Activiti内部实现中,各主要部件关系
对外,提供Service服务,它是无状态的。
这些Service包括:
- protected RepositoryService repositoryService = new RepositoryServiceImpl();
- protected RuntimeService runtimeService = new RuntimeServiceImpl();
- protected HistoryService historyService = new HistoryServiceImpl();
- protected IdentityService identityService = new IdentityServiceImpl();
- protected TaskService taskService = new TaskServiceImpl();
- protected FormService formService = new FormServiceImpl();
- protected ManagementService managementService = new ManagementServiceImpl();
对service提供的服务,基本上每一个需要执行具体任务的方法,都有一个对应的Command实现与之对应。
- 一般来说,一个Command对应一个完整事物;
- 调用Command之前,都会经过CommandInterceptor,这个在初始化时就确定了,如:LogInterceptor >> CommandContextInterceptor >> CommandInvoker
如果Command不涉及节点相关内容,而是直接对数据库进行操作,则直接关联DB,入DbSqlSession的缓存;
否则,一般会通过ExecutionEntity来完成具体的操作,这里,封装了一些基本的原子操作,它们都是AtomicOperation的接口实现:
流程实例类:
- AtomicOperationProcessStart
- AtomicOperationProcessStartInitial
- AtomicOperationProcessEnd
流程活动类:
- AtomicOperationActivityStart
- AtomicOperationActivityExecute
- AtomicOperationActivityEnd
流程活动流转类:
- AtomicOperationTransitionNotifyListenerEnd
- AtomicOperationTransitionDestroyScope
- AtomicOperationTransitionNotifyListenerTake
- AtomicOperationTransitionCreateScope
- AtomicOperationTransitionNotifyListenerStart
流程执行树清理类:
- AtomicOperationDeleteCascade
- AtomicOperationDeleteCascadeFireActivityEnd
其中,活动执行时,具体动作是由ActivityBehavior的实现类来决定的:
关于默认ID生成器
Activiti的默认生成器是DbIdGenerator,实际是一次从数据库中取一块数据,然后慢慢用,用完后再取。
/**
* @author Tom Baeyens
*/
public class DbIdGenerator implements IdGenerator {
protected int idBlockSize;
protected long nextId = 0;
protected long lastId = -1;
protected CommandExecutor commandExecutor;
protected CommandConfig commandConfig;
public synchronized String getNextId() {
if (lastId<nextId) {
getNewBlock();
}
long _nextId = nextId++;
return Long.toString(_nextId);
}
protected synchronized void getNewBlock() {
IdBlock idBlock = commandExecutor.execute(commandConfig, new GetNextIdBlockCmd(idBlockSize));
this.nextId = idBlock.getNextId();
this.lastId = idBlock.getLastId();
}
- 在ProcessEngineConfiguration中定义的块默认大小100;
- 在ProcessEngineComfigurationImpl中,完成初始化:
// id generator /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
protected void initIdGenerator() {
if (idGenerator==null) {
CommandExecutor idGeneratorCommandExecutor = null;
if (idGeneratorDataSource!=null) {
ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = new StandaloneProcessEngineConfiguration();
processEngineConfiguration.setDataSource(idGeneratorDataSource);
processEngineConfiguration.setDatabaseSchemaUpdate(DB_SCHEMA_UPDATE_FALSE);
processEngineConfiguration.init();
idGeneratorCommandExecutor = processEngineConfiguration.getCommandExecutor();
} else if (idGeneratorDataSourceJndiName!=null) {
ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = new StandaloneProcessEngineConfiguration();
processEngineConfiguration.setDataSourceJndiName(idGeneratorDataSourceJndiName);
processEngineConfiguration.setDatabaseSchemaUpdate(DB_SCHEMA_UPDATE_FALSE);
processEngineConfiguration.init();
idGeneratorCommandExecutor = processEngineConfiguration.getCommandExecutor();
} else {
idGeneratorCommandExecutor = getCommandExecutor();
}
DbIdGenerator dbIdGenerator = new DbIdGenerator();
dbIdGenerator.setIdBlockSize(idBlockSize);
dbIdGenerator.setCommandExecutor(idGeneratorCommandExecutor);
dbIdGenerator.setCommandConfig(getDefaultCommandConfig().transactionRequiresNew());
idGenerator = dbIdGenerator;
}
}
注意:此处对getNextId()方法加了synchronize关键字,它在单机部署下,确定不会出现网上分析的什么ID重复问题。
关于task的start_time_字段取值问题
在TaskEntity中:
/** creates and initializes a new persistent task. */
public static TaskEntity createAndInsert(ActivityExecution execution) {
TaskEntity task = create();
task.insert((ExecutionEntity) execution);
return task;
}
public void insert(ExecutionEntity execution) {
CommandContext commandContext = Context.getCommandContext();
DbSqlSession dbSqlSession = commandContext.getDbSqlSession();
dbSqlSession.insert(this);
if(execution != null) {
execution.addTask(this);
}
commandContext.getHistoryManager().recordTaskCreated(this, execution);
}
/*
* 。。。。
*/
/** Creates a new task. Embedded state and create time will be initialized.
* But this task still will have to be persisted. See {@link #insert(ExecutionEntity)}. */
public static TaskEntity create() {
TaskEntity task = new TaskEntity();
task.isIdentityLinksInitialized = true;
task.createTime = ClockUtil.getCurrentTime();
return task;
}
由此知道,活动的时间是由ClockUtil.getCurrentTime()决定的。再来看看CockUtil的源码:
/**
* @author Joram Barrez
*/
public class ClockUtil {
private volatile static Date CURRENT_TIME = null;
public static void setCurrentTime(Date currentTime) {
ClockUtil.CURRENT_TIME = currentTime;
}
public static void reset() {
ClockUtil.CURRENT_TIME = null;
}
public static Date getCurrentTime() {
if (CURRENT_TIME != null) {
return CURRENT_TIME;
}
return new Date();
}
}
注意:
因为可能多线程情况,而且只有set,不会执行类似++,--这样的操作,所以这里用volatile关键字完全满足需要。
默认实现在分布式中问题
在上面介绍了DbIdGenerator以及ClockUtil之后,可以清楚明白他们的原理,那么在分布式部署中,如果还是使用这种默认的实现而不加以改善,会出现什么问题。
1.DbIdGenerator的getNextId()/getNewBlock()两个方法,在分布式主机中,synchronize不能顺利实现锁控制;
2.ClockUtil严重依赖容器所在服务器时间,但是分布式主机的时间不可能达到完全的同步;
3.在分布式主机中,对同一个任务,可以同时执行,因为他们都是DbSqlSession缓存,不会立马入库;也就是说,可能存在一个任务被同时自行两次的情况。
对1,2两点分析,基本上是确定会存在的,至于第三点,限于猜想,不知道实际是否有相关的解决策略,目前对activiti关于此处的设置猜想还没有完全弄清楚。
其实之所以那么在乎任务Id以及任务执行时间,主要是在流程跟踪图中,需要根据有序的历史任务结果集模仿重现走过的路径,而做到有序,这两个要素是非常关键的。
对分布式应用,如果同库,那ID的生成问题都会是一个问题,常见的解决方式是把他扔给数据库去解决,比如一个序列、一个类似序列的自定义函数等都是不错的选择。
当然,放到DB中以后,那么频繁访问数据库,activiti中设计的blocksize也就基本失效了,这个也算是衡量的结果吧。
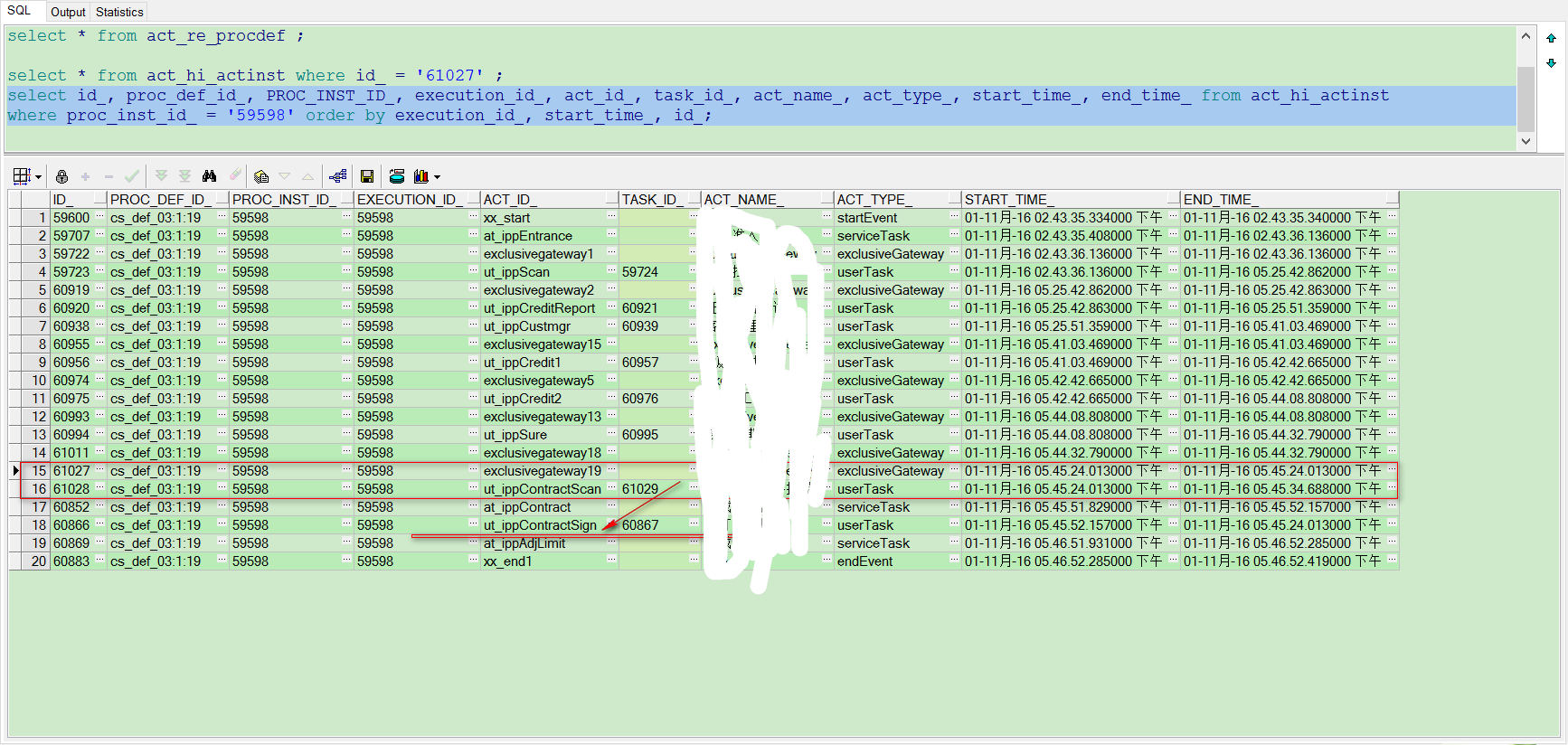
实际问题分析
上述数据,是在生产上出现的问题数据,环境是为了负载均衡做了两个应用Server,同时连接一个DB;
从数据可以分析出“活动节点会在双机中运行”;
61011(A) >> 60852(B) >> 60866(B) >> 61022(A) >> 61028(A) >> 60889(B) >> 60893(B)
A机器上的61011执行完毕以后,事件如何转到B机器上的60852,这个还不明白,待解决!!