2018-03-12
一、选择法排序:
选择法排序的思路:
把第一位和其他所有的进行比较,只要比第一位小的,就换到第一个位置来;比较完后,第一位就是最小的
然后再从第二位和剩余的其他所有进行比较,只要比第二位小,就换到第二个位置来;比较完后,第二位就是第二小的,以此类推。
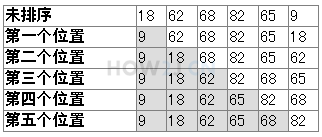
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int a [] = new int[]{18,62,68,82,65,9}; //排序前,先把内容打印出来 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); //选择法排序 //第一步: 把第一位和其他所有位进行比较 //如果发现其他位置的数据比第一位小,就进行交换 for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if(a[i]<a[0]){ int temp = a[0]; a[0] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; } } //把内容打印出来 //可以发现,最小的一个数,到了最前面 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); //第二步: 把第二位的和剩下的所有位进行比较 for (int i = 2; i < a.length; i++) { if(a[i]<a[1]){ int temp = a[1]; a[1] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; } } //把内容打印出来 //可以发现,倒数第二小的数,到了第二个位置 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); //可以发现一个规律 //移动的位置是从0 逐渐增加的 //所以可以在外面套一层循环 for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1; j++) { for (int i = j+1; i < a.length; i++) { if(a[i]<a[j]){ int temp = a[j]; a[j] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; } } } //把内容打印出来 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); } }
二、冒泡法排序:
冒泡法排序的思路:
第一步:从第一位开始,把相邻两位进行比较
如果发现前面的比后面的大,就把大的数据交换在后面,循环比较完毕后,最后一位就是最大的
第二步: 再来一次,只不过不用比较最后一位,以此类推。

public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int a [] = new int[]{18,62,68,82,65,9}; //排序前,先把内容打印出来 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); //冒泡法排序 //第一步:从第一位开始,把相邻两位进行比较 //如果发现前面的比后面的大,就把大的数据交换在后面 for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) { if(a[i]>a[i+1]){ int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[i+1]; a[i+1] = temp; } } //把内容打印出来 //可以发现,最大的到了最后面 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); //第二步: 再来一次,只不过不用比较最后一位 for (int i = 0; i < a.length-2; i++) { if(a[i]>a[i+1]){ int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[i+1]; a[i+1] = temp; } } //把内容打印出来 //可以发现,倒数第二大的到了倒数第二个位置 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); //可以发现一个规律 //后边界在收缩 //所以可以在外面套一层循环 for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < a.length-j-1; i++) { if(a[i]>a[i+1]){ int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[i+1]; a[i+1] = temp; } } } //把内容打印出来 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); } }