一、前端项目结构
在上一节的基础上,我们分别在src下创建如下文件夹:
- assets:静态文件;
- components:公共组件,比如面包屑、编辑器、svg图标、分页器等等;
- hooks:函数组件,使用 React 16.8引进的Hook 特性实现;
- layout:布局组件;
- redux:redux目录,负责状态管理;
- routes:路由,负责路由管理;
- styles:全局样式;
- utils:工具包;
- views:视图层;
二、redux目录构建
我们项目使用redux进行状态管理,在使用redux状态管理器之前,我们需要安装依赖包:
npm install redux --save npm install react-redux --save npm install redux-logger --save npm install redux-thunk --save npm install redux-devtools-extension --save
1、在redux文件夹下创建root_reducers.js文件,用于保存整个项目使用到的reducer:
/** * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 * @Description: 合并reducer */ import {combineReducers} from 'redux'; export default combineReducers({})
这里利用 combineReducers 函数来把多个 reducer 函数合并成一个 reducer 函数,目前还没有引入redux函数,后面我们会逐渐完善。
2、在redux文件夹下创建Index.js文件:
/** * @author zy * @date 2020/4/4 * @Description: redux状态管理器配置 * 不懂原理的可以参考:https://github.com/brickspert/blog/issues/22#middleware */ import thunk from 'redux-thunk'; import {compose, createStore, applyMiddleware} from 'redux'; import rootReducers from './root_reducers'; import {composeWithDevTools} from 'redux-devtools-extension'; const storeEnhancers = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? compose(applyMiddleware(thunk)) : compose()(composeWithDevTools(applyMiddleware(thunk))); /** * 创建store * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 */ const configureStore = () => { //创建store对象 const store = createStore(rootReducers, storeEnhancers); //reducer热加载 if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { if (module.hot) { module.hot.accept('./root_reducers', () => { store.replaceReducer(rootReducers) }) } } return store; } export default configureStore();
这里我们利用createStore创建了一个状态管理器,并传入了redux,此外我们还使用了thunk中间件来处理异步请求。
如果不理解这部分代码,可以先去看一下redux相关知识:
三、routes目录构建
路由构建是使用React Route路由库实现的,在使用之前,我们需要安装以下依赖:
npm install react-router-dom --save
1、在routes文件夹下创建web.js文件:
/** * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 * @Description: web路由 * 不懂的可以参考:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000020812860 * https://reacttraining.com/react-router/web/api/Route */ import React from 'react'; import PageNotFound from '@/components/404'; function Home(props) { console.log('Home=>', props); return ( <div> <h2>Home</h2> {props.children} </div> ) } function About(props) { console.log('About=>', props); return <h2>About</h2>; } /** * web路由配置项 * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 */ export default { path: '/', name: 'home', component: Home, exact: false, childRoutes: [ {path: 'about', component: About}, {path: '*', component: PageNotFound} ] }
2、在routes下创建index.js文件:
import React from 'react'; import {Switch, Route} from 'react-router-dom'; import _ from 'lodash'; import webRouteConfig from './web'; //保存所有路由配置的数组 const routeConfig = [webRouteConfig] /** * 路由配置 * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 */ export default function () { /** * 生成路由嵌套结构 * @author: zy * @date: 2020-03-05 * @param routeConfig: 路由配置数组 * @param contextPath: 路由根路径 */ const renderRouters = (routeConfig, contextPath = '/') => { const routes = []; const renderRoute = (item, routeContextPath) => { //基路径 let path = item.path ? `${contextPath}/${item.path}` : contextPath; path = path.replace(//+/g, '/'); if (!item.component) { return; } //这里使用了嵌套路由 routes.push( <Route key={path} path={path} component={()=> <item.component> {item.childRoutes && renderRouters(item.childRoutes, path)} </item.component> } exact={item.childRoutes?false:true} /> ); } _.forEach(routeConfig, item => renderRoute(item, contextPath)) return <Switch>{routes}</Switch>; }; return renderRouters(routeConfig); }
这里我们使用了嵌套路由,其中/为根路由,然后他有两个子路由,分别为/about,/*,最终生成的代码等价于:
<Switch>
<Route key="/" path="/" exact={false}>
<Home>
<Switch>
<Route key="/about" path="/about" exact={true} component={About}>
<Route key="/*" path="/*" exact={true} component={PageNotFound}>
</Switch>
</Home>
</Route>
</Switch>
这里使用了Swich和exact:
- <Switch>是唯一的,因为它仅仅只会渲染一个路径,当它匹配完一个路径后,就会停止渲染了。相比之下(不使用<Switch>包裹的情况下),每一个被location匹配到的<Route>将都会被渲染;
- exact:只有页面的路由和<Route>的path属性精确比对后完全相同该<Route>才会被渲染;
当我们访问/about时,由于/不是精确匹配,因此首先匹配匹配到/,然后会继续匹配其子元素,由于子元素是精确匹配,因此匹配到/about就会停止。我们为什么采用嵌套路由呢,以江南大学为例: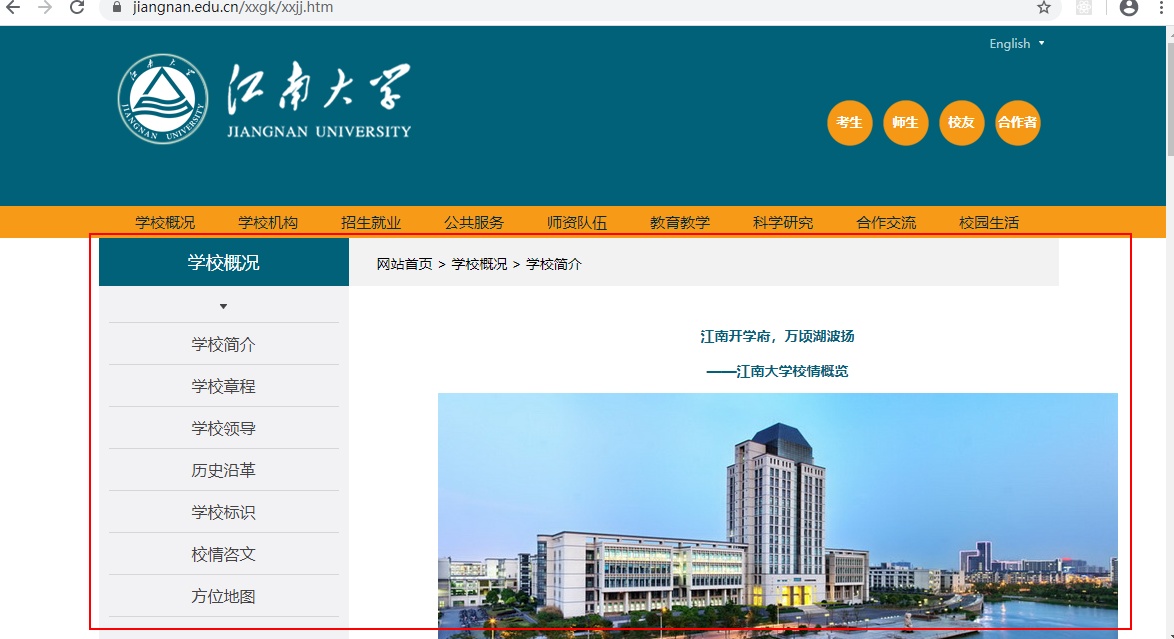
我们访问不同的页面会发现,它们都有导航栏,页面之间只是存在部分差异,因此我们可以把页面的整体布局放置到路由/对应的组件中,而差异部分放置到路由精确匹配的子组件中,这样我们就不必写太多的重复代码。
需要注意的是Home组件之所以可以嵌套子组件,是因为我们的代码中指定了显示子组件:
function Home(props) { console.log('Home=>', props); return ( <div> <h2>Home</h2> {props.children} </div> ) }
如果不理解这部分代码,可以先去看一下react router相关知识:
四、components目录构建
在web.js中我们使用到了PageNotFound组件,我们需要在components下创建404文件,并在该文件夹下创建index.jsx文件,代码如下:
/** * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 * @Description: 找不到页面 */ import React from 'react'; import {Result, Button} from 'antd'; /** * 页面找不到组件 * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 */ function PageNotFound(props) { return ( <Result status='404' title='404' subTitle='Sorry, the page you visited does not exist.' extra={ <Button type='primary' onClick={() => { props.history.push('/') }}> Back Home </Button> } /> ) } export default PageNotFound
由于此处我们使用了antd组件,因此需要引入依赖:
cnpm install antd --save
关于更多antd组件的使用请查看:antd官网。
五、hooks目录构建
1、useBus
我们在hooks文件夹下创建use_bus.js文件,使用event bus可以解决非父子组件间的通信:
/** * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 * @Description: 事件监听器 * useContext Hook 是如何工作的:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000020111320?utm_source=tag-newest * useEffect Hook 是如何工作的:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000020104281 * 微型库解读之200byte的EventEmitter - Mitt:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012997458?utm_source=tag-newest * 使用event bus进行非父子组件间的通信:https://blog.csdn.net/wengqt/article/details/80114590 我们可以通过对event的订阅和发布来进行通信,这里举一个栗子:A和B是两个互不相关的组件,A组件的功能是登录,B组件的功能是登录之后显示用户名,这里就需要A组件将用户名传递给B组件。那么我们应该怎么做呢? 1、在A组件中注册/发布一个type为login的事件; 2、在B组件中注册一个监听/订阅,监听login事件的触发; 3、然后当登录的时候login事件触发,然后B组件就可以触发这个事件的回调函数。 */ import React, {useEffect} from 'react'; import mitt from 'mitt'; //创建上下文 const context = React.createContext(); //外层提供数据的组件 const Provider = context.Provider; //useContext 接收一个 context 对象(React.createContext 的返回值)并返回该 context 的当前值 export function useBus() { return React.useContext(context); } /** * 事件监听器函数 * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 * @param name:监听的事件名称 * @param fn:事件触发时的回调函数 */ export function busListener(name, fn) { //获取 context 的当前值 // eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/rules-of-hooks const bus = useBus(); //组件第一次挂载执行,第二个参数发生变化时执行 // eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/rules-of-hooks useEffect(() => { //事件订阅 bus.on(name, fn); //组件卸载之前执行 return () => { //取消事件订阅 bus.off(name, fn); } }, [bus, name, fn]) } //外层提供数据的组件 向后代组件跨层级传值bus,这样后代组件都可以通过useBus获取到bus的值 export function BusProvider({children}) { const [bus] = React.useState(() => mitt()); return <Provider value={bus}>{children}</Provider> }
这里使用到了React 16.8引进的Hook新特性,感兴趣可以查看以下博客:
[3]微型库解读之200byte的EventEmitter - Mitt
2、useMount
我们在hooks下创建use_mount.js文件,用于模拟类组件componentDidMount函数:
/** * @author zy * @date 2020/4/6 * @Description: 利用useEffect实现组件第一次挂载 */ import {useEffect} from 'react' /** * useMount函数 * @author zy * @date 2020/4/6 */ export default function useMount(func) { //由于第二个参数不变,因此只会执行一次func函数 useEffect(() => { typeof func === 'function' && func(); // eslint-disable-next-line }, []) }
六、App.js文件
我们修改App.js文件代码如下:
/** * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 * @Description: 根组件 */ import React from 'react'; import Routes from '@/routes'; import {BrowserRouter} from 'react-router-dom'; export default function App(props) { return ( <BrowserRouter> <Routes/> </BrowserRouter> ) }
七、index.js文件
我们修改index.js文件如下:
/** * @author zy * @date 2020/4/5 * @Description: 入口文件 */ import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; import App from './App'; import {AppContainer} from 'react-hot-loader'; import {BusProvider} from '@/hooks/use_bus'; import {Provider} from 'react-redux'; import store from '@/redux'; ReactDOM.render( <AppContainer> <BusProvider> <Provider store={store}> <App/> </Provider> </BusProvider> </AppContainer>, document.getElementById('root') )
这里我们引入了局部热更新,这样当我们修改部门文件时,不会造成整个页面的刷新,可以保留状态值。
npm install react-hot-loader --save
此外,我们还引入了状态管理器store,用来管理我们所有组件的状态。
在import文件的时候,我们引入了@别名,@指的的是src路径,其配置在webpack.config.js文件中:
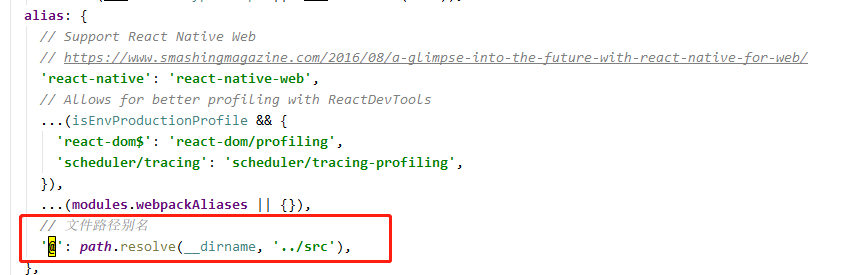
至此,我们整个前端框架搭建完毕,我们可以运行程序,访问http://localhost:3000:
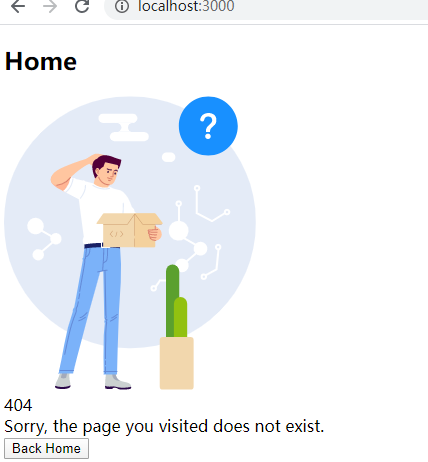
此外,我们还可以访问about页面:

我们可以看到,访问/会加载Home组件和PageNotFound组件,访问/about会加载Home和About组件。
参考文章:
[5]antd官方手册