Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following operations: get and put.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.put(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reached its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting a new item.
Follow up:
Could you do both operations in O(1) time complexity?
题意:实现一个LRU缓存
Solution: HashMap + doubly LinkedList
删除操作分为2种情况:
- 给定node data删除node: 单链表和双向链表都需要从头到尾进行遍历从而找到对应node进行删除,时间复杂度都为O(n)。
- 给定node address删除node: 单链表需要从头到尾遍历直到找到该node的pre node,时间复杂度为O(n)。双向链表只需O(1)时间即能找到该node的pre node。
HashMap保存node address,可以基本保证在O(1)时间内找到该node
具体实现如下:
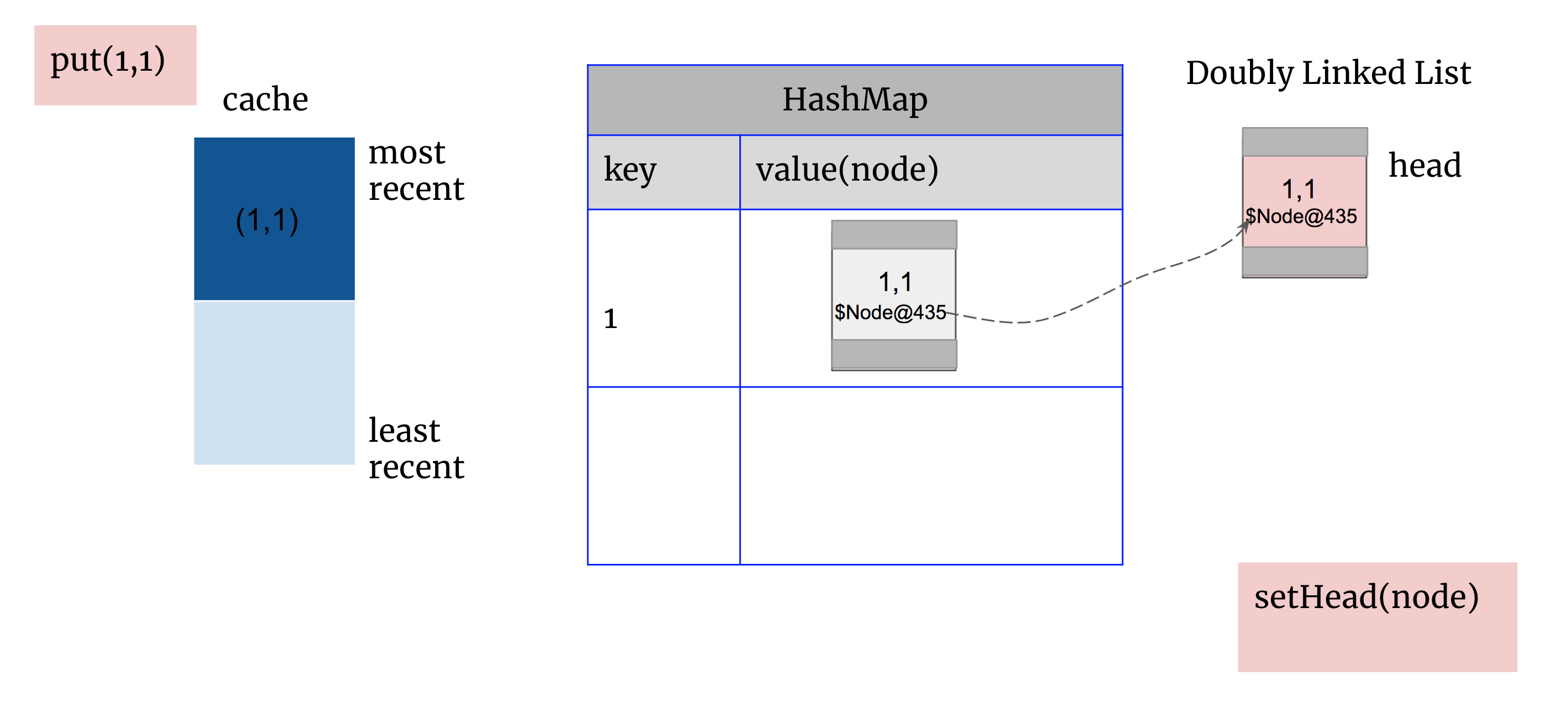
put(1,1): 先create 一个newNode(1,1)地址为$Node@435,HashMap存入(1, $Node@435), 双向链表将newNode(1,1)设为head
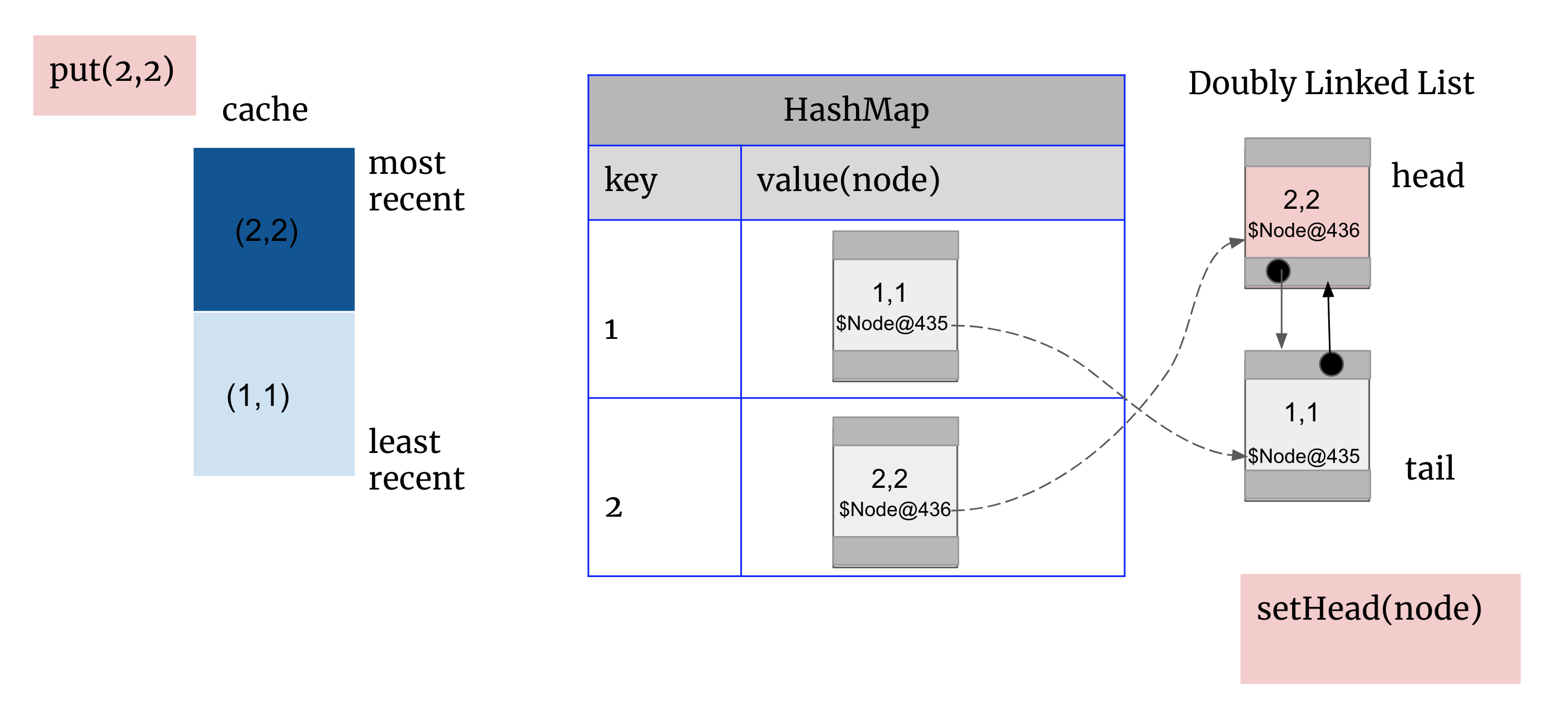
put(2,2): 先create 一个newNode(2,2)地址为$Node@436,HashMap存入(2, $Node@436), 双向链表将newNode(2,2)设为head
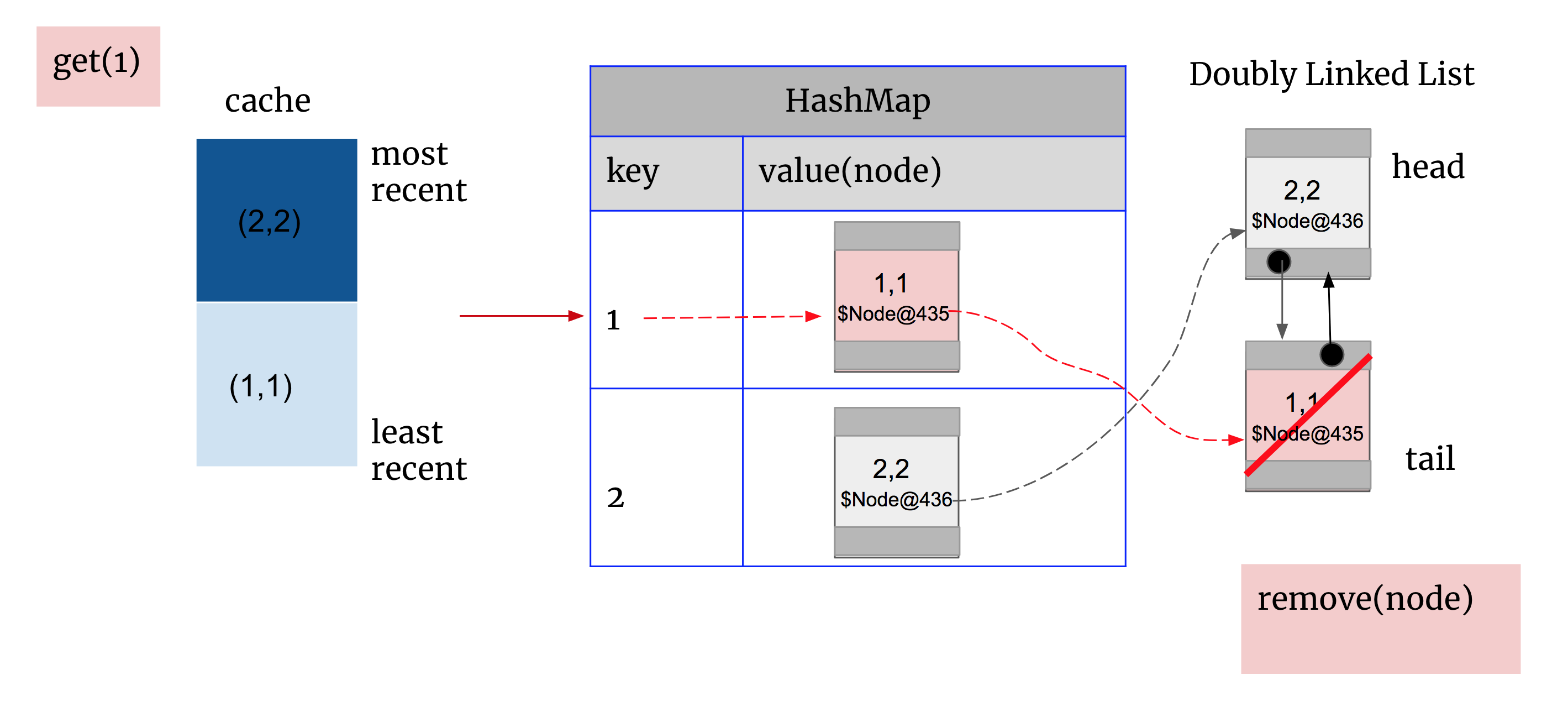
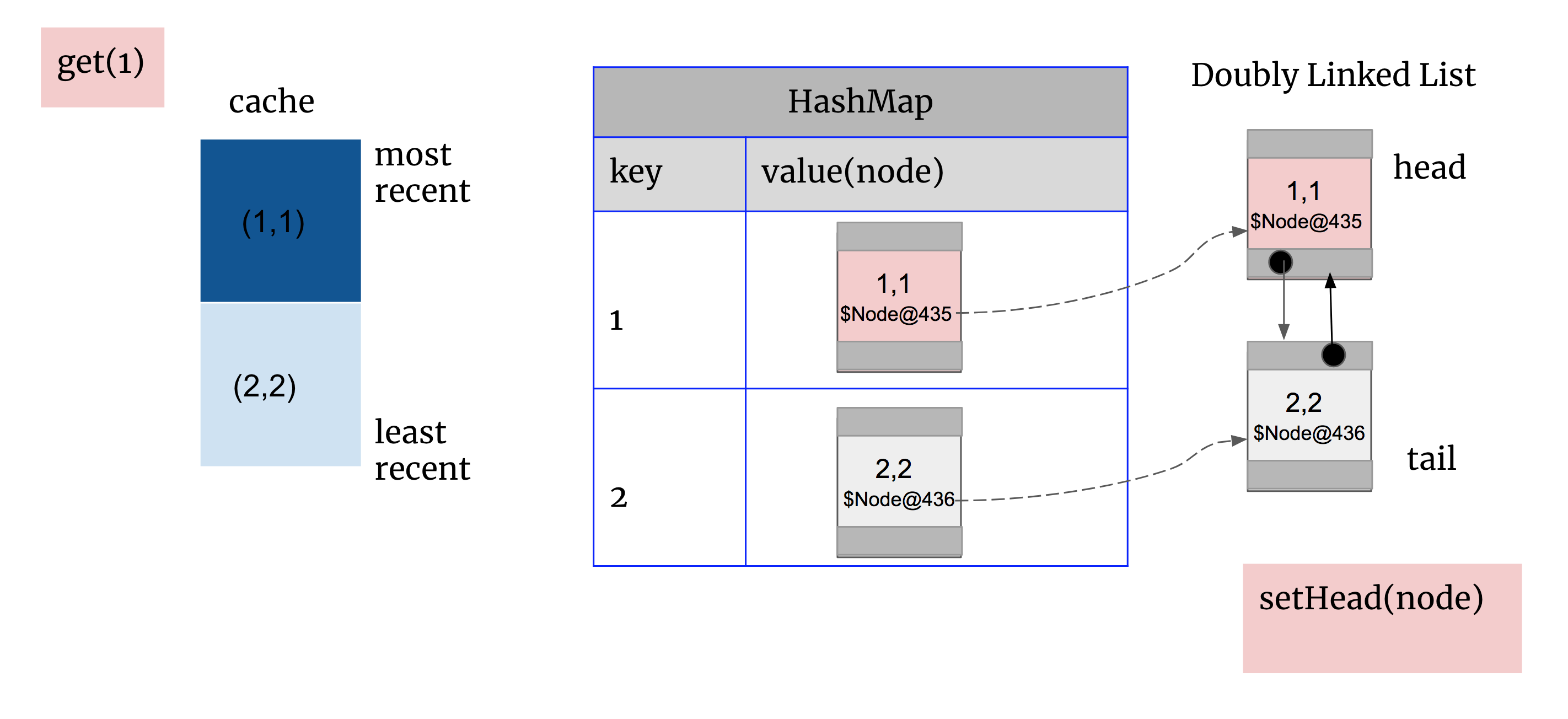
get(1): 先在HashMap中找到1对应node的地址$Node@435,通过该地址找到双向链表对应node(1,1) 。删除该node(1,1)再重新setHead
put(3,3): 先create 一个newNode(3,3)地址为$Node@437, 发现Cache is full! We need to evict something to make room.
1. 首先释放HashMap空间,通过双向链表中tailNode的key找到要在HashMap中删除的key
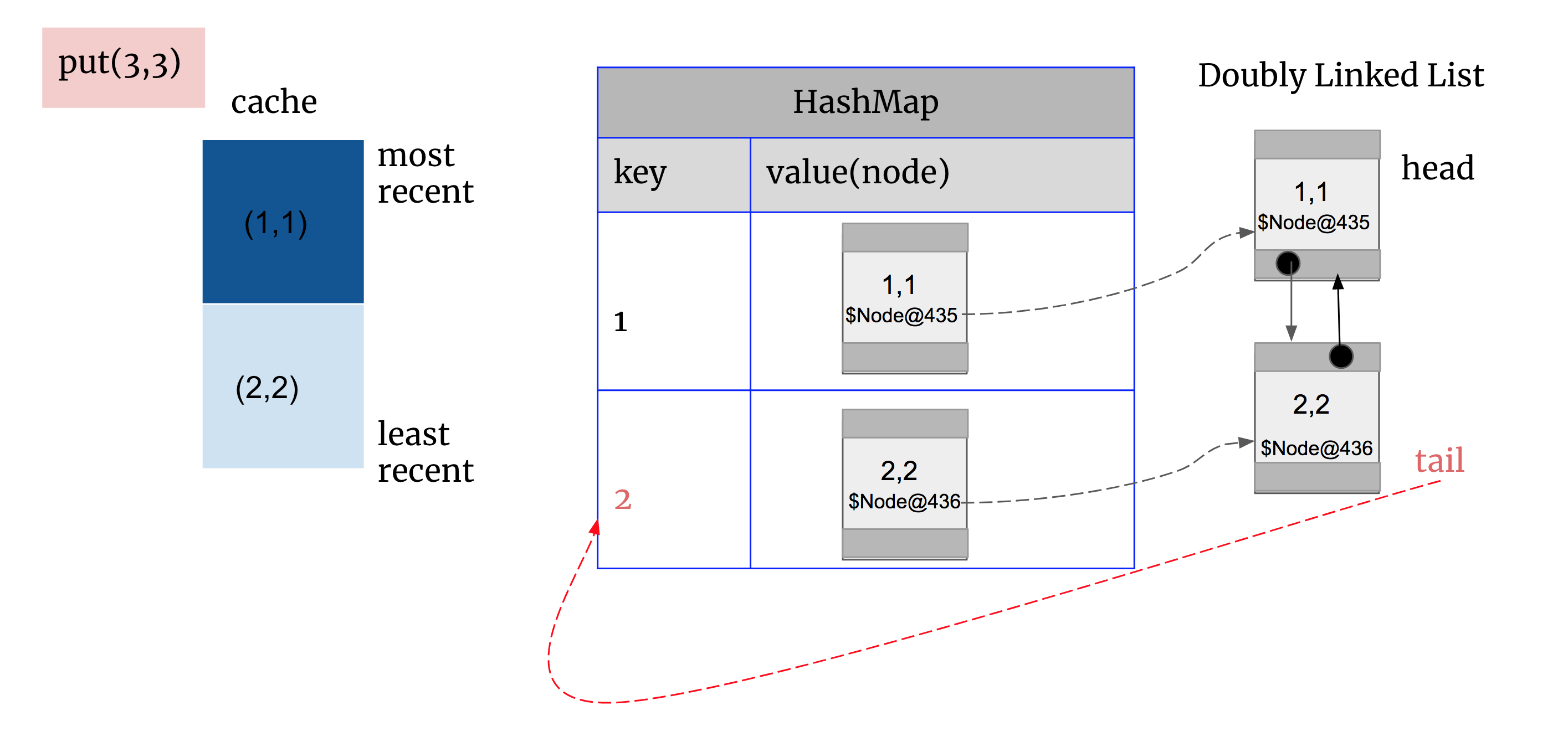
2. 然后删掉双向链表的tailNode
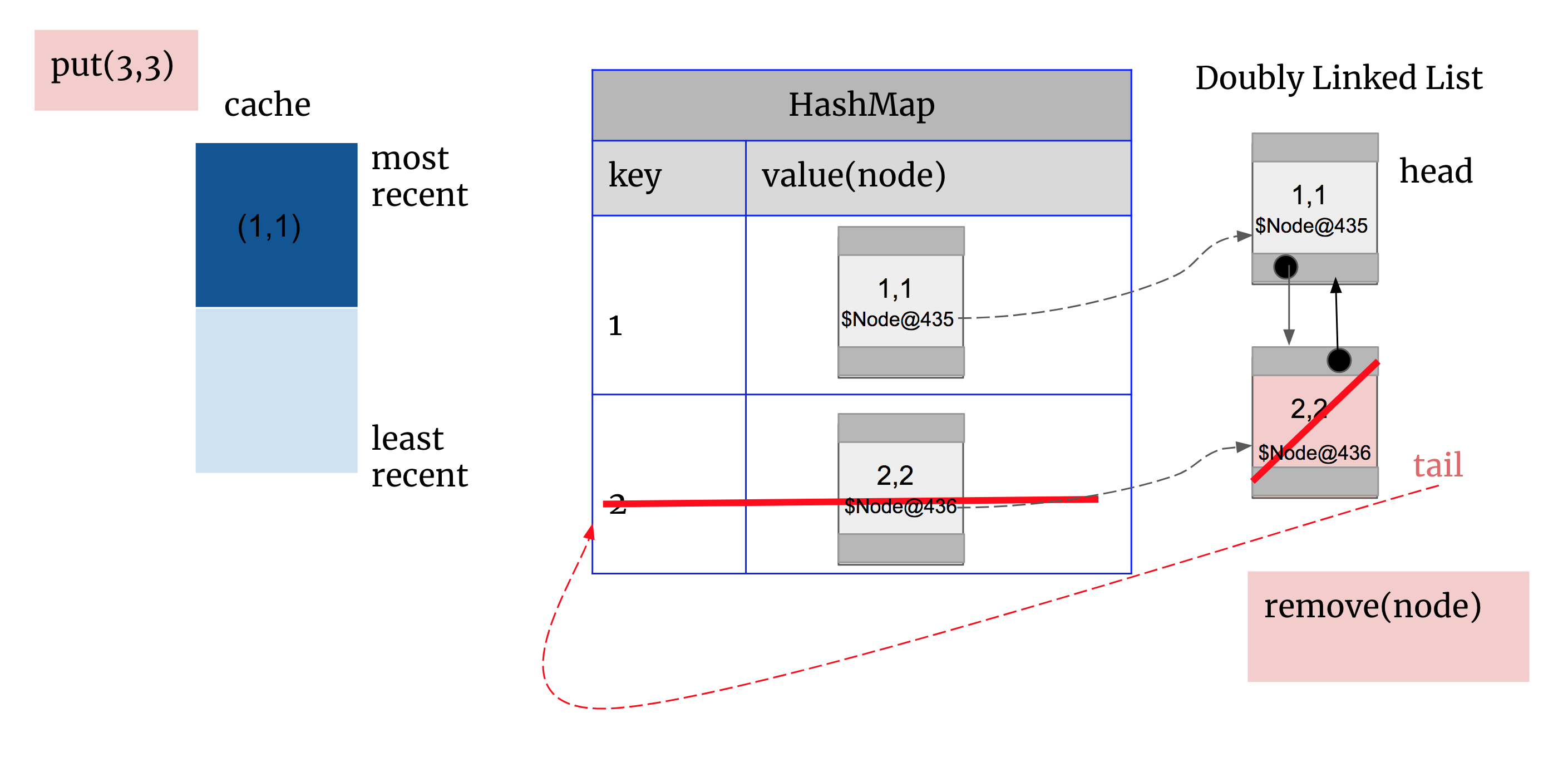
3. 将newNode(3,3)在双向链表中setHead
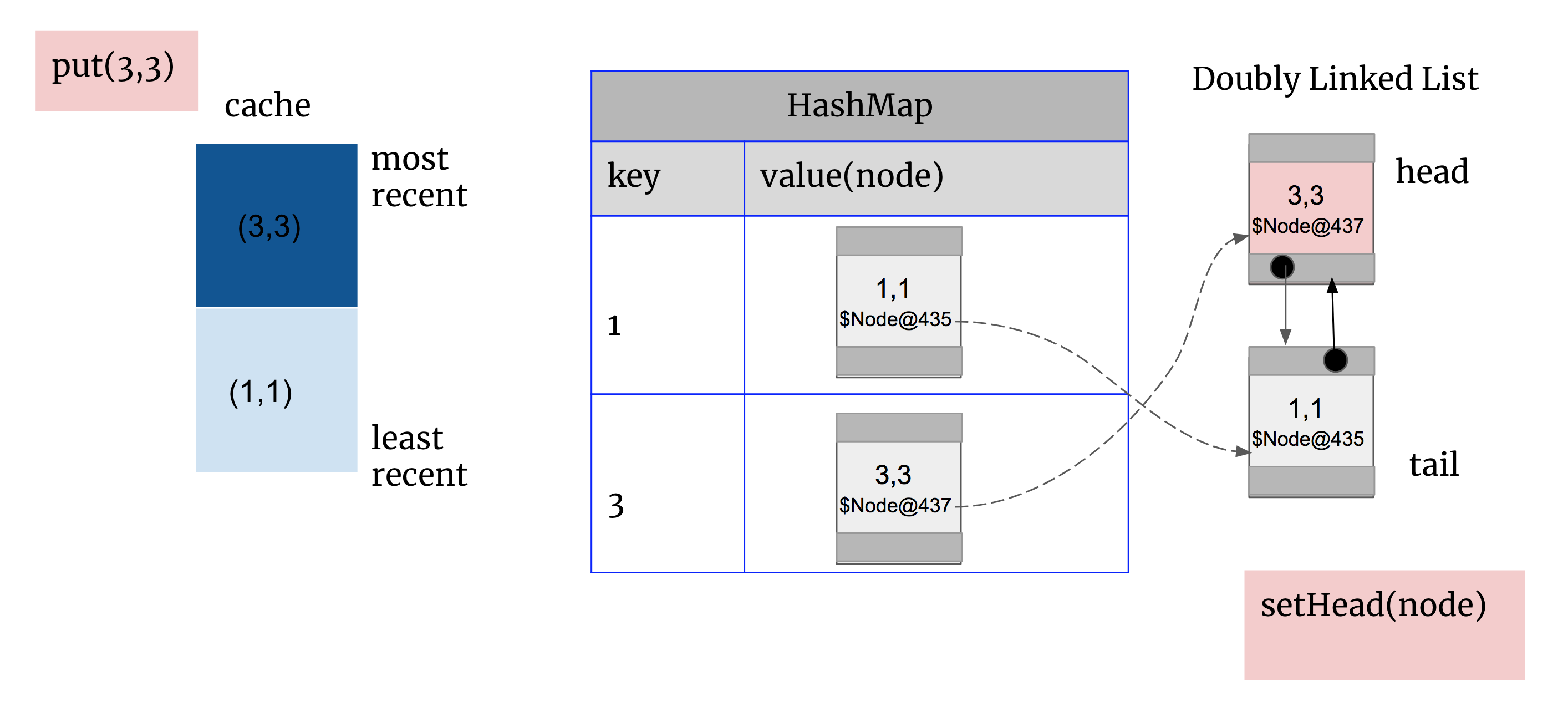
思考:
1. why not using java.util.LinkedinList?
因为java自带的linkedlist中,删除操作是从头到尾scan特定值再删除,时间为O(n)。但题目要求O(1)。
2. why not using java.util.LinkedHashMap?
这题说白了,就是考察java自带的LinkedHashMap是怎么实现的,我们当然不能。
code
1 public class LRUCache { 2 private int capacity; 3 private final HashMap<Integer, Node> map; 4 private Node head; 5 private Node tail; 6 7 public LRUCache(int capacity) { 8 this.capacity = capacity; 9 map = new HashMap<>(); 10 } 11 12 public int get(int key) { 13 // no key exists 14 if (!map.containsKey(key)) return -1; 15 // key exists, move it to the front 16 Node n = map.get(key); 17 remove(n); 18 setHead(n); 19 return n.value; 20 21 } 22 23 public void put(int key, int value) { 24 // key exits 25 if (map.containsKey(key)) { 26 // update the value 27 Node old = map.get(key); 28 old.value = value; 29 // move it to the front 30 remove(old); 31 setHead(old); 32 } 33 // no key exists 34 else { 35 Node created = new Node(key, value); 36 // reach the capacity, move the oldest item 37 if (map.size() >= capacity) { 38 map.remove(tail.key); 39 remove(tail); 40 setHead(created); 41 } 42 // insert the entry into list and update mapping 43 else { 44 setHead(created); 45 } 46 map.put(key, created); 47 } 48 } 49 50 private void remove(Node n) { 51 if (n.prev != null) { 52 n.prev.next = n.next; 53 } else { 54 head = n.next; 55 } 56 if (n.next != null) { 57 n.next.prev = n.prev; 58 } else { 59 tail = n.prev; 60 } 61 62 } 63 64 private void setHead(Node n) { 65 n.next = head; 66 n.prev = null; 67 if (head != null) head.prev = n; 68 head = n; 69 if (tail == null) tail = head; 70 } 71 72 // doubly linked list 73 class Node { 74 int key; 75 int value; 76 Node prev; 77 Node next; 78 79 public Node(int key, int value) { 80 this.key = key; 81 this.value = value; 82 } 83 } 84 }