#朴素贝叶斯 from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB clf=MultinomialNB().fit(x_train,y_train)
!pip install nltk
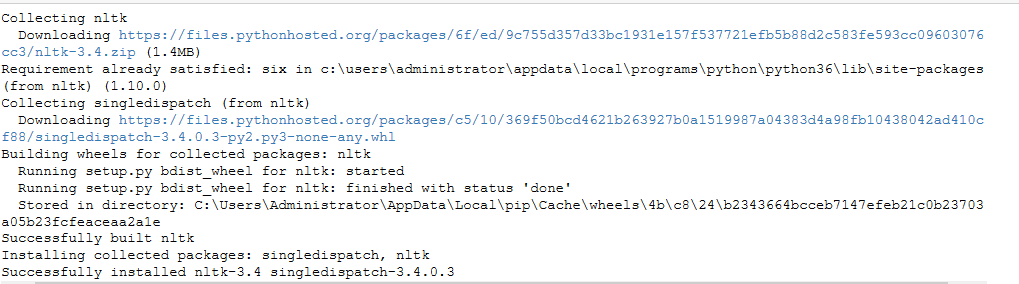
#读取文件 text = 'Be assured that individual statistics are not disclosed and this is for internal use only..I am pleased to inform you that you have been accepted to join the workshop scheduled for 22-24 Nov,2008.' import nltk nltk.download('punkt') nltk.download('stopwords') nltk.download('wordnet') from nltk.corpus import stopwords from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer #预处理 def preprocessing(text): #text = text.decode("utf-8") tokens = [word for sent in nltk.sent_tokenize(text) for word in nltk.word_tokenize(sent)] stops = stopwords.words('english') tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in stops] tokens = [token.lower() for token in tokens if len(token) >= 3] lmtzr = WordNetLemmatizer() tokens = [lmtzr.lemmatize(token) for token in tokens] preprocessed_text = ''.join(tokens) return preprocessed_text preprocessing(text)
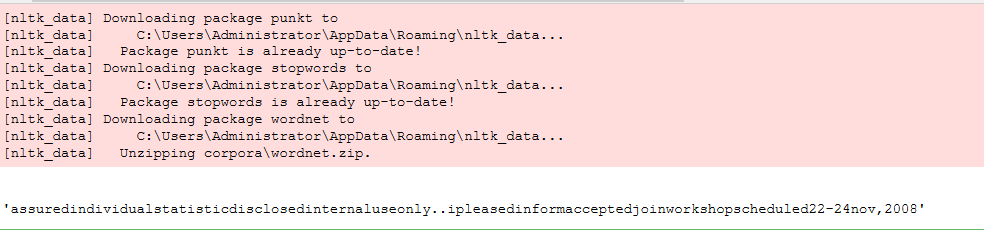
#划分数据集 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 生成100条数据:100个2维的特征向量,对应100个标签 x = [["feature ","one "]] * 50 + [["feature ","two "]] * 50 y = [1] * 50 + [2] * 50 # 随机抽取30%的测试集 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=0) print ("train:",len(x_train), "test:",len(x_test)) # 查看被划分出的测试集 for i in range(len(x_test)): print ("".join(x_test[i]), y_test[i])
#朴素贝叶斯 from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB clf=MultinomialNB().fit(x_train,y_train)
#测试模型 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix from sklearn.metrics import classification_report cm=confusion_matrix(y_test.y_nb_pred) print(cm) cr=classification_report(y_test.y_nb_pred) print(cr)