Time limit : 2sec / Memory limit : 256MB
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
You are given an undirected connected graph with N vertices and M edges that does not contain self-loops and double edges.
The i-th edge (1≤i≤M) connects Vertex ai and Vertex bi.
An edge whose removal disconnects the graph is called a bridge.
Find the number of the edges that are bridges among the M edges.
Notes
- A self-loop is an edge i such that ai=bi (1≤i≤M).
- Double edges are a pair of edges i,j such that ai=aj and bi=bj (1≤i<j≤M).
- An undirected graph is said to be connected when there exists a path between every pair of vertices.
Constraints
- 2≤N≤50
- N−1≤M≤min(N(N−1)⁄2,50)
- 1≤ai<bi≤N
- The given graph does not contain self-loops and double edges.
- The given graph is connected.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M a1 b1 a2 b2 : aM bM
Output
Print the number of the edges that are bridges among the M edges.
Sample Input 1
7 7 1 3 2 7 3 4 4 5 4 6 5 6 6 7
Sample Output 1
4
The figure below shows the given graph:
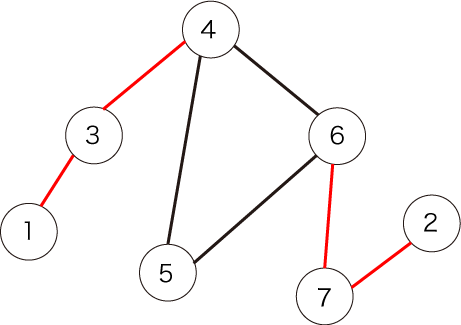
The edges shown in red are bridges. There are four of them.
Sample Input 2
3 3 1 2 1 3 2 3
Sample Output 2
0
It is possible that there is no bridge.
Sample Input 3
6 5 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6
Sample Output 3
5
It is possible that every edge is a bridge.
题目意思:判断给定的图像中的不属于环的边有几条;
主要思路:1.遍历判断每一条边中的一点能否到达另一点
代码1:每次判断每条边时,都创建一个地图副本,把每次走过的边都消除,
比较容易理解,但是遇到多的数据的时候,会很慢;

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include <map> #include <string.h> using namespace std; struct S { int Map[55][55]; }; int N,M; int a[55],b[55],Map[55][55]; bool dfs(S s,int l,int r) { // cout<<" -> "<<l<<" "<<r<<endl; int falg = false; for(int i = 1;i<=N;i++){ if((l>i&&s.Map[i][l])||(l<i&&s.Map[l][i])){ if(l>i) s.Map[i][l] = 0; else s.Map[l][i] = 0; if(i==r) return true; if(dfs(s,i,r)) return true; } } return falg; } int main() { cin>>N>>M; for(int i = 1;i <=M; i++){ cin>>a[i]>>b[i]; if(a[i]>b[i]) Map[b[i]][a[i]] = 1; else Map[a[i]][b[i]] = 1; } int sum = 0; for(int i = 1;i<=M;i++){ S s; memcpy(s.Map,Map,sizeof(Map)); if(a[i]>b[i]) s.Map[b[i]][a[i]] = 0; else s.Map[a[i]][b[i]] = 0; if(!dfs(s,a[i],b[i])) sum++; // cout<<a[i]<<" "<<b[i]<<" <-> "<<sum<<endl; } cout<<sum<<endl; return 0; }
代码2;相当与上面代码的改进,用一个临时数组来储存每次经过的头

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <set> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; int N,M; int a[55],b[55],Map[55][55]; int visit[55]; bool dfs(int l,int r,int num) { int j ; if(l==r||Map[l][r]==1) return true; visit[num] = l; for(int i = 1;i<=M;i++){ for(j=0;j<num;j++){ if(visit[j]==i) break; } if(j<num&&visit[j]==i) continue; if(Map[l][i]!=1) continue; if(dfs(i,r,num+1)) return true; } return false; } int main(){ cin>>N>>M; for(int i = 1;i<=M;i++){ cin>>a[i]>>b[i]; Map[a[i]][b[i]] = Map[b[i]][a[i]] = 1; } int sum = 0; for(int i = 1;i<=M;i++){ memset(visit,0,sizeof(visit)); Map[a[i]][b[i]] = 0; if(!dfs(a[i],b[i],0)) sum++; Map[a[i]][b[i]] = 1; } cout<<sum<<endl; return 0; }
代码3:使用了Floyd算法,来判断俩点之间的连通性;

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <set> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; #define inf (int)(1e9) int main(){ int N, M, i, j, k, l, ans = 0; cin>>N>>M; int a[55],b[55],e[55][55]; for(i = 0; i < M; i++){ cin>>a[i]>>b[i]; a[i]--; b[i]--; } for(l = 0; l < M; l++){ for(int i = 0;i<N;i++) for(int j = 0;j<N;j++) e[i][j] = inf; for(i = 0; i < M; i++){ if(i != l){ e[a[i]][b[i]] = 1; e[b[i]][a[i]] = 1; } } for(k = 0; k < N; k++){ for(i = 0; i < N; i++){ for(j = 0; j < N; j++){ if(e[i][j] > e[i][k] + e[k][j]){ e[i][j] = e[i][k] + e[k][j]; } } } } if(e[a[l]][b[l]] == inf){ ans++; } } printf("%d ", ans); return 0; }
代码4:储存每个结点连接的边的个数,每次都值为1的点出发,当前结点的值和相邻的点的值都减一;
当没有值为一的点时结束;过程中值为1的点的个数就是不循环的边的个数;

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <set> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; int N,M; int Map[55][55],a[55],b[55]; int visit[55]; int main(){ cin>>N>>M; for(int i = 1;i<=M;i++){ cin>>a[i]>>b[i]; visit[a[i]]++; visit[b[i]]++; Map[a[i]][b[i]] = Map[b[i]][a[i]] = 1; } int sum = 0; int xi; bool falg = true; while(1){ falg = true; for(int i = 1;i<=N;i++){ if(visit[i]==1){ sum++; xi = i; falg = false; visit[i]--; break; } } if(falg) break; for(int i = 1;i<=N;i++){ if(Map[xi][i]==1) visit[i]--; } } cout<<sum<<endl; return 0; } Submission
