package test4;
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Child c = new Child();
}
}

结论:通过super调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
2:方法覆盖
package test4;
public class Fruit {
public String toString()
{
return "Fruit toString.";
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Fruit f=new Fruit();
System.out.println("f="+f);
// System.out.println("f="+f.toString());
}
}
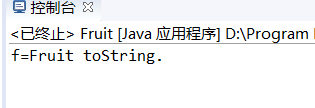
结论:
在“+”运算中,当任何一个对象与一个String对象,连接时,会隐式地调用其toString()方法,默认情况下,此方法返回“类名@+hashCode”。为了返回有意义的信息,子类可以重写toString()方法。
3.
package test4;
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.print("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
}
}
运行结果:
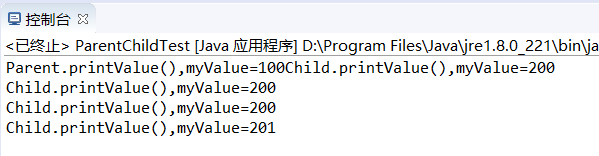
结论:
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪种方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。