1086 Tree Traversals Again(25 分)
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
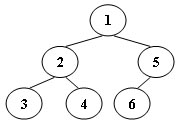
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1题目大意:二叉树的中根遍历,可以通过栈来实现,那么现在给出一棵二叉树的中根遍历操作,要求输出后根遍历结果。
//完全可以通过输入来确定这棵二叉树的中根遍历,即已知中根遍历求后根遍历。但是我不会啊。
代码转自:https://www.liuchuo.net/archives/2168
#include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <stack> #include <cstring> using namespace std; vector<int> pre, in, post,value; void postorder(int root, int start, int end) { if (start > end) return; int i = start; while (i < end && in[i] != pre[root]) {//中序遍历序列中存的节点的id,唯一的! i++; printf("%d %d " ,in[i],pre[root]); } postorder(root + 1, start, i - 1); //左子树共有i-start+1个节点。 postorder(root + 1 + i - start, i + 1, end); post.push_back(pre[root]); } int main() { int n; scanf("%d", &n); char str[5]; stack<int> s; int key=0; while (~scanf("%s", str)) { if (strlen(str) == 4) { int num; scanf("%d", &num); value.push_back(num); pre.push_back(key);//对应num有一个序号,从0开始。 s.push(key++); } else { in.push_back(s.top());//现在存了中序遍历 //存的是id对应的序号(为了防止重复呢。) s.pop(); } } postorder(0, 0, n - 1); printf(" "); printf("%d", value[post[0]]); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) printf(" %d",value[post[i]]); return 0; }
//这个代码简直太难了,看了好几遍都理解不了那个中序转后序的,气死了。
//这个明天还要搜一下别的题解,简直气死我了。
//更要重点掌握一套,二叉树的各种访问序列转换方法。
2018-11-17更——————
我的AC:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include<stack> using namespace std; vector<int> in,pre,post; void postOrder(int inL,int inR,int preL,int preR){ if(inL>inR)return ; // int i=0;//标识中根遍历中的根节点下标 int i=0; while(in[i]!=pre[preL])i++; //遍历左右子树 postOrder(inL,i-1,preL+1,preR+i-inL); postOrder(i+1,inR,preL+i-inL+1,preR); post.push_back(in[i]); } int main() { //push的顺序就是前序,弹出的顺序就是中序。 int n,id; cin>>n; string s; stack<int> tree; for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++){ cin>>s; if(s[1]=='u'){ cin>>id; tree.push(id); pre.push_back(id);//前序遍历放进来。 }else{ int temp=tree.top(); tree.pop(); in.push_back(temp); } } // cout<<pre.size(); postOrder(0,n-1,0,n-1); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ cout<<post[i]; if(i!=n-1)cout<<" "; } return 0; }
//在牛客网上通不过,说内存超限,通过率为0,因为递归层数太深?
遇到的问题:
1.postOrder函数,作为递归出口应该是in的左右去判断,如果是pre的,则不会输出结果
2.在postOrder的while循环中,i可以从0开始判断。
3.柳神的代码考虑了key不唯一的情况,但是我没考虑,而且PAT上应该也没考虑,否则就不会AC了。
4.关于这个key的问题,是应该考虑一下不唯一的情况的,因为题目里并没有说。