用户交互、运算符
一、与用户交互
- 用户交互就是人往计算机中input/输入数据,计算机print/输出结果(本质就是 输入、输出)
- python2 一定要声明你输入的类型
- python3 接受用户的输入,无论用户输入什么类型,最终返回的一定是字符串
pyton3
input('name:')
name:Yang
'Yang'
python2
raw_input('name:')
name:Yang
'Yang'
- python2中raw_input与python3中input的功能是一模一样的
二、格式化输出
1. %s占位符:可以接收任意类型的变量
%d占位符:只能接收数字类型
例子一:
print('亲爱的%s您好!您%s月的话费是%d,余额还有%d' %('Tony',11,83,1))
亲爱的Tony您还!您11月的话费是83,余额还有1
例子二:
>>> name = 'yang'
>>> age = 22
>>> hobby = 'play, money'
>>> print('my name is %s, my age is %d,my hobby is %s' %(name, age, hobby))
my name is yang, my age is 22,my hobby is play, money
保留两位小数:'%.2f'
>>> a = 3.1415926
>>> print('%.2f' %a)
3.14
2. .format
username = 'Yang'
ages = 22
print('name:{user},age:{age}'.format(user=username,age=ages))
name:Yang,age:22
3.f-string
name = 'chen'
age = 18
hobby = 'yang'
print(f'姓名:{name},年龄:{age},爱好:{hobby}')
姓名:chen,年龄:18,爱好:yang
三、运算符
- 算术运算符
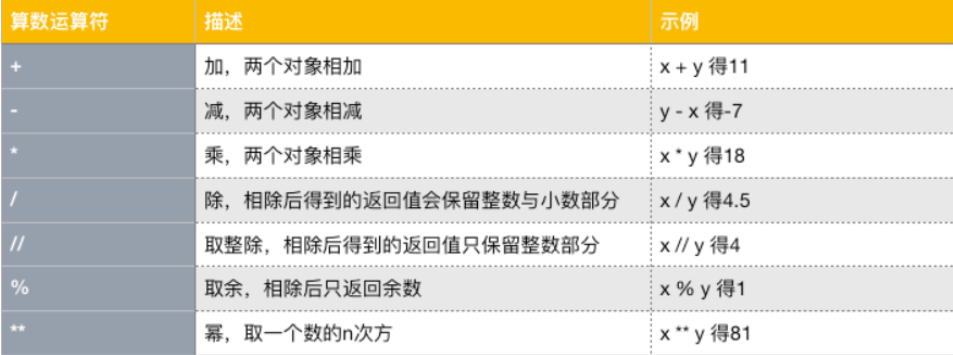
- 比较运算符

-
赋值运算符
-
增量赋值 x=10 x+=1(x=x+1)
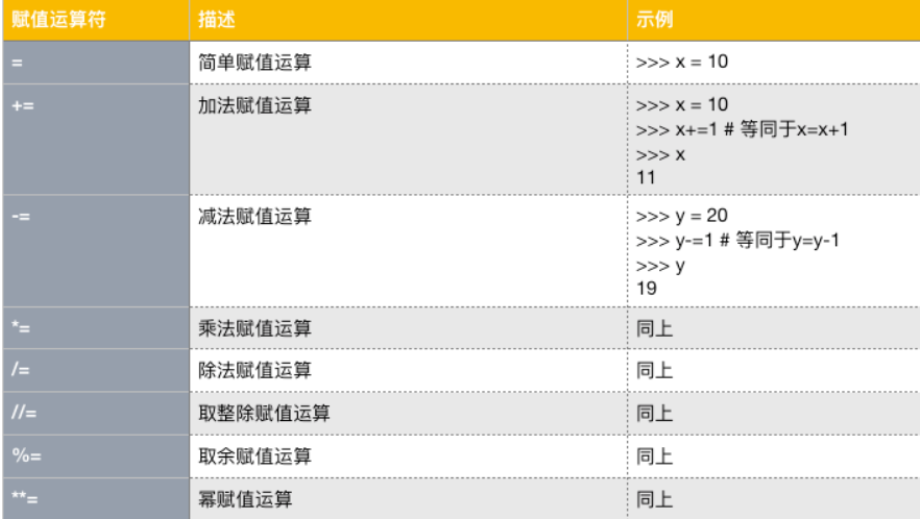
-
链式赋值 x=y=z=10
-
交叉赋值 m=1,n=2 m,n=n,m
-
解压赋值
>>> L1=[1,2,3,4,5] >>> a,b,c,d,e=L1 >>> a,b,c,d,e (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) #如果变量名少了或者多了,都会报错 >>> a,b,*_=L1 #取头尾的几个值,可以用*_ >>> a,b (1, 2) -
-
逻辑运算符
and
or
not

成员运算符
in
not in

>>> 'hello' in 'hello world!'
True
>>> 'hello' not in 'hello world!'
False
- 身份运算符

>>> x=y=10
>>> id(x)
1737518848
>>> id(y)
1737518848
>>> x is y
True
>>> x is not y
False