#include<QString>
class Prototype
{
public:
Prototype();
virtual ~Prototype();
virtual Prototype* clone();
QString GetName();
void SetName(QString name);
int GetAge();
void SetAge(int* age);
protected:
QString m_Name;
int* m_Age;
};
class ConcretePrototype : public Prototype
{
public:
ConcretePrototype();
virtual ~ConcretePrototype() override;
virtual Prototype* clone() override;
};
#endif // PROTOTYPE_H
- prototype.cpp
#include "prototype.h"
Prototype::Prototype()
{
}
Prototype::~Prototype()
{
}
Prototype *Prototype::clone()
{
return new Prototype(*this);
}
QString Prototype::GetName()
{
return m_Name;
}
void Prototype::SetName(QString name)
{
m_Name = name;
}
int Prototype::GetAge()
{
return *m_Age;
}
void Prototype::SetAge(int* age)
{
m_Age = age;
}
ConcretePrototype::ConcretePrototype()
{
}
ConcretePrototype::~ConcretePrototype()
{
}
Prototype *ConcretePrototype::clone()
{
return new ConcretePrototype(*this);
}
- main.cpp
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
#include "prototype.h"
#define DELETEOBJECT(x) if(x != nullptr) { delete x; x = nullptr;}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
int age = 25;
Prototype* proto = new Prototype();
proto->SetAge(&age);
proto->SetName("虞姬");
qDebug() << proto->GetName();
qDebug() << proto->GetAge();
int age1 = 35;
Prototype* proto1 = proto->clone();
proto1->SetAge(&age1);
proto1->SetName("霸王");
qDebug() << proto1->GetName();
qDebug() << proto1->GetAge();
DELETEOBJECT(proto);
DELETEOBJECT(proto1);
return a.exec();
}
- 运行结果
"虞姬"
25
"霸王"
35
优点
原型模式的优点:
-
相对于new创建新对象
首先,用new新建对象不能获取当前对象运行时的状态,其次就算new了新对象,在将当前对象的值复制给新对象,效率也不如原型模式高。
-
相对于拷贝构造函数
原型模式与拷贝构造函数是不同的概念,拷贝构造函数涉及的类是已知的,原型模式涉及的类可以是未知的。
原型模式生成的新对象可能是一个派生类。拷贝构造函数生成的新对象只能是类本身。原型模式是描述了一个通用方法(或概念),它不管是如何实现的,而拷贝构造则是描述了一个具体实现方法。
缺点
原型模式的缺点:
- 配备克隆方法需要对类的功能进行通盘考虑,这对于全新的类不是很难,但对于已有的类不一定很容易,特别当一个类引用不支持串行化的间接对象,或者引用含有循环结构的时候。
- 实现原型模式每个派生类都必须实现 Clone接口。
- 逃避构造函数的约束。
参考《大话设计模式》和 https://design-patterns.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/index.html