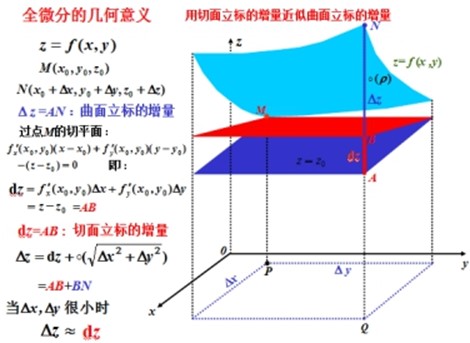
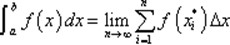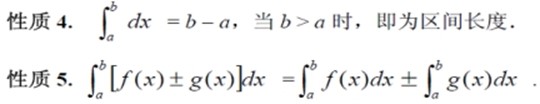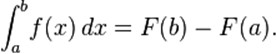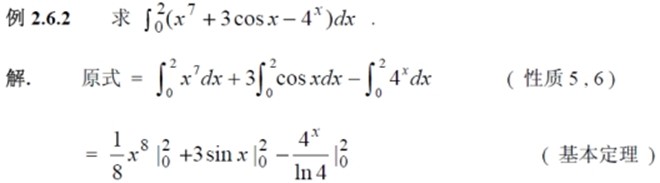全微分
total differential
|
|
|
|
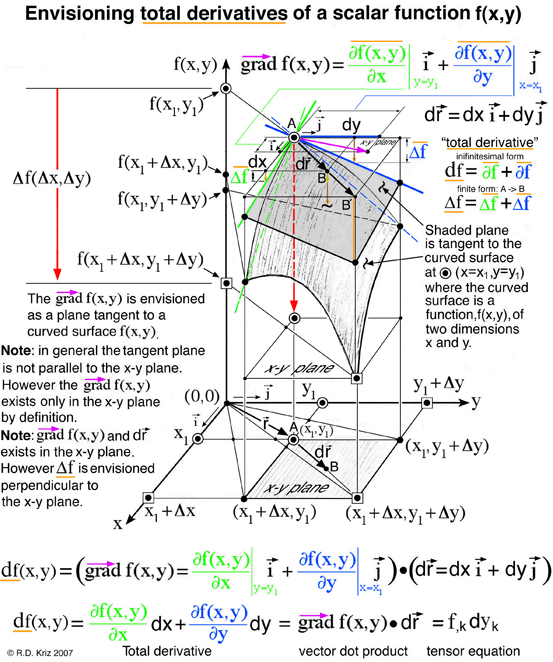
※ Envisioning total derivatives of a scalar function f(x,y)
|
梯度、方向导数和全微分的关系
梯度、方向导数是向量; 全微分是个点积, 即梯度点积微分向量.
gradient: n. 坡度;斜度 a slope or a degree of slope, especially in a road or railway Physics The rate at which a physical quantity, such as temperature or pressure, changes relative to change in a given variable, especially distance. 梯度:一个物理量,如温度或压力,相对于另一给定可变量(尤指距离)的变化的变化率
A vector having coordinate components that are the partial derivatives of a function with respect to its variables.
slope 斜率:一个矢量,其坐标分量是一个函数对其变量的偏微分 |
不定积分
原函数的概念:
定积分的概念:
不定积分的英文解释:
If f(x) has original functions, then all of its original functions {F(x) | F'(x) = f(x)} are defined as the indefinite integral of f(x). The indefinite integral of f(x), denoted ∫f(x) dx, is defined to be the antiderivative of f(x). In other words, the derivative of ∫f(x) dx is f(x). ※ indefinite integral (不定积分) = antiderivative, primitive integral |
基本积分公式表
|
不定积分的四则运算
|
|
定积分
Given a function
The result of performing the integral is a number that represents the area under the curve of ƒ(x) between the limits and the x -axis. |
Fundamental theorem of calculus (Newton-Leibniz theorem) ※ If f is a continuous real-valued function defined on a closed interval [a, b], then, once an antiderivative F of f is known, the definite integral of over that interval is given by
|
|
积分的两种理解
|











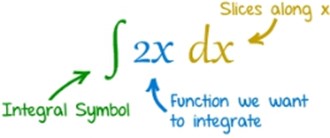

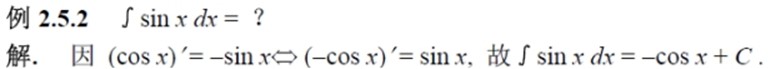

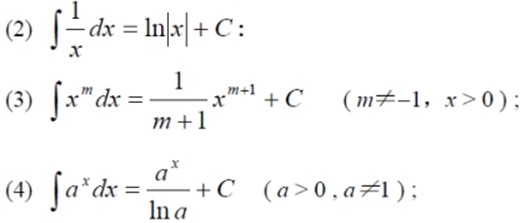
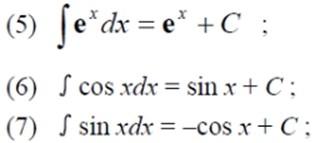
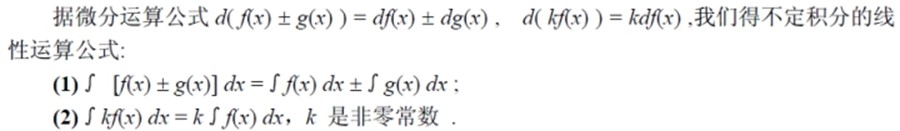



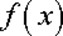

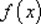








 . Then the
. Then the