spark streaming 学习:
spark streaming 与strom 的区别:
Spark Streaming 与strom 的区别:
1、Strom是纯实时的流式处理框架,SparkStreaming 是准实时处理框架(微批处理),因为微批处理,SparkStreaming 的吞吐量比strom的要高
2、Strom的事物机制要比spark streamming 完善
3、Strom 支持动态资源调度,(Spark1.2 开始以后也支持)
4、SparkSteaming擅长复杂的业务处理,Strom不擅长复杂的业务处理,擅长简单的汇总型计算
spark streaming 进行统计wordcount简单源码:
public static void main(String[] args){ SparkConf conf = new SparkConf(); conf.setAppName("SparkStreaming").setMaster("local[2]"); // JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf); JavaStreamingContext jsc = new JavaStreamingContext(conf, Durations.seconds(5)); JavaReceiverInputDStream<String> sts = jsc.socketTextStream("mynode2", 9999); JavaPairDStream<String, Integer> result= sts.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() { @Override public Iterator<String> call(String str) throws Exception { String[] s = str.split(" "); List<String> strings = Arrays.asList(s); return strings.iterator(); } }).mapToPair(new PairFunction<String, String, Integer>() { @Override public Tuple2<String, Integer> call(String str) throws Exception { return new Tuple2<String, Integer>(str, 1); } }).reduceByKey(new Function2<Integer, Integer, Integer>() { @Override public Integer call(Integer v1, Integer v2) throws Exception { return v1 + v2; } }); result.print(); jsc.start(); try { jsc.awaitTermination(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } jsc.stop(); }
注: conf.setmaster("local")和conf.setmaster("local[2]")的区别:
local是指进行单核处理,只能对数据进行接受
local[2]是指对数据进行双核处理,不仅能够接受数据,还能都输出数据
在运行代码的时候,需要打开代码中设置的9999端口(端口可以随意设置),打开端口的命令:
nc -lk 9999
端口的作用: 进行tcp通信
JavaReceiverInputDStream<String> sts = jsc.socketTextStream("mynode2", 9999);
此行代码的作用就是创建一个tcp连接的流
当代码运行之后,查看代码运行结果:
localhost:4040/streaming
sparkstreaming 处理任务流程图:
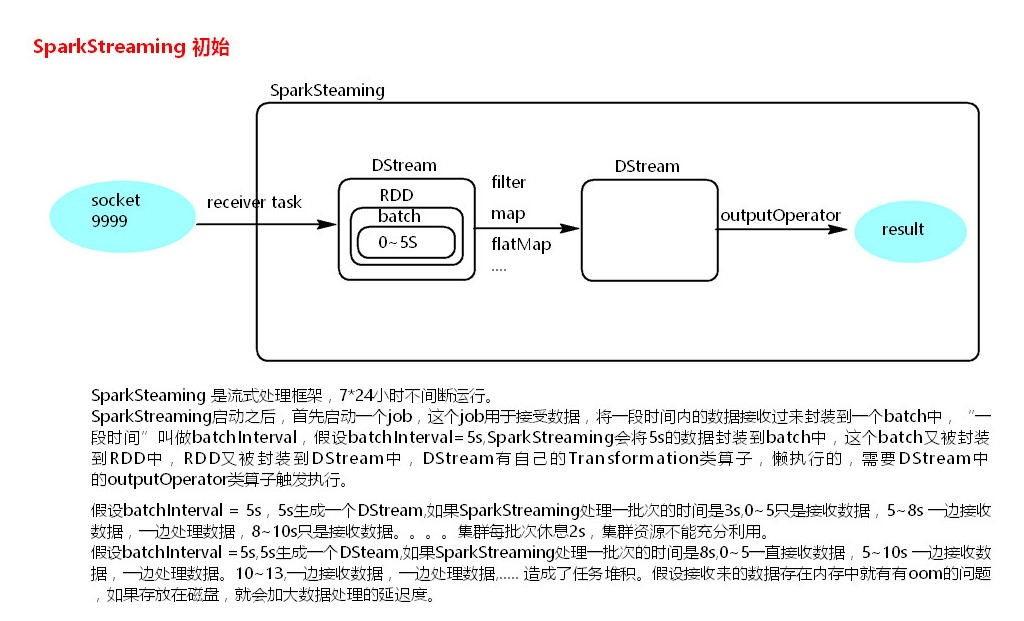
在进行socket tcp 输出测试时,如果本地环境没有对输入数据进行输出,可以换一个端口号进行尝试
* 1.SparkStreaming batchInterval 设置每批次的间隔时间【多久生成一批次】
* 2.setMaster("local[2]")至少设置2个线程模拟运行,一个task接收数据,一个task处理数据
* 3.SparkStreaming 启动之后不能添加新的逻辑
* 4.SparkStreaming.stop() 默认停掉SparkStreaming的同时,将SparkContext也会回收,stop(false)在停掉SparkStreaming之后,不会将SparkContext回收掉。
* 5.创建StreamingContext的两种方式new StreamingContext(SparkConf|SparkContext)
* 6.代码逻辑中需要一个outputOperator类算子触发执行
* 7.StreamingContext停掉之后,不能重新调用start方法启动。
/** * 1.SparkStreaming batchInterval 设置每批次的间隔时间【多久生成一批次】 * 2.setMaster("local[2]")至少设置2个线程模拟运行,一个task接收数据,一个task处理数据 * 3.SparkStreaming 启动之后不能添加新的逻辑 * 4.SparkStreaming.stop() 默认停掉SparkStreaming的同时,将SparkContext也会回收,stop(false)在停掉SparkStreaming之后,不会将SparkContext回收掉。 * 5.创建StreamingContext的两种方式new StreamingContext(SparkC * 7.StreamingContext停掉之后,不能重新调用start方法启动。 */ object SparkStreamingTest1 { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]").setAppName("streamingTest") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) // sc.setLogLevel("Error") val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc,Durations.seconds(5)) /** * hello spark * hello java */ val lines: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = ssc.socketTextStream("mynode2",9998) val words: DStream[String] = lines.flatMap(line => { line.split(" ") }) val pairWords: DStream[(String, Int)] = words.map(word=>{ // println("++++++++++++++++++++ DStream Map +++++++++++++++") new Tuple2(word,1) }) val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = pairWords.reduceByKey((v1, v2)=>{v1+v2}) /** * foreachRDD * 可以遍历DStream中的RDD,可以对DStream中的RDD进行rdd的Transformation类算子操作 * 注意:1.对获取的RDD一定要使用rdd的action算子触发执行 * 2.DStream中RDD的transforamtion类算子外部,foreachRDD内部的代码是在Driver端执行的,可以通过这个特点做到动态的改变广播变量 */ // result.foreachRDD(rdd=>{ // val bc: Broadcast[List[String]] = rdd.context.broadcast(List[String]("a","b")) //// println("========= rdd1 Transformation 外部 ===============") // val rdd1: RDD[String] = rdd.map(one => { //// println("************** rdd1 *************") // val value: List[String] = bc.value // one._1 + "_" + one._2 // }) // rdd1.foreach(println) // // }) /** * print() DStream的outPutOperator类算子 */ result.print() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() // ssc.stop() }
注:对foreachRdd方法的使用,以及该方法的作用
sparkStreaming transform算子的使用:
/** * * transform算子可以获取Dstream中的RDD,需要返回RDD类型的数据 * 注意:1、transform算子必须返回一个RDD,这个RDD被封装到一个Dstream中进行返回 * 2、transform算子内,获取的RDD的算子外部的代码是在Driver端执行的,可以根据这个特点做到动态的改变广播变量的值 * 3、 * * @param args */ def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]").setAppName("transForm") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc.setLogLevel("Error") val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc,Durations.seconds(5)) val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("mynode2",9998) val result = lines.transform(rdd => { val myrdd = rdd.map(line => { line + "#" }) myrdd }) result.print() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination()
SparkStreaming updateStateByKey算子
object UpdateStateByKey { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]").setAppName("streamingTest") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc.setLogLevel("Error") val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc,Durations.seconds(5)) /** * updateStateByKey 算子状态默认在内存中,多久将内存中的状态更新到Checkpoint一次?【必须开启checkpoint】 * 1.如果batchInterval 小于10s,那么就10s更新一次 * 2.如果batchInterval 大于10s,那么就batchInterval 更新一次,这样做为了防止频繁访问磁盘 * */ ssc.checkpoint("./data/ck") val lines: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = ssc.socketTextStream("node5",9999) val words: DStream[String] = lines.flatMap(line => { line.split(" ") }) val pairWords: DStream[(String, Int)] = words.map(word=>{ new Tuple2(word,1) }) val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = pairWords.updateStateByKey((seq: Seq[Int], option: Option[Int]) => { val i: Int = option.getOrElse(0) var oldValue = i for (elem <- seq) { oldValue += elem } Option(oldValue) }) result.print() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination()
checkpoint知识点总结:
checkpoint的意思就是建立检查点,类似于快照,例如在spark计算里面 计算流程DAG特别长,服务器需要将整个DAG计算完成得出结果,但是如果在这很长的计算流程中突然中间算出的数据丢失了,spark又会根据RDD的依赖关系从头到尾计算一遍,这样子就很费性能,当然我们可以将中间的计算结果通过cache或者persist放到内存或者磁盘中,但是这样也不能保证数据完全不会丢失,存储的这个内存出问题了或者磁盘坏了,也会导致spark从头再根据RDD计算一遍,所以就有了checkpoint,其中checkpoint的作用就是将DAG中比较重要的中间数据做一个检查点将结果存储到一个高可用的地方(通常这个地方就是HDFS里面)
说道checkpoint就得说说RDD的依赖
比如我们计算wordcount的时候:
sc.textFile("hdfspath").flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_,1)).reduceByKey(_+_).saveAsTextFile("hdfspath")
1.在textFile读取hdfs的时候就会先创建一个HadoopRDD,其中这个RDD是去读取hdfs的数据key为偏移量value为一行数据,因为通常来讲偏移量没有太大的作用所以然后会将HadoopRDD转化为MapPartitionsRDD,这个RDD只保留了hdfs的数据
2.flatMap 产生一个RDD MapPartitionsRDD
3.map 产生一个RDD MapPartitionsRDD
4.reduceByKey 产生一个RDD ShuffledRDD
5.saveAsTextFile 产生一个RDD MapPartitionsRDD
可以根据查看RDD的依赖:
scala> val rdd = sc.textFile("hdfs://lijie:9000/checkpoint0727/c1a51ee9-1daf-4169-991e-b290f88bac20/rdd-0/part-00000").flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_,1)).reduceByKey(_+_) rdd: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(String, Int)] = ShuffledRDD[29] at reduceByKey at <console>:27 scala> rdd.toDebugString res3: String = (2) ShuffledRDD[29] at reduceByKey at <console>:27 [] +-(2) MapPartitionsRDD[28] at map at <console>:27 [] | MapPartitionsRDD[27] at flatMap at <console>:27 [] | hdfs://lijie:9000/checkpoint0727/c1a51ee9-1daf-4169-991e-b290f88bac20/rdd-0/part-00000 MapPartitionsRDD[26] at textFile at <console>:27 [] | hdfs://lijie:9000/checkpoint0727/c1a51ee9-1daf-4169-991e-b290f88bac20/rdd-0/part-00000 HadoopRDD[25] at textFile at <console>:27 []
怎么建立checkpoint
首先需要用sparkContext设置hdfs的checkpoint的目录(如果不设置使用checkpoint会抛出异常:throw new SparkException(“Checkpoint directory has not been set in the SparkContext”):
scala> sc.setCheckpointDir("hdfs://lijie:9000/checkpoint0727")
执行了上面的代码,hdfs里面会创建一个目录:
/checkpoint0727/c1a51ee9-1daf-4169-991e-b290f88bac20
然后执行checkpoint
scala> val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(1 to 10000) rdd1: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Int] = ParallelCollectionRDD[0] at parallelize at <console>:27 scala> rdd1.checkpoint
发现hdfs中还是没有数据,通过collect然后hdfs就有数据了,说明checkpoint也是个transformation的算子
scala> rdd1.sum res2: Double = 5.0005E7
#其中hdfs [root@lijie hadoop]
# hadoop dfs -ls /checkpoint0727/c1a51ee9-1daf-4169-991e-b290f88bac20/rdd-0
DEPRECATED: Use of this script to execute hdfs command is deprecated.
Instead use the hdfs command for it. Found 2 items -rw-r--r-- 3 root supergroup
53404 2017-07-24 14:26 /checkpoint0727/c1a51ee9-1daf-4169-991e-b290f88bac20/rdd-0/part-00000 -rw-r--r-- 3 root supergroup
53404 2017-07-24 14:26 /checkpoint0727/c1a51ee9-1daf-4169-991e-b290f88bac20/rdd-0/part-00001
但是执行的时候相当于走了两次流程,sum的时候前面计算了一遍,然后checkpoint又会计算一次,所以一般我们先进行cache然后做checkpoint就会只走一次流程,checkpoint的时候就会从刚cache到内存中取数据写入hdfs中,如下:
rdd.cache()
rdd.checkpoint()
rdd.collect
其中作者也说明了,在checkpoint的时候强烈建议先进行cache,并且当你checkpoint执行成功了,那么前面所有的RDD依赖都会被销毁,如下:
/**
* Mark this RDD for checkpointing. It will be saved to a file inside the checkpoint
* directory set with `SparkContext#setCheckpointDir` and all references to its parent
* RDDs will be removed. This function must be called before any job has been
* executed on this RDD. It is strongly recommended that this RDD is persisted in
* memory, otherwise saving it on a file will require recomputation.
*/
updateStateByKey 错误解决:
19/06/26 09:56:55 ERROR StreamingContext: Error starting the context, marking it as stopped java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: requirement failed: No output operations registered, so nothing to execute at scala.Predef$.require(Predef.scala:219) at org.apache.spark.streaming.DStreamGraph.validate(DStreamGraph.scala:168) at org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext.validate(StreamingContext.scala:513) at org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext.liftedTree1$1(StreamingContext.scala:573) at org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext.start(StreamingContext.scala:572) at com.bjsxt.myscala.UpdateStateByKey$.main(UpdateStateByKey.scala:58) at com.bjsxt.myscala.UpdateStateByKey.main(UpdateStateByKey.scala) Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: requirement failed: No output operations registered, so nothing to execute at scala.Predef$.require(Predef.scala:219) at org.apache.spark.streaming.DStreamGraph.validate(DStreamGraph.scala:168) at org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext.validate(StreamingContext.scala:513) at org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext.liftedTree1$1(StreamingContext.scala:573) at org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext.start(StreamingContext.scala:572) at com.bjsxt.myscala.UpdateStateByKey$.main(UpdateStateByKey.scala:58) at com.bjsxt.myscala.UpdateStateByKey.main(UpdateStateByKey.scala)
代码执行的时候,需要出发print()方法,否则会报错
窗口操作:

def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]").setAppName("windowsoption") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc.setLogLevel("Error") val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc,Durations.seconds(5)) val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("mynode2",9996) val words = lines.flatMap(line => (line.split(" "))) val pairWords = words.map(word=>{new Tuple2(word,1)}) /** * 窗口操作的普通机制 * * 滑动间隔和窗口长度必须是 batchInterval 的整数倍 * 代码中参数的作用:每隔5秒计算过去15秒批次的数据 */ /*val windowsResult = pairWords.reduceByKeyAndWindow((v1: Int, v2: Int) => { v1 + v2 }, Durations.seconds(15), Durations.seconds(5)) */ /** * 窗口操作优化机制 * * */ ssc.checkpoint("./data/streamingCheckpoint") val windowResult = pairWords.reduceByKeyAndWindow( (v1: Int, v2: Int) => { v1 + v2 }, (v1: Int, v2: Int) => { v1 - v2 }, Durations.seconds(15), Durations.seconds(5) ) windowResult.print() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination()
Spark Streaming 监控一个目录:
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("monitorFile") val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf,Durations.seconds(10)) ssc.sparkContext.setLogLevel("Error") val lines = ssc.textFileStream("./data/streamingCopyFile") val words = lines.flatMap(line=>{line.split(" ")}) val pairWords = words.map(word=>{(word,1)}) val result = pairWords.reduceByKey((v1:Int,v2:Int)=>{v1+v2}) result.saveAsTextFiles("./data/streamingSavePath/prefix","suffix") result.print() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() ssc.stop()
生成文件的代码:
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { /** * 此复制文件的程序是模拟在data目录下动态生成相同格式的txt文件,用于给sparkstreaming 中 textFileStream提供输入流。 * @author root * */ while(true){ import java.util.UUID Thread.sleep(5000) val uuid = UUID.randomUUID.toString System.out.println(uuid) copyFile(new File("./data/words"), new File(".\data\streamingCopyFile\" + uuid + "----words.txt")) } } def copyFile(fromFile: File, toFile: File): Unit = { val ins = new FileInputStream(fromFile) val out = new FileOutputStream(toFile) val buffer = new Array[Byte](1024 * 1024) var size = 0 while(size!= -1){ out.write(buffer,0,buffer.length) size = ins.read(buffer) } ins.close() out.close() }