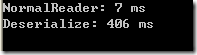
反序列化xml配置文件到一个实体类,和直接读取xml到实体类相比,效率对比相当大,我简单测试了一下,各自占用的时间如下:
部分测试代码:
class Program
{
static void Main ( string[] args )
{
System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch sw1 = new System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch ();
sw1.Start ();
Config cfg = LoadConfig_Xml ( "MyTest.config" );
sw1.Stop ();
if ( cfg != null )
Console.WriteLine ( "NormalReader: " + sw1.ElapsedMilliseconds + " ms" );
sw1.Reset ();
sw1.Start ();
cfg = LoadConfig_Deserialize ( "MyTest.config" );
sw1.Stop ();
if ( cfg != null )
Console.WriteLine ( "Deserialize: " + sw1.ElapsedMilliseconds + " ms" );
Console.Read ();
}
public static Config LoadConfig_Deserialize ( string file )
{
if ( !System.IO.File.Exists ( file ) ) return null;
XmlSerializer xs = new XmlSerializer ( typeof ( Config ) );
using ( StreamReader sr = new StreamReader ( file ) )
{
return xs.Deserialize ( sr ) as Config;
}
}
public static Config LoadConfig_Xml ( string file )
{
if ( !System.IO.File.Exists ( file ) ) return null;
try
{
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument ();
doc.Load ( file );
if ( doc == null ) return null;
XmlNode parent = doc.SelectSingleNode ( @"//Config" );
if ( parent == null ) return null;
Config cfg = new Config ();
foreach ( XmlNode node in parent.ChildNodes )
{
if ( node.Name == "MyBooleanAttribute1" )
cfg.MyBooleanAttribute1 = Convert.ToBoolean ( node.InnerText );
if ( node.Name == "MyAttribute2" )
cfg.MyAttribute2 = node.InnerText;
if ( node.Name == "MyBooleanAttribute3" )
cfg.MyBooleanAttribute3 = Convert.ToBoolean ( node.InnerText );
if ( node.Name == "CachedFileList" )
{
if ( node.ChildNodes.Count > 0 )
{
cfg.CachedFileList = new CachedFileList ();
foreach ( XmlNode child in node.ChildNodes )
{
cfg.CachedFileList.Add ( new CachedFile ( child.Attributes["FileLocation"].InnerText,
child.Attributes["FileName"].InnerText, child.Attributes["FileFormat"].InnerText,
Convert.ToInt64 ( child.Attributes["FileChecksum"].InnerText ) ) );
}
}
}
}
return cfg;
}
catch { return null; }
}
}
Config类定义:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using System.IO;
[Serializable]
public class Config
{
private bool myBooleanAttribute1 = true;
public bool MyBooleanAttribute1 { get { return myBooleanAttribute1; } set { myBooleanAttribute1 = value; } }
private string myAttribute2 = "";
public string MyAttribute2 { get { return myAttribute2; } set { myAttribute2 = value; } }
private bool myBooleanAttribute3 = true;
public bool MyBooleanAttribute3 { get { return myBooleanAttribute3; } set { myBooleanAttribute3 = value; } }
private CachedFileList cachedFileList = new CachedFileList ();
public CachedFileList CachedFileList
{
get { return cachedFileList; }
set { cachedFileList = value; }
}
}
[Serializable]
public class CachedFileList : List<CachedFile>
{
}
public class CachedFile
{
private string fileLocation = "";
private string fileName = "";
private string fileFormat = "";
private long fileChecksum = 0;
[XmlAttribute ( "FileLocation" )]
public string FileLocation { get { return fileLocation; } set { fileLocation = value; } }
[XmlAttribute ( "FileName" )]
public string FileName { get { return fileName; } set { fileName = value; } }
[XmlAttribute ( "FileFormat" )]
public string FileFormat { get { return fileFormat; } set { fileFormat = value; } }
[XmlAttribute ( "FileChecksum" )]
public long FileChecksum { get { return fileChecksum; } set { fileChecksum = value; } }
public CachedFile ( string location, string name, string format, long checksum )
:this()
{
this.fileLocation = location;
this.fileName = name;
this.fileFormat = format;
this.fileChecksum = checksum;
}
public CachedFile ()
{
}
}
由此可见,反序列化的性能很差,占用时间非常大。在简洁代码的背后是效率的代价。应该根据需要按需选择。
使用XSD安全装载XML并反序列化
如果有XML Schema,就是XSD的情况下,可以首先装载XSD,然后读取XML会比较快;尤其是读取大型XML文件(比如几M)。而且类型安全。
最后再反序列化到实体类。以下是一个例子:
private XmlReader GetValidatingReader(string filePath)
{
Stream stream = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetManifestResourceStream("MySchema.xsd");
XmlTextReader schemaReader = new XmlTextReader(stream);
stream.Dispose();
XmlReaderSettings settings = new XmlReaderSettings();
settings.Schemas.Add("http://schemas.microsoft.com/pag/mynamespacefile", schemaReader);
XmlReader settingReader = XmlReader.Create(filePath, settings);
return settingReader;
}
private Config ReadConfig (string configPath)
{
try
{
XmlSerializer serializer = new XmlSerializer ( typeof ( Config ) );
using ( XmlReader reader = GetValidatingReader () )
{
return (Config)serializer.Deserialize ( reader );
}
}
catch ( Exception ex )
{
throw new ConfigReaderException ( String.Format (
CultureInfo.CurrentCulture,
Resources.ErrorReadingConfig,
configPath ), ex );
}
}
Links: