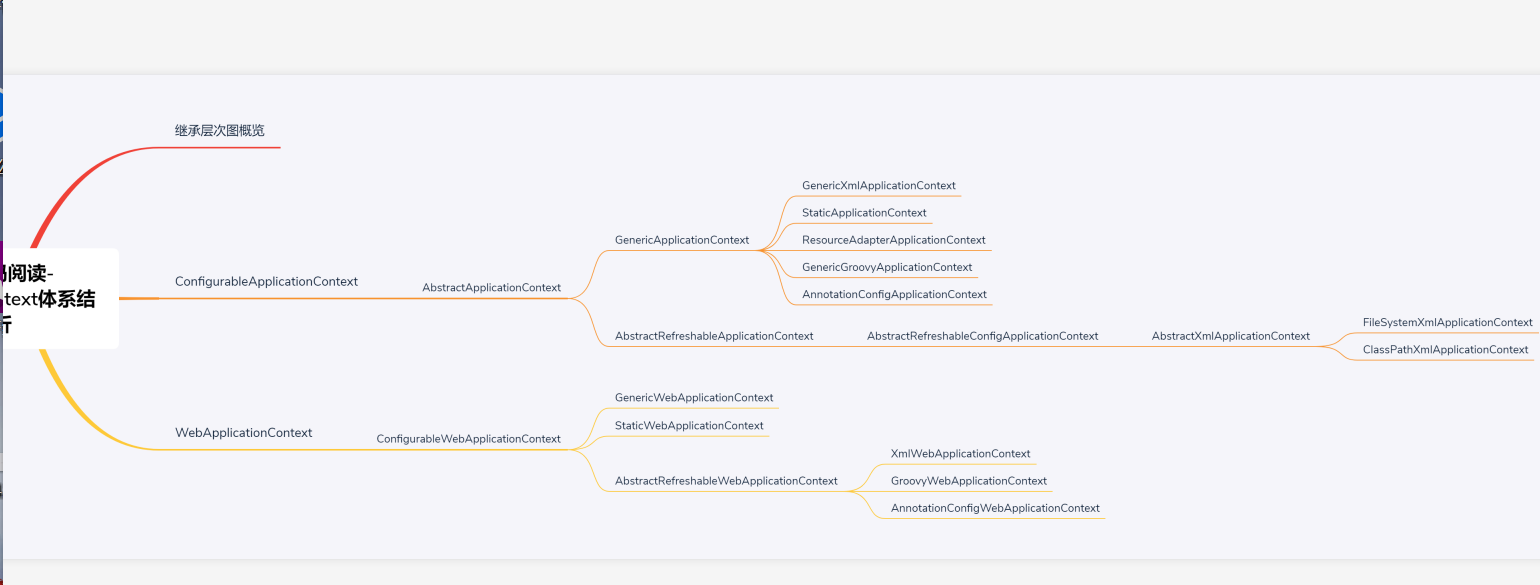
上一篇文中提到父容器root applicationContext最后是调用XmlWebApplicationContext去实现的,
但是什么时候开始解析标签(默认标签、自定义标签)、注册bean以及注解的bean加载等一些列的操作;
知识点普及:
在 Spring 项目中,加载 applicationContext.xml 的方法
1、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
这个方法是从文件绝对路径加载配置文件,例如:
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( "G:/Test/applicationcontext.xml ");
如果在参数中写的不是绝对路径,那么方法调用的时候也会默认用绝对路径来找,我测试的时候发现默认的绝对路径是eclipse所在的路径。
采用绝对路径的话,程序的灵活性就很差了,所以这个方法一般不推荐。
(如果要使用classpath路径,需要加入前缀classpath: )
2、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
这个方法是从classpath下加载配置文件(适合于相对路径方式加载),
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( "/applicationcontext.xml ");
下面我们就围绕这些问题展开摸索:
参数中classpath: 前缀是不需要的,默认就是指项目的classpath路径下面;
这也就是说用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext时默认的根目录是在WEB-INF/classes下面,而不是项目根目录。这个需要注意!
3、XmlWebApplicationContext
专为web工程定制的方法,推荐Web项目中使用。例如:
ServletContext servletContext = request.getSession().getServletContext();
ApplicationContext ctx = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
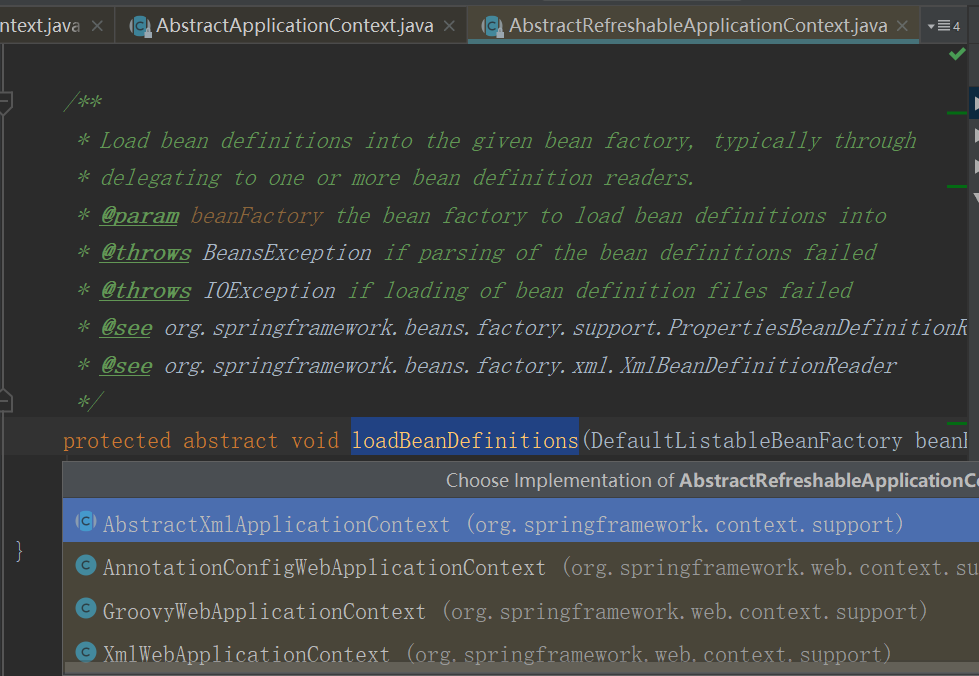
public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext {....}
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext extends
AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext implements ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, ThemeSource {..}
看标红的东东这个就是我们的入口
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
implements BeanNameAware, InitializingBean
/** * Triggers {@link #refresh()} if not refreshed in the concrete context's * constructor already. */ @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { if (!isActive()) { refresh(); } }
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {..}
1 @Override 2 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 3 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 4 // Prepare this context for refreshing. 5 prepareRefresh(); 6 7 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 8 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 9 10 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 11 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 12 13 try { 14 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 15 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 16 17 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 18 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 19 20 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 21 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 22 23 // Initialize message source for this context. 24 initMessageSource(); 25 26 // Initialize event multicaster for this context. 27 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 28 29 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 30 onRefresh(); 31 32 // Check for listener beans and register them. 33 registerListeners(); 34 35 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 36 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 37 38 // Last step: publish corresponding event. 39 finishRefresh(); 40 } 41 42 catch (BeansException ex) { 43 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 44 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + 45 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); 46 } 47 48 // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. 49 destroyBeans(); 50 51 // Reset 'active' flag. 52 cancelRefresh(ex); 53 54 // Propagate exception to caller. 55 throw ex; 56 } 57 58 finally { 59 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we 60 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... 61 resetCommonCaches(); 62 } 63 } 64 }
1、boot AppliccationConetxt的Map在哪
2、Servlet ApplicationContext的Map在哪,如何进行参数绑定的?


/** * Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class. * <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping. */ private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { // Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later. } } // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering // a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found. if (this.handlerMappings == null) { this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default"); } } }
DispatcherServlet.java
/** * Create a List of default strategy objects for the given strategy interface. * <p>The default implementation uses the "DispatcherServlet.properties" file (in the same * package as the DispatcherServlet class) to determine the class names. It instantiates * the strategy objects through the context's BeanFactory. * @param context the current WebApplicationContext * @param strategyInterface the strategy interface * @return the List of corresponding strategy objects */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { String key = strategyInterface.getName(); String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key); if (value != null) { String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value); List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<T>(classNames.length); for (String className : classNames) { try {
// 加载这个class Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
// 实例化 Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz); strategies.add((T) strategy); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + "] for interface [" + key + "]", ex); } catch (LinkageError err) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "Error loading DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + "] for interface [" + key + "]: problem with class file or dependent class", err); } } return strategies; } else { return new LinkedList<T>(); } }
1 # Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces. 2 # Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context. 3 # Not meant to be customized by application developers. 4 5 org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver 6 7 org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver 8 9 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping, 10 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping 11 12 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter, 13 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter, 14 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter 15 16 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver, 17 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver, 18 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 19 20 org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator 21 22 org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver 23 24 org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
public abstract class ApplicationObjectSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {...}
@Override public final void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException { if (context == null && !isContextRequired()) { // Reset internal context state. this.applicationContext = null; this.messageSourceAccessor = null; } else if (this.applicationContext == null) { // Initialize with passed-in context. if (!requiredContextClass().isInstance(context)) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Invalid application context: needs to be of type [" + requiredContextClass().getName() + "]"); } this.applicationContext = context; this.messageSourceAccessor = new MessageSourceAccessor(context); initApplicationContext(context); } else { // Ignore reinitialization if same context passed in. if (this.applicationContext != context) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Cannot reinitialize with different application context: current one is [" + this.applicationContext + "], passed-in one is [" + context + "]"); } } }
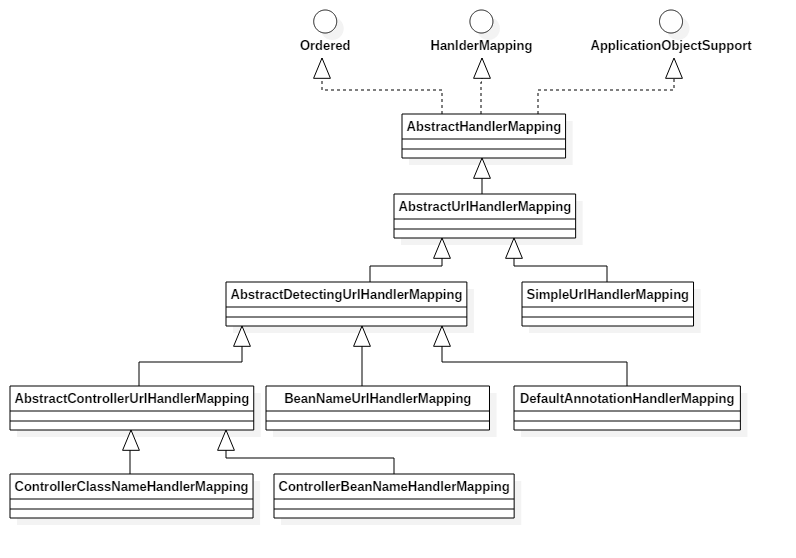
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport implements HandlerMapping, Ordered {...}
/** * Initializes the interceptors. * @see #extendInterceptors(java.util.List) * @see #initInterceptors() */ @Override protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException { extendInterceptors(this.interceptors); detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors); initInterceptors(); }
public abstract class AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping extends AbstractUrlHandlerMapping {....}
/** * Calls the {@link #detectHandlers()} method in addition to the * superclass's initialization. */ @Override public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException { super.initApplicationContext(); detectHandlers(); }
/** * Register all handlers found in the current ApplicationContext. * <p>The actual URL determination for a handler is up to the concrete * {@link #determineUrlsForHandler(String)} implementation. A bean for * which no such URLs could be determined is simply not considered a handler. * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException if the handler couldn't be registered * @see #determineUrlsForHandler(String) */ protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Looking for URL mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext()); } String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); // Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for. for (String beanName : beanNames) { String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) { // URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler. registerHandler(urls, beanName); } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Rejected bean name '" + beanName + "': no URL paths identified"); } } } }
demo
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping"> <property name="mappings"> <props> <prop key="/userlist.htm">userController</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping"/> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping"/> <bean id="userController" name="/users" class="cn.com.infcn.web.controller.UserController"></bean>
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.java
/** * Checks name and aliases of the given bean for URLs, starting with "/". */ @Override protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) { List<String> urls = new ArrayList<String>(); if (beanName.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(beanName); } String[] aliases = getApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName); for (String alias : aliases) { if (alias.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(alias); } } return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls); }
DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping.java
/** * Checks for presence of the {@link org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping} * annotation on the handler class and on any of its methods. */ @Override protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) { ApplicationContext context = getApplicationContext(); Class<?> handlerType = context.getType(beanName); RequestMapping mapping = context.findAnnotationOnBean(beanName, RequestMapping.class); if (mapping != null) { // @RequestMapping found at type level this.cachedMappings.put(handlerType, mapping); Set<String> urls = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); String[] typeLevelPatterns = mapping.value(); if (typeLevelPatterns.length > 0) { // @RequestMapping specifies paths at type level String[] methodLevelPatterns = determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, true); for (String typeLevelPattern : typeLevelPatterns) { if (!typeLevelPattern.startsWith("/")) { typeLevelPattern = "/" + typeLevelPattern; } boolean hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings = false; for (String methodLevelPattern : methodLevelPatterns) { if (methodLevelPattern == null) { hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings = true; } else { String combinedPattern = getPathMatcher().combine(typeLevelPattern, methodLevelPattern); addUrlsForPath(urls, combinedPattern); } } if (hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings || org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerType)) { addUrlsForPath(urls, typeLevelPattern); } } return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls); } else { // actual paths specified by @RequestMapping at method level return determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, false); } } else if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, Controller.class) != null) { // @RequestMapping to be introspected at method level return determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, false); } else { return null; } }