五子棋游戏开发
此游戏具有双人对战功能和人机对战功能
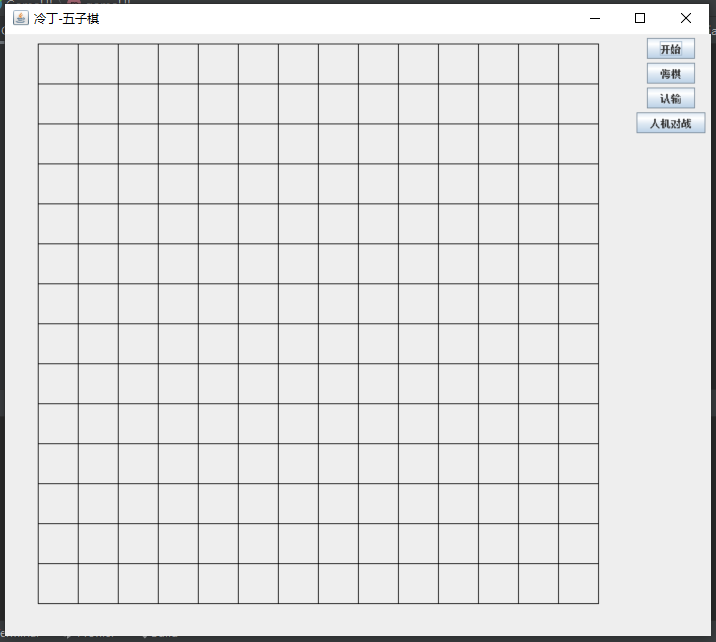
一、游戏界面的实现
一个游戏首先从设计界面开始
1、首先创建一个类,作用是通过对窗体组件的一些设置来实现简单游戏界面
public void gameUI(){
//窗体组件
MyFrame jf = new MyFrame();
jf.setSize(900, 800);
jf.setTitle("冷丁-五子棋");
//居中显示
jf.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
//设置退出进程
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(3);
//流式布局管理器
FlowLayout flow=new FlowLayout();
jf.setLayout(flow);
//边框布局
BorderLayout border=new BorderLayout();
jf.setLayout(border);
//面板: JPanel 默认流式布局
JPanel eastPanel=new JPanel();
Dimension dm=new Dimension(100,0);
//除了JFrame,其他组件设置大小都是该方法
eastPanel.setPreferredSize(dm);
jf.add(eastPanel,BorderLayout.EAST);
}
2、加入功能按钮
JButton jbu=new JButton("开始");
eastPanel.add(jbu,BorderLayout.EAST);
JButton jbu2=new JButton("悔棋");
eastPanel.add(jbu2,BorderLayout.EAST);
JButton jbu3=new JButton("认输");
eastPanel.add(jbu3,BorderLayout.EAST);
JButton jbu4=new JButton("人机对战");
eastPanel.add(jbu4,BorderLayout.EAST);
//设置窗体可见
jf.setVisible(true);
每个按钮添加ActionListner监听
jbu.addActionListener(mouse);
jbu2.addActionListener(mouse);
jbu3.addActionListener(mouse);
jbu4.addActionListener(mouse);
在GameMouse类中对过对actionPerformed方法的重新来判断当前是哪个按钮按下,并实现对应的功能
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//获取按钮上的内容
String name=e.getActionCommand();
System.out.println("点击按钮:"+name);
if(name.equals("开始")){
jf.removeMouseListener(this);
jf.addMouseListener(this);
startflag=false;
flag=false;
gameOver=false;
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
for(int j=0;j<15;j++){
arrChess[i][j]=0;
}
}
jf.paint(gr);
}else if(name.equals("悔棋")){
arrChess[nowx][nowy]=0;
jf.paint(gr);
this.flag=!this.flag;
}
else if(name.equals("认输")){
if(this.flag){
gr.setColor(Color.red);
gr.setFont(new Font("TimesRoman", Font.BOLD, 50));
gr.drawString("黑方获胜!",300,300);
}else{
gr.setColor(Color.red);
gr.setFont(new Font("TimesRoman", Font.BOLD, 50));
gr.drawString("白方获胜!",300,300);
}
}else if(name.equals("人机对战")){
jf.removeMouseListener(this);
jf.addMouseListener(this);
startflag=false;
flag=false;
gameOver=false;
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
for(int j=0;j<15;j++){
arrChess[i][j]=0;
}
}
this.aiflag=true;
jf.paint(gr);
}
}
3、游戏效果是通过画笔画在组件上实现的,获取画笔:图形显示在哪个组件上,画笔就从该组件上获取。
注意从窗体上获取画笔对象,一定要在窗体显示可见之后
Graphics g = jf.getGraphics();
4、当我们点击按钮时,应该实现相应的功能,为了实现人机交互,需要添加监听器
监听器
a.事件源:当前动作所发生的组件
b.确定监听器方法:鼠标监听器方法
c.绑定处理类
给窗口添加鼠标监听器方法
注意:由于接口不能创建对象,重新定义类继承(实现)接口,重写接口中的抽象方法
GameMouse mouse = new GameMouse();
mouse.setJf(jf);
jbu.addActionListener(mouse);
jbu2.addActionListener(mouse);
jbu3.addActionListener(mouse);
jbu4.addActionListener(mouse);
mouse.setGr(g);
//把GameMouse类中的数组传递给MyFrame类
jf.setArrChess(mouse.getArrChess());
二、完成自定义窗口类
单纯使用JFrame存在一个问题,就是当我们移动窗口或窗口产生改变时,之前画在窗口组件上的画面就消失不见了
原因是每当窗口组件受到影响或发生改变时,都会自动的调用其paint函数,这时候画面就会被刷新,之前画的东西就不见了
为了解决这个问题,我们需要自定义一个自己的窗口类MyFrame,继承JFrame,通过重写JFrame的paint方法来解决此问题
自定义窗口类MyFrame
public class MyFrame extends JFrame implements Config{
private int[][] arrChess;
public void setArrChess(int[][] arrChess){
this.arrChess = arrChess;
}
//重写绘制组件的方法
//super 表示当前类的父类对象
//this 表示本类对象
public void paint(Graphics g){
//1.绘制组件
super.paint(g);
System.out.println("绘制自定义窗体类!");
//2.绘制棋盘,棋子
g.setColor(Color.black);
for(int i=0;i<LINE;i++){
g.drawLine(X0, Y0+i*SIZE, (LINE-1)*SIZE+X0, Y0+i*SIZE);
g.drawLine(X0+i*SIZE, Y0, X0+i*SIZE, (LINE-1)*SIZE+Y0);
}
//遍历arrChess
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
for(int j=0;j<15;j++){
if(arrChess[i][j]==1){
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.fillOval(i*SIZE+25, j*SIZE+25, 50, 50);
}
else if(arrChess[i][j]==2){
g.setColor(Color.white);
g.fillOval(i*SIZE+25, j*SIZE+25, 50, 50);
}
}
}
}
}
这里通过循环和drawLine方法绘制出棋盘
arrChess是一个二维数组存放了当前的棋局情况,后面会详细说明。此类中通过遍历此数组每次重新画一遍棋局就可以维持游戏画面的正确。
三、游戏功能实现
1、首先要将棋子黑白交替的画在棋盘的交点上
首先mouseClicked类传进的参数为MouseEvent e
调用e.getX();e.getY();方法可以得到鼠标点击的位置坐标
由于玩家在玩游戏时点击的位置不一定正好是棋盘交点的位置,但是我们可以简单的计算出鼠标点击位置最近的焦点,只需要计算出这个位置最近的
交点是第几行和第几列就可以了
用当前坐标x-原点X0 对棋子的大小SIZE取余,如果这个值大于棋子大小SIZE/2 则判断横坐标xx=(x-X0)/SIZE+1
否则判断横坐标xx=(x-X0)/SIZE
y坐标同理 代码如下
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e){
System.out.println(this.aiflag);
this.flag=!flag;
System.out.println("点击");
//获取当前坐标
int x = e.getX();
int y = e.getY();
//计算交点值
if((x-X0)%SIZE > SIZE/2 ){
xx = (x-X0)/SIZE+1;
}else{
xx = (x-X0)/SIZE;
}
if((y-Y0)%SIZE > SIZE/2 ){
yy = (y-Y0)/SIZE+1;
}else{
yy = (y-Y0)/SIZE;
}
}
2、交替画黑白棋
交替画黑白棋只需要加入一个flag标志,每次判断这个标志
如果flag为true则画黑棋,将数组赋值为1
如果flag为false则画白棋,将数组赋值为2
每次画完棋后,将flag取反
代码如下
if (arrChess[xx][yy] == 0) {
if (this.flag == true)
arrChess[xx][yy] = 1;
else arrChess[xx][yy] = 2;
if (this.flag)
gr.setColor(Color.black);
else gr.setColor(Color.white);
gr.fillOval(xx * SIZE + 25, yy * SIZE + 25, 50, 50);
} else {
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
3、判断输赢方法的实现
判断输赢通过遍历数组实现,在上述讲解中我们知道,整个棋局的情况都存储在二维数组arrChess[][]中
若arrChess[3][5]=1,就说明第三行第五列这个位置上为黑棋
所以通过遍历这个数组我们就可以掌握整个棋局从而对输赢做出判断
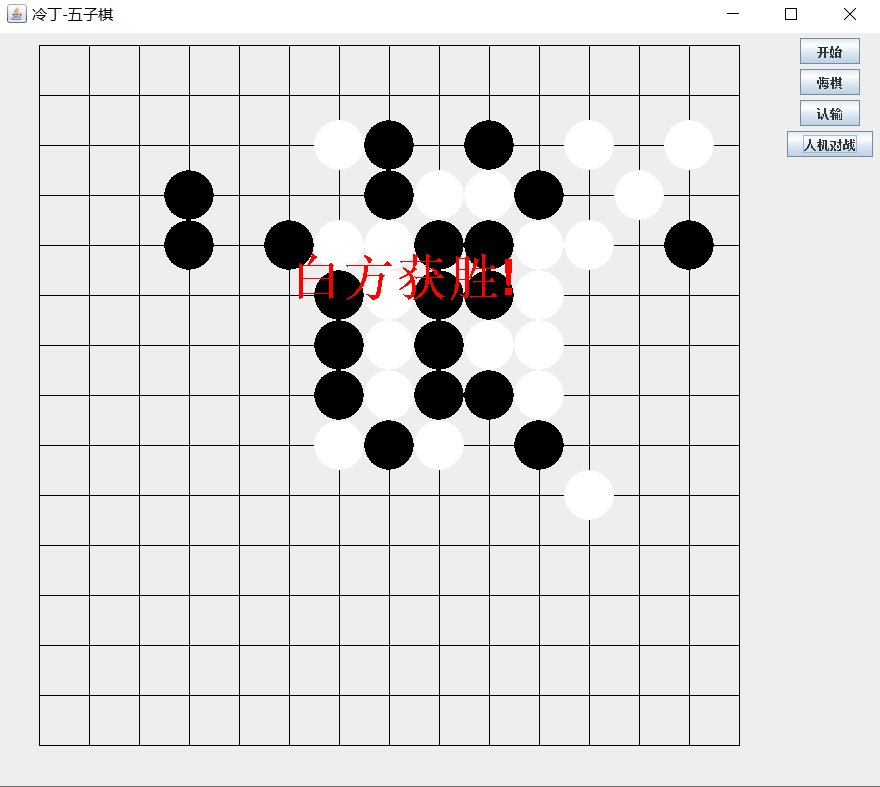
五子棋在横着、竖着、斜着三个方向任意一个方向上连成五个相同颜色的棋子都可以获胜
这里将三个方向分为四种情况判断,
第一种情况:棋子横向连珠的数目,也就是一个棋子向左找,向右找,和自己颜色相同的数目和
第二种情况:棋子纵向连珠的数目,一个棋子向上找和向下找,和自己颜色相同的数目和
第三种情况:棋子正对角线连珠的数目,一个棋子向右上方找、左下方找和自己颜色相同的数目和
第四种情况:棋子反对角线连珠的数目,一个棋子向左上方找、右下方找和自己颜色相同的数目和
第一种情况:棋子横向连珠的数目,也就是一个棋子向左找,向右找,和自己颜色相同的数目和
代码如下
int sum = 0;
for (int i = xx; i > 0; i--) {
if (arrChess[i][yy] == 1) sum++;
else if (arrChess[i][yy] == 2||arrChess[i][yy]==0) break;
}
for (int i = xx + 1; i < 15; i++) {
if (arrChess[i][yy] == 1) sum++;
else if (arrChess[i][yy] == 2||arrChess[i][yy]==0) break;
}
if (sum >= 5) {
System.out.println("black win!");
gr.setColor(Color.red);
gr.setFont(new Font("TimesRoman", Font.BOLD, 50));
gr.drawString("黑方获胜!",300,300);
gameOver = true;
}
第二种情况:棋子纵向连珠的数目,一个棋子向上找和向下找,和自己颜色相同的数目和
代码如下
sum = 0;
for (int i = yy; i > 0; i--) {
if (arrChess[xx][i] == 1) sum++;
else if (arrChess[xx][i] == 2||arrChess[xx][i] == 0) break;
}
for (int i = yy + 1; i < 15; i++) {
if (arrChess[xx][i] == 1) sum++;
else if (arrChess[xx][i] == 2||arrChess[xx][i] == 0) break;
}
if (sum >= 5) {
System.out.println("black win!");
gr.setColor(Color.red);
gr.setFont(new Font("TimesRoman", Font.BOLD, 50));
gr.drawString("黑方获胜!",300,300);
gameOver = true;
}
第三种情况:棋子正对角线连珠的数目,一个棋子向右上方找、左下方找和自己颜色相同的数目和
if (!gameOver) {
sum = 1;
int temp = min(5, xx);
temp = min(temp, yy);
for (int i = 1; i < temp; i++) {
if (arrChess[xx - i][yy - i] == 1) sum++;
else if (arrChess[xx - i][yy - i] == 2||arrChess[xx - i][yy - i] == 0) break;
}
temp = min(5, 15 - xx);
temp = min(temp, 15 - yy);
for (int i = 1; i < temp; i++) {
if (arrChess[xx + i][yy + i] == 1) sum++;
else if (arrChess[xx + i][yy + i] == 2||arrChess[xx + i][yy + i] == 0) break;
}
if (sum >= 5) {
System.out.println("black win!");
gr.setColor(Color.red);
gr.setFont(new Font("TimesRoman", Font.BOLD, 50));
gr.drawString("黑方获胜!",300,300);
gameOver = true;
}
}
第四种情况:棋子反对角线连珠的数目,一个棋子向左上方找、右下方找和自己颜色相同的数目和
if (!gameOver) {
sum = 1;
int temp = min(5, 15 - xx);
temp = min(temp, yy);
for (int i = 1; i < temp; i++) {
if (arrChess[xx + i][yy - i] == 1) sum++;
else if (arrChess[xx + i][yy - i] == 2||arrChess[xx + i][yy - i] == 0) break;
}
temp = min(5, xx);
temp = min(temp, 15 - yy);
for (int i = 1; i < temp; i++) {
if (arrChess[xx - i][yy + i] == 1) sum++;
else if (arrChess[xx - i][yy + i] == 2||arrChess[xx - i][yy + i] == 0) break;
}
if (sum >= 5) {
System.out.println("black win!");
gr.setColor(Color.red);
gr.setFont(new Font("TimesRoman", Font.BOLD, 50));
gr.drawString("黑方获胜!",300,300);
gameOver = true;
}
}
}
上面展示了黑棋获胜的判断方法 白棋获胜的判断方法同理
4、AI电脑下棋 实现人机对战
人机对战使用权值算法来实现,通过对棋局情况的判断,自己设定好每种情况权值的大小
电脑以防守为主
权值设置如下
public void setHm() {
this.hm.put("1",40);
this.hm.put("11",400);
this.hm.put("111",4000);
this.hm.put("1111",6000);
this.hm.put("12",40);
this.hm.put("112",400);
this.hm.put("1112",4000);
this.hm.put("11112",6000);
this.hm.put("2",20);
this.hm.put("22",200);
this.hm.put("222",2000);
this.hm.put("2222",8000);
this.hm.put("21",10);
this.hm.put("221",100);
this.hm.put("2221",1000);
this.hm.put("22221",2000);
}
简单解释一下 1112代表三个黑棋一个白棋 权值为4000
而11112代表四个黑棋和一个白棋 这种情况显然更危险,权值设置为6000
人机下棋的思路主要是,遍历棋盘上每个空位置周围的棋局情况
因为机器可以选择任何一个空位置下棋
每个空位置周围的棋局情况一定对应已经设置好的权值中的一个,如果一个位置周围有多个权值对应
则把他们权值相加综合判断
当确定好每个空位置的权值后,选择权值最大的也就是最危险的位置下棋,已实现防守
ai算法的时候和使用到了前面判断输赢的方法,总体原理和之前判断输赢相同
只不过多了一步计算权值
权值表存储在HashMap中,遍历的过程将每个空位周围有棋子的情况用字符串存储起来
最后在通过从HashMap中查找对应的权值来找到该位置的权值 Integer value=hm.get(s);
实现代码如下
public void ai(){
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
for(int j=0;j<15;j++){
chessValue[i][j]=0;
}
}
this.setHm();
for (int i = 0; i <15 ; i++) {
for(int j=0;j<15;j++){
//向下
if(arrChess[i][j]==0){
String s="";
int c=0;
for(int k=j+1;k<15;k++){
if(arrChess[i][k]==0){
break;
}else{
if(c==0){
c=arrChess[i][k];
s+=arrChess[i][k];
}else if(arrChess[i][k]==c){
s+=arrChess[i][k];
}else{
s+=arrChess[i][k];
break;
}
}
}
Integer value=hm.get(s);
if(value!=null){
chessValue[i][j]+=value;
}
}
//向上
if(arrChess[i][j]==0){
String s="";
int c=0;
for(int k=j-1;k>0;k--){
if(arrChess[i][k]==0){
break;
}else{
if(c==0){
c=arrChess[i][k];
s+=arrChess[i][k];
}else if(arrChess[i][k]==c){
s+=arrChess[i][k];
}else{
s+=arrChess[i][k];
break;
}
}
}
Integer value=hm.get(s);
if(value!=null){
chessValue[i][j]+=value;
}
}
//向左
if(arrChess[i][j]==0){
String s="";
int c=0;
for(int k=i-1;k>0;k--){
if(arrChess[k][j]==0){
break;
}else{
if(c==0){
c=arrChess[k][j];
s+=arrChess[k][j];
}else if(arrChess[k][j]==c){
s+=arrChess[k][j];
}else{
s+=arrChess[k][j];
break;
}
}
}
Integer value=hm.get(s);
if(value!=null){
chessValue[i][j]+=value;
}
}
//向右
if(arrChess[i][j]==0){
String s="";
int c=0;
for(int k=i+1;k<15;k++){
if(arrChess[k][j]==0){
break;
}else{
if(c==0){
c=arrChess[k][j];
s+=arrChess[k][j];
}else if(arrChess[k][j]==c){
s+=arrChess[k][j];
}else{
s+=arrChess[k][j];
break;
}
}
}
Integer value=hm.get(s);
if(value!=null){
chessValue[i][j]+=value;
}
}
//对角线1--
if(arrChess[i][j]==0){
int temp=100;
temp=min(temp,i);
temp=min(temp,j);
String s="";
int c=0;
for(int k=1;k<=temp;k++){
if(arrChess[i-k][j-k]==0){
break;
}else{
if(c==0){
c=arrChess[i-k][j-k];
s+=arrChess[i-k][j-k];
}else if(arrChess[i-k][j-k]==c){
s+=arrChess[i-k][j-k];
}else{
s+=arrChess[i-k][j-k];
break;
}
}
}
Integer value=hm.get(s);
if(value!=null){
chessValue[i][j]+=value;
}
}
//对角线2 -- ++
if(arrChess[i][j]==0){
int temp=100;
temp=min(temp,14-i);
temp=min(temp,14-j);
String s="";
int c=0;
for(int k=1;k<=temp;k++){
if(arrChess[i+k][j+k]==0){
break;
}else{
if(c==0){
c=arrChess[i+k][j+k];
s+=arrChess[i+k][j+k];
}else if(arrChess[i+k][j+k]==c){
s+=arrChess[i+k][j+k];
}else{
s+=arrChess[i+k][j+k];
break;
}
}
}
Integer value=hm.get(s);
if(value!=null){
chessValue[i][j]+=value;
}
}
//对角线2 -- ++ +-
if(arrChess[i][j]==0){
int temp=100;
temp=min(temp,14-i);
temp=min(temp,j);
String s="";
int c=0;
for(int k=1;k<=temp;k++){
if(arrChess[i+k][j-k]==0){
break;
}else{
if(c==0){
c=arrChess[i+k][j-k];
s+=arrChess[i+k][j-k];
}else if(arrChess[i+k][j-k]==c){
s+=arrChess[i+k][j-k];
}else{
s+=arrChess[i+k][j-k];
break;
}
}
}
Integer value=hm.get(s);
if(value!=null){
chessValue[i][j]+=value;
}
}
//对角线2 -- ++ +- -+
if(arrChess[i][j]==0){
int temp=100;
temp=min(temp,i);
temp=min(temp,14-j);
String s="";
int c=0;
for(int k=1;k<=temp;k++){
if(arrChess[i-k][j+k]==0){
break;
}else{
if(c==0){
c=arrChess[i-k][j+k];
s+=arrChess[i-k][j+k];
}else if(arrChess[i-k][j+k]==c){
s+=arrChess[i-k][j+k];
}else{
s+=arrChess[i-k][j+k];
break;
}
}
}
Integer value=hm.get(s);
if(value!=null){
chessValue[i][j]+=value;
}
}
}
}
int maxx=-1;
int mx=0,my=0;
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
for(int j=0;j<15;j++){
if(chessValue[i][j]>maxx){
maxx=chessValue[i][j];
mx=i;
my=j;
}
}
}
gr.setColor(Color.white);
gr.fillOval(mx*SIZE+25, my*SIZE+25, 50, 50);
arrChess[mx][my]=2;
Judge2(mx,my);
}
}
游戏过程如下