1.异常的概念
异常( Exception 也称例外)就是在程序的运行过程中所发生的不正常的事件,它会中断正在运行的程序
当 Java 程序出现异常时,就会在所处的方法中产生一个异常对象。这个异常对象包括异常的类型,异常出现时程序的运行状态以及对该异常的详细描述。
2.异常的分类
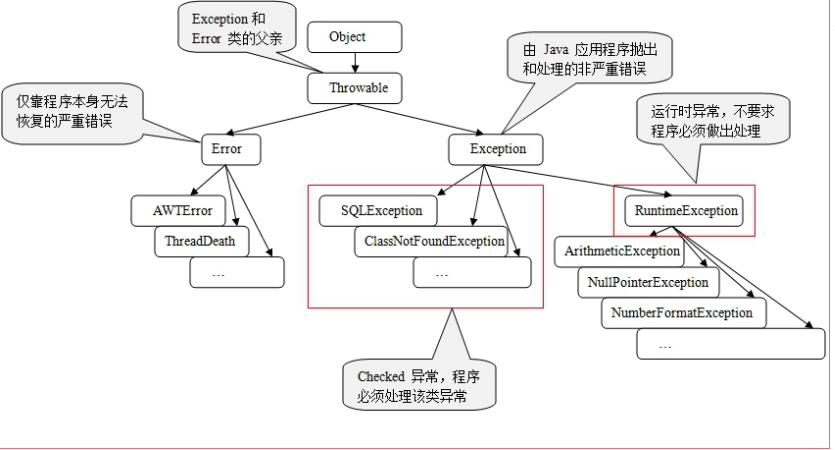
1.运行时异常 RuntimeException
a) 算术异常 ArithmeticException
b) 空指针异常 NullPointerException
c) 类型转换异常 ClassCastException
d) 数组下标越界 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
e) 期 望 的 数 据 类 型 与 实 际 输 入 类 型 不 匹 配
InputMismatchException

import java.util.Scanner; public class TestRuntimeException { public static void main(String[] args) { //(1)算术异常 int b=0; if(b!=0){ int result=1/b; }else{ System.out.println("对不起除数不能为0"); } //(2)空指针异常,没有创建对象(new)而调用了对象的属性或方法 NullPointerException String str=null; if(str!=null){ System.out.println(str.length()); } //(3)类型转换异常ClassCastException Animal dog=new Dog(); //向上类型转换 if(dog instanceof Cat){ //boolean Cat c=(Cat)dog; //向下类型转换,转换成真实的子类对象 } //(4)数组下标越界ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException int []arr={11,22,33};//长度3 int index=3; if(index<arr.length-1){ System.out.println(arr[index]); }else{ System.out.println("数组下标越出了边界"); } //(5)期望的数据类型与输入的数据类型不相匹配InputMismatchException Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); if(input.hasNextInt()){ //boolean -->true, false int a=input.nextInt(); System.out.println(a); }else{ System.out.println("对不起,输入的类型与期望的类型不匹配"); } } } class Animal{ } class Dog extends Animal{ } class Cat extends Animal{ }
2.检查时异常 Checked Exception
a) SQLException
b) IOException
c) ParseException
要求必须做处理,
(1) throws 向上声明
(2) try-catch-finally
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 4 public class TestCheckedException { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 //检查时异常,N多个程序在编译期间必须处理的异常的一总称 7 File f=new File("D:\a.txt"); 8 try { 9 f.createNewFile(); 10 } catch (IOException e) { 11 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 }//在D盘创建一个名称为a.txt的文件 14 } 15 }
3.异常的处理方式一_捕获异常
捕获异常所使用的关键字 try、catch、finally
1) try-catch 组合
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class TestTryCatch { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 try{ 7 System.out.println("请输入被除数:"); 8 int numA = input.nextInt(); 9 System.out.println("请输入除数:"); 10 int numB = input.nextInt(); 11 int result = numA / numB; 12 System.out.println(numA + "/" + numB + "=" + result); 13 14 }catch(ArithmeticException e){//ArithmeticException e=new InputMismatchException();不成功 15 //catch(Exception e){//相当于Exception e=new ArithmeticException()多态的表示形式,父类引用指向了子类对象 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 19 System.out.println("程序结束,谢谢您的使用!"); 20 } 21 }
2) try-finally 组合
finally 是无论是否产生异常,都执行的代码,但是有一种情况 finally 不执行,即退出 Java 虚拟机(System.exit(0))。
3) try-catch-finally 组合
a) 正常情况:执行 try-finally
b) 异常情况:类型相匹配,执行 try-catch-finally
c) 异常情况:类型不相匹配,执行 try-finally
如果在 catch 中存在 return 语句,则先执行完 finally 语句
再回头执行 return 语句
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class TestTryCatchFinally { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 6 try{ 7 8 System.out.println("请输入被除数:"); 9 int numA=input.nextInt(); 10 System.out.println("请输入除数:"); 11 int numB=input.nextInt(); 12 int result=numA/numB; 13 System.out.println(numA+"/"+numB+"="+result); 14 }catch(ArithmeticException e){ 15 System.err.println("除数不能为0"); 16 System.out.println("获取异常的字符串描述"+e.getMessage()); 17 return ; 18 //e.printStackTrace();//打印堆栈信息 19 }finally{ 20 System.out.println("finally中的代码"); 21 } 22 } 23 }

4.异常处理方式二_声明异常
声明异常的关键字 throws
方法名的后面,用于声明该方法可能会产生一个异常
如果方法声明的是 Exception 类型的异常或者是 Checked
Exception 异常,要求方法的调用处必须做处理。
(1)继续使用 throws 向上(方法的调用处)声明
(2)使用 try-catch-finally 进行处理
如果声明的是 RuntimeException 类型的异常,那么方法的调
用处可处理可不处理。
1 public class TestThrows { 2 3 public static void show()throws Exception{ 4 5 } 6 public static void method()throws RuntimeException{ 7 8 } 9 public static void main(String[] args){//throws Exception { 10 //调用本类中的静态方法show() 11 try { 12 show(); 13 } catch (Exception e) { 14 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 method(); 18 } 19 }
继承关系中的声明异常
1) 父类的方法声明了 Exception 类型的异常,子类在重写
方法时,可以声明也可以不声明。但是如果子类重写
后的方法使用 super 关键字调用父类的方法,那么要
求必须对异常进行处理。
2) 如果父类的方法没有异常,那么子类的方法如果一定
会有 Exception 或 Checked 异常,要求子类必须自己
使用 try-catch 处理,或者给父类方法加上异常的声明
3) 如果子类在重写父类的方法时,产生的异常是
RuntimeException 异常时,那么可以不用处理

import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class Father { public void show(){ } public void method() throws IOException{ } public void fun(){ } } class Son extends Father{ @Override public void show() { try { super.show(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void method() throws IOException { File f=new File("D:\a.txt"); f.createNewFile(); } @Override public void fun()throws RuntimeException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.fun(); } }
throw 抛出异常对象
写在方法里
在捕获一个异常前,必须有一段代码先生成异常对象
并把它抛出。这个过程我们以手工做,也可以由 JRE 来实
现,但是他们调用的都是 throw 子句
1 public class TestThrow { 2 3 public static void show(){ 4 5 try { 6 throw new Exception(); 7 } catch (Exception e) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 } 11 12 } 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 show(); 15 } 16 }
throws 与 throw
(1) throws 用于声明方法可能会产生的异常类型
throw 手动抛出异常对象
(2) throws 写在方法名称后面
throw 用于写在方法里
5.自定义异常:在程序中,可能会遇到任何标准异常类都没有充分的描述
清楚问题,这种情况下可以创建自己的异常类
自定义异常的步骤
1) 继承 Exception 或 RuntimeException
2) 定义构造方法
3) 使用异常
定义异常
1 public class SexException extends Exception { 2 3 public SexException() { 4 super(); 5 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 6 } 7 8 public SexException(String message) { 9 super(message); 10 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 11 } 12 13 }
使用异常
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class TestSexException { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 6 System.out.println("请输入您的性别:"); 7 String gender=input.next(); 8 if("男".equals(gender)||"女".equals(gender)){ 9 System.out.println("性别录入正确"); 10 }else{ 11 try { 12 throw new SexException("性别只能是男或者女"); 13 } catch (SexException e) { 14 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 System.err.println(e.getMessage());//性别只能是男或者女 17 } 18 } 19 20 } 21 }

