硬件环境:
RTX2070super 显卡
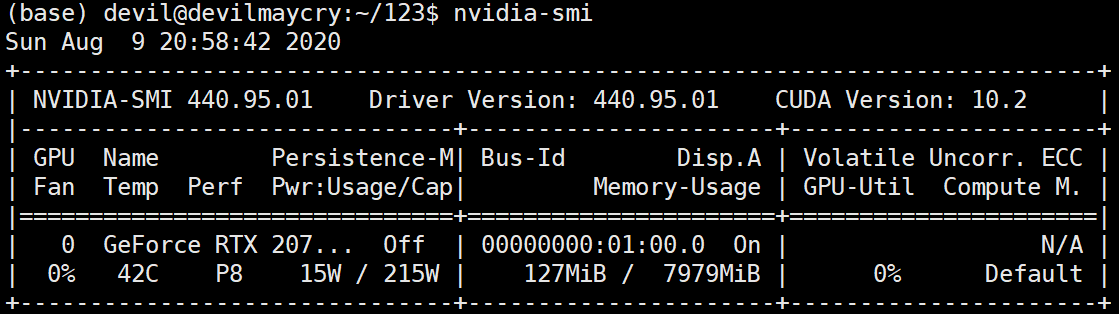
软件环境:
Ubuntu18.04.5
Tensorflow = 1.14.0

---------------------------------------------------------------------
运行代码:
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True) def dense(x, size, scope): return tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(x, size, activation_fn=None, scope=scope) def dense_relu(x, size, scope): with tf.variable_scope(scope): h1 = dense(x, size, 'dense') return tf.nn.relu(h1, 'relu') tf.reset_default_graph() x = tf.placeholder('float32', (None, 784), name='x') y = tf.placeholder('float32', (None, 10), name='y') phase = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, name='phase') h1 = dense_relu(x, 100, 'layer1') h1 = tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h1, center=True, scale=True, is_training=phase, scope='bn_1') h2 = dense_relu(h1, 100, 'layer2') h2 = tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h2, center=True, scale=True, is_training=phase, scope='bn_2') logits = dense(h2, 10, scope='logits') with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast( tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(logits, 1)), 'float32')) with tf.name_scope('loss'): loss = tf.reduce_mean( tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y)) def train(): update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS) with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops): train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(loss) sess = tf.Session() sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) history = [] iterep = 500 for i in range(iterep * 30): x_train, y_train = mnist.train.next_batch(100) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={'x:0': x_train, 'y:0': y_train, 'phase:0': 1}) if (i + 1) % iterep == 0: epoch = (i + 1)/iterep tr = sess.run([loss, accuracy], feed_dict={'x:0': mnist.train.images, 'y:0': mnist.train.labels, 'phase:0': 1}) t = sess.run([loss, accuracy], feed_dict={'x:0': mnist.test.images, 'y:0': mnist.test.labels, 'phase:0': 0}) history += [[epoch] + tr + t] print( history[-1] ) return history train()
报错, 具体如下:

2020-08-09 21:03:53.837785: E tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:329] Could not create cudnn handle: CUDNN_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR 2020-08-09 21:03:53.837987: W ./tensorflow/stream_executor/stream.h:1995] attempting to perform DNN operation using StreamExecutor without DNN support Traceback (most recent call last): File "/home/devil/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 1356, in _do_call return fn(*args) File "/home/devil/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 1341, in _run_fn options, feed_dict, fetch_list, target_list, run_metadata) File "/home/devil/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 1429, in _call_tf_sessionrun run_metadata) tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.InternalError: cuDNN launch failure : input shape ([100,100,1,1]) [[{{node bn_1/cond/FusedBatchNorm}}]] During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
不使用 显卡 进行计算,正常运行:

或:

主要语句:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=-1
正常运行:

如果 这种情况要仍然要使用 RTX 显卡, 那么 加入下面语句(对 会话session 的创建不使用默认设置,而是进行配置):
使用非交互的session时候,如下:
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.5)
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options))
或
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions( allow_growth = True )
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options))
或
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions( per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.5, allow_growth = True )
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options))
总之,就是不能使用默认配置的session,需要配置一下。
其中,
per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.5
是指为该程序分配使用的显卡其内存不超过总内存的 0.5倍。
--------------------------------------------------------
发生该问题的原因:
Could not create cudnn handle: CUDNN_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR 这个问题大部分是因为RTX显卡不兼容它出生前的接口有关。
原因解释出自资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/pkuyjxu/article/details/89402298
-------------
对上面代码中对 tensor 进行运算的代码中 feed_dict 的形式不是很熟悉,即:

因为以前经常使用的形式为:

于是很好奇,将代码改为如下:

发现报错:

从报错中可以知道,原来 feed_dict 中的key 是可以用 所构建的图的tensor(用函数tf.placeholder生成的tensor) 在图内的名字来表示的,即 "<op_name>:<output_index>" , 也就是这里的 “x:0” 。
而我们以前常用的形式是 将构建图中tensor (用tf.placeholder生成的tensor)的那个变量 即 x 作为 feed_dict 中的key 的。
比如:

这里,我们相当于构建了一个tensor (用函数tf.placeholder生成的tensor), tensor的名字为 'xxx:0' , 但是所构建的这个tensor 的变量为 x 。
详细的说就是:
x = tf.placeholder('float32', (None, 784), name='x') 中, name="x" 是说这个tf.placeholer函数在图中所定义的操作( operation)的名字(name) 是 “xxx” , 而图中的这个操作产生的第0个tensor在图中的名字为 “xxx:0” , 而这个名字为 “xxx:0” 的tensor又传递给了python变量x , 因此在 feed_dict 中我们可以使用变量x 来表示这个tensor, 也可以使用这个tensor的图内的名字“xxx:0” 来表示。需要注意的是“xxx”是操作(operation)的名字,而不是tensor的名字。
对于 tensor 的这个 "<op_name>:<output_index>" 形式的表示还是很长知识的。
注:
这里传给 feed_dict 的变量都是使用 tf.placeholder生成的 tensor 的变量, 这种变量也是整个图所依赖的起始tensor的变量。
-----------------------------------------------------
以下给出 feed_dict 的两个混合写法的 代码:

import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True) def dense(x, size, scope): return tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(x, size, activation_fn=None, scope=scope) def dense_relu(x, size, scope): with tf.variable_scope(scope): h1 = dense(x, size, 'dense') return tf.nn.relu(h1, 'relu') tf.reset_default_graph() x = tf.placeholder('float32', (None, 784), name='x') y = tf.placeholder('float32', (None, 10), name='y') phase = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, name='phase') h1 = dense_relu(x, 100, 'layer1') h1 = tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h1, center=True, scale=True, is_training=phase, scope='bn_1') h2 = dense_relu(h1, 100, 'layer2') h2 = tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h2, center=True, scale=True, is_training=phase, scope='bn_2') logits = dense(h2, 10, scope='logits') with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast( tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(logits, 1)), 'float32')) with tf.name_scope('loss'): loss = tf.reduce_mean( tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y)) def train(): update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS) with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops): train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(loss) gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions( per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.5, allow_growth = True ) sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)) #sess = tf.Session() sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) history = [] iterep = 500 for i in range(iterep * 30): x_train, y_train = mnist.train.next_batch(100) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: x_train, 'y:0': y_train, phase: 1}) if (i + 1) % iterep == 0: epoch = (i + 1)/iterep tr = sess.run([loss, accuracy], feed_dict={'x:0': mnist.train.images, y: mnist.train.labels, phase: 1}) t = sess.run([loss, accuracy], feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels, 'phase:0': 0}) history += [[epoch] + tr + t] print( history[-1] ) return history train()