
1. dict为空,则dict.keys()=0
2. ",".join列表或元组变字符串
# first_check.py/get_hit_apps_rule_results
# application_ids = ",".join(str(u["application_id"]) for u in uid_info_dict.values())
uid_info_dict = {921137L:{'application_id':393049L,'uid':921137L},921138L:{'application_id':3934049L,'uid':921138L}}
a = (u for u in uid_info_dict.values())
print a # <generator object <genexpr> at 0x05920DC8>
a = ",".join(str(u['application_id']) for u in uid_info_dict.values())
print a, type(a) # 393049,3934049 <type 'str'>
for u in uid_info_dict.values():
print u['application_id'] # 393049
3. ipython输出历史记录
%hist > xxx.txt
4. dict.get()和setdefault()功能基本相同,不同点:setdefault在key不存在时会把这个key添加到dict中,即新建了
5. pass,continue,break
stackoverflow 有个答案好懂:
>>> a = [0, 1, 2]
>>> for element in a:
... if not element:
... pass # 不做任何动作,后续代码继续执行
... print element
...
0
1
2
>>> for element in a:
... if not element:
... continue # 跳过本次循环,if后续代码不执行
... print element
...
1
2
6. pickle.dumps , pickle.dump
summer = Bird()
with open("summer.pkl", 'w') as f:
pickle.dump(summer, f) # 序列化并保存对象
pickle_string = pickle.dumps(summer) # 分开两步 序列化对象
with open("summer.pkl",'wb') as f:
f.write(pickle_string)
7. json.dumps , json.loads
json.loads 输出python对象
json.dumps 输出json对象
8. jupyter book 输出多个变量值
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
9. re 正则的使用
# 正则的使用,match , search, findall, pattern
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'd+')
m = pattern.match('2323asa') # match从头开始,若开始不是数字则匹配不到
search = pattern.search('sf34343')
print m, '
', search.group() # 34343
print m.group(), m.start(), m.end(), m.span() # 2323 0 4
results = pattern.findall('hello 123456 789')
results2 = pattern.findall('one1two2three3four4', 0, 10)
print results, results2 # ['123456', '789'] ['1', '2']
# finditer finditer 方法的行为跟 findall 的行为类似,也是搜索整个字符串,获得所有匹配的结果。但它返回一个顺序访问每一个匹配结果(Match 对象)的迭代器
p = re.compile(r'[s\,;]+')
print p.split('a,b;; c d')
# ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
p2 = re.compile(r'(w+) (w+)') # 空格
s = 'hello 123, hello 456'
def fun(m):
return 'hi' + m.group(2)
print p2.sub(r'hello world', s) # hello world, hello world
print p2.sub(r'2 1', s) # 123 hello, 456 hello
print p2.sub(fun, s) # hi123, hi456
print p2.sub(fun, s, 1) # 最多替换一次 hi123, hello 456
result_iter1 = pattern.finditer('hello 123456 789')
result_iter2 = pattern.finditer('one1two2three3four4', 0, 10)
print type(result_iter1)
print type(result_iter2)
print 'result1...'
for m1 in result_iter1: # m1 是 Match 对象
print 'matching string: {}, position: {}'.format(m1.group(), m1.span())
print 'result2...'
for m2 in result_iter2:
print 'matching string: {}, position: {}'.format(m2.group(), m2.span())
10. for ... else ... for 有break/return则不执行else, continue会执行
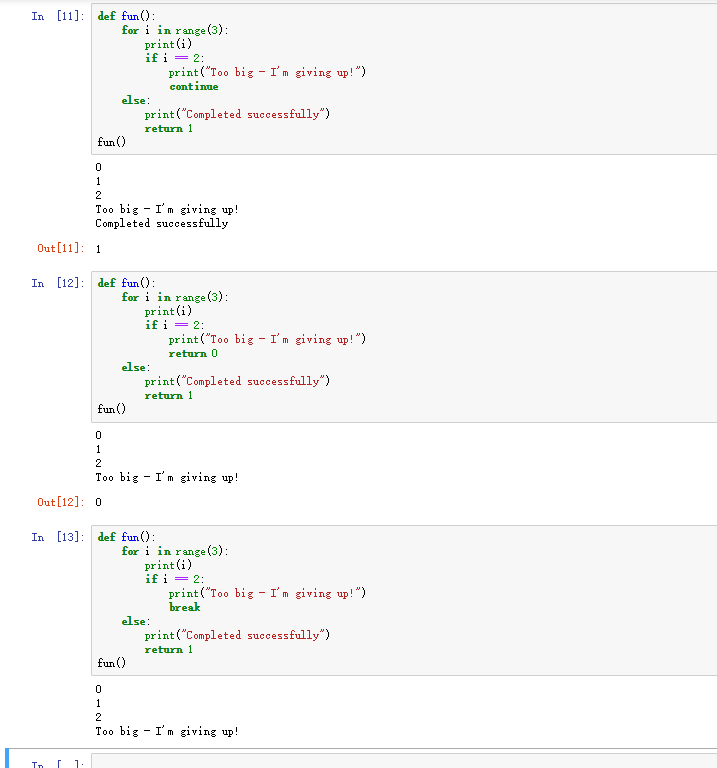
11. 列表索引取值超过范围不会报错
12. 字符串拼接的6种方式
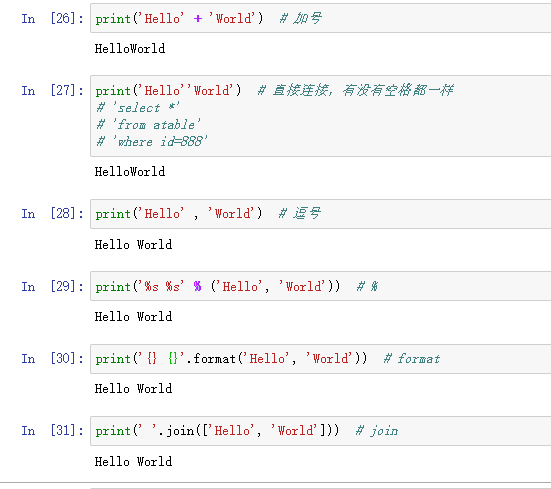
13. jupyter notebook 插入图片

14. 虚拟环境venv
$ python3.7 -m venv ./py37async
$ source ./py37async/bin/activate # Windows: .py37asyncScriptsactivate.bat