P2158 [SDOI2008] 仪仗队:
一开始还确实没来思路,但是昨晚看了一个水题也是用到了斜率,所以就想到了斜率。
很明显斜率相同的会被遮挡,也就是说不是最简分数的形式就会被遮挡。
很显然求一下互质的坐标数就行。
这里的话左下角那个人是不算的,然后我们要以左下角为(0,0)点来看才对。

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int N = 4e4 + 5; const int M = 2e4 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 1e9 + 7; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int f = 1;int x = 0;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} bool vis[N]; int prime[N],tot = 0,phi[N]; void init() { for(int i = 2;i < N;++i) { if(!vis[i]) { prime[++tot] = i; phi[i] = i - 1; } for(int j = 1;j <= tot && prime[j] * i < N;++j) { vis[prime[j] * i] = 1; if(i % prime[j] == 0) { phi[i * prime[j]] = phi[i] * prime[j]; break; } else phi[i * prime[j]] = phi[i] * phi[prime[j]]; } } } void solve() { init(); int n;n = read(); if(n == 1) printf("0 "); else { LL ans = 1LL * (n - 1) * (n - 1) + 3; for(int i = 2;i < n;++i) { ans -= (i - phi[i] - 1) * 2 + 1; } printf("%lld ",ans - 1); } } int main() { solve(); system("pause"); return 0; }
P2398 GCD SUM:
测评机炸了一会..
这题有好几种推法来着。
$sum_{d = 1}^{n}sum_{i = 1}^{n}sum_{j = 1}^{n} d * [gcd(i,j) = d]$
$sum_{d=1}^{n}dsum_{i=1}^{frac{n}{d}}sum_{j=1}^{frac{n}{d}} [gcd(i,j)=1]$
$sum_{d = 1}^{n}dsum_{t = 1}^{left lfloor frac{n}{d} ight floor} mu (t) * [frac{n}{dt}] *left lfloor frac{n}{dt} ight floor$
后面可以代换一个n / d = T然后就是一个T / t的求和,可以发现这里两重是调和级数,所以我们第二维暴力算也是可以的。
我这里写的整除分块。

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int N = 1e5 + 5; const int M = 2e4 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 1e9 + 7; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int f = 1;int x = 0;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} bool vis[N]; int prime[N],tot = 0,mu[N]; void init() { mu[1] = 1; for(int i = 2;i < N;++i) { if(!vis[i]) { prime[++tot] = i; mu[i] = -1; } for(int j = 1;j <= tot && prime[j] * i < N;++j) { vis[prime[j] * i] = 1; if(i % prime[j] == 0) break; else mu[i * prime[j]] = -mu[i]; } } for(int i = 1;i < N;++i) mu[i] += mu[i - 1]; } LL cal(int x) { LL sum = 0; for(int L = 1,r = 0;L <= x;L = r + 1) { r = x / (x / L); sum += 1LL * (x / L) * (x / L) * (mu[r] - mu[L - 1]); } return sum; } void solve() { int n;n = read(); LL ans = 0; for(int d = 1;d <= n;++d) ans += cal(n / d) * d; printf("%lld ",ans); } int main() { init(); solve(); system("pause"); return 0; }
P6028 算术:
一开始想的是杜教筛方向的,因为感觉怎么样都要杜教筛做。
但是没想到后面那个式子可以化简开来。
这里有一步非常巧妙的推算:
$(p - 1) sum_{j = 0}^{alpha (i)}p^{j} = (p^1 - p) + (p^2 - p^1) + ... + (p ^ {(alpha (i) + 1)} - p ^ {alpha (i)}) = p ^ {(alpha (i) + 1)} - 1$
然后就可以化简这个式子了。
上下都提取一下(p - 1)最后就是$frac{prod_{i = 1}^{k}sum_{j = 0}^{alpha (i)}p^j}{n}$
对上面整体展开可以分析一下,都是n的各个素因子的乘积组成的数,且幂次都<=n,那么显然这就是n的因子和。就有下面的化简。
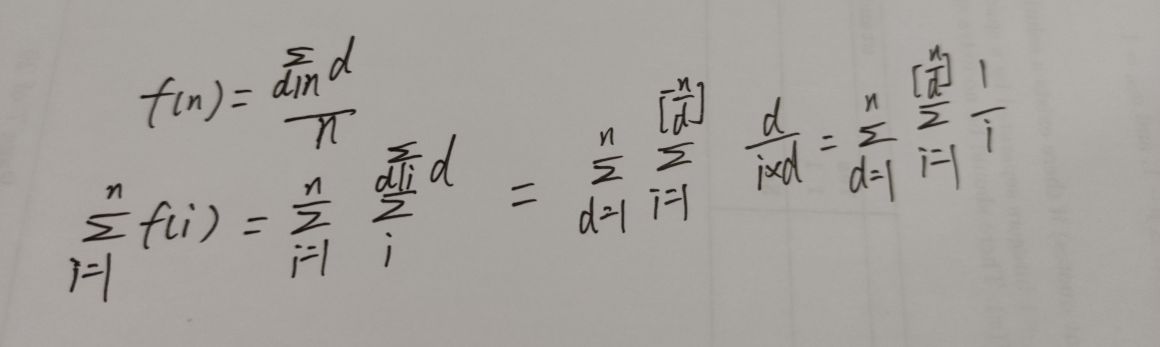
这里我们小范围内可以求一下1 / i的前缀和。
大范围内有近似操作1 / n的前缀和可以近似为lg(n) + y,y约等于0.5772156649

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<LL,int> pii; const int N = 1e7 + 5; const int M = 7e5 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 1e9 + 7; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int f = 1;int x = 0;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} long double sum[N]; void init() { for(int i = 1;i < N;++i) sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + 1.0 / i; } long double cal(LL x) { if(x >= N) return log(x) + 0.5772156649; else return sum[x]; } void solve() { init(); LL n;scanf("%lld",&n); long double ans = 0; for(LL L = 1,r = 0;L <= n;L = r + 1) { r = n / (n / L); ans += cal(n / L) * (r - L + 1); } printf("%.10Lf ",ans); } int main() { solve(); // system("pause"); return 0; }
P3807 【模板】卢卡斯定理/Lucas 定理:
Lucas定理模板题:当模数p<n,可以利用Lucas定理:
C(n,m) = C(n / p,m / p) + C(n % p,m % p).
思想就是对每段%p相同的进行分段处理。

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<int,int> pii; #define rg register const int N = 1e5 + 5; const int M = 2e4 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 1e9 + 7; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { rg int f = 1,x = 0;rg char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} LL f[N],inv[N]; LL quick_mi(LL a,LL b,LL p) { LL re = 1; while(b) { if(b & 1) re = re * a % p; b >>= 1; a = a * a % p; } return re; } void init(int p) { f[0] = 1; for(int i = 1;i < p;++i) f[i] = f[i - 1] * i % p; inv[p - 1] = quick_mi(f[p - 1],p - 2,p); for(int i = p - 2;i >= 0;--i) inv[i] = inv[i + 1] * (i + 1) % p; } LL C(LL n,LL m,LL p) { return f[n] * inv[m] % p * inv[n - m] % p; } LL Lucas(LL n,LL m,LL p) { if(m == 0) return 1; return Lucas(n / p,m / p,p) * C(n % p,m % p,p) % p; } void solve() { int n,m,p;n = read(),m = read(),p = read(); init(p); printf("%lld ",Lucas(n + m,n,p)); } int main() { int ca;ca = read(); while(ca--) { solve(); } //system("pause"); return 0; }
UVA294 约数 Divisors:
可以看到r - L的范围非常小,所以可以遍历这个区间,主要就是对每个数的因子个数的求解。
普通的做法需要sqrt(n)的复杂度,显然会TLE。
这里可以利用:
约数(因子)个数定理:对于一个数n,质因子分解为$prod_{i = 1}^{k}pi^{ki}$
那么他的约数个数为$prod_{i = 1}^{k}(ki + 1)$

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<int,int> pii; #define rg register const int N = 1e5 + 5; const int M = 2e4 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 1e9 + 7; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { rg int f = 1,x = 0;rg char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} bool vis[N]; int prime[N],tot = 0; void init() { for(int i = 2;i < N;++i) { if(!vis[i]) prime[++tot] = i; for(int j = 1;j <= tot && prime[j] * i < N;++j) { vis[prime[j] * i] = 1; if(i % prime[j] == 0) break; } } } int a[N]; void solve() { init(); int n;n = read(); while(n--) { LL L,r;scanf("%lld %lld",&L,&r); LL ans = 0,mx = 0; for(LL i = L;i <= r;++i) { int x = i,len = 0; for(int j = 1;j <= tot;++j) { if(x % prime[j] == 0) { int cnt = 0; while(x % prime[j] == 0) x /= prime[j],++cnt; a[++len] = cnt; } } LL ma = 1; for(int j = 1;j <= len;++j) ma *= (a[j] + 1); if(i == 1 && ma > mx) mx = ma,ans = i; if(len != 0 && ma > mx) mx = ma,ans = i; } printf("Between %lld and %lld, %lld has a maximum of %lld divisors. ",L,r,ans,mx); } } int main() { solve(); //system("pause"); return 0; }
P2424 约数和:
推错了式子结果写成了杜教筛..不过这题确实可以杜教筛做的。
其实题目就是$sum_{i = 1}^{n}sum_{d | i}^{}d$
化简得:$sum_{d = 1}^{n}d * sum_{i = 1}^{frac{n}{d}} = sum_{d = 1}^{n}d * frac{n}{d}$
整除分块即可。

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<int,int> pii; #define rg register const int N = 1e5 + 5; const int M = 2e4 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 1e9 + 7; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { rg int f = 1,x = 0;rg char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} LL check(LL n) { LL sum = 0; for(LL L = 1,r = 0;L <= n;L = r + 1) { r = n / (n / L); sum += 1LL * (r + L) * (r - L + 1) / 2 * (n / L); } return sum; } void solve() { LL x,y;scanf("%lld %lld",&x,&y); printf("%lld ",check(y) - check(x - 1)); } int main() { solve(); //system("pause"); return 0; }
P3758 [TJOI2017]可乐:
很显然有个dp[i][j] - 第i秒在j位置的方案数,但是这里复杂度差不多M * t,究极卡常才能勉强冲过去。
然后我们考虑一下自爆的处理,连虚点0,然后停在原地的操作我们就连自环。
然后考虑去优化这个dp,我们发现如果我们用邻接矩阵来存图的话,dp就是关于邻接矩阵的一个递推。
转移矩阵就是这个邻接矩阵,所以我们可以矩阵快速幂加速t,这样复杂度就很低了。

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int N = 1e6 + 5; const int M = 2e4 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 2017; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int f = 1,x = 0;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} struct Mat{ int m[31][31]; Mat operator * (const Mat &a)const{ Mat c;memset(c.m,0,sizeof(c.m)); for(int k = 0;k <= 30;++k) for(int i = 0;i <= 30;++i) for(int j = 0;j <= 30;++j) c.m[i][j] = ADD(c.m[i][j],MUL(m[i][k],a.m[k][j])); return c; } }; Mat e; Mat quick_Mat(Mat a,int b) { Mat re;memset(re.m,0,sizeof(re.m)); for(int i = 0;i <= 30;++i) re.m[i][i] = 1; while(b) { if(b & 1) re = re * a; b >>= 1; a = a * a; } return re; } void solve() { int n,m;n = read(),m = read(); while(m--) { int u,v;u = read(),v = read(); e.m[u][v] = 1; e.m[v][u] = 1; } for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) e.m[i][0] = 1; for(int i = 0;i <= n;++i) e.m[i][i] = 1; int t;t = read(); Mat a = e; Mat ans;memset(ans.m,0,sizeof(ans)); ans.m[0][1] = 1; a = quick_Mat(a,t); ans = ans * a; int ma = 0; for(int i = 0;i <= n;++i) { ma = ADD(ma,ans.m[0][i]); } printf("%d ",ma); } int main() { solve(); return 0; }
P6561 [SBCOI2020] 人:
首先考虑dp,但是发现dp复杂度和空间都实现不了。
然后我们对这题进行转化。
2 *i 和 2*i - 1看成一组,显然这一组两个位置不能都选。
我们把这一组选了2 * i - 1位置看成A,选了2 * i看成B,都没选看成C
那么题目就转化成了由A,B,C组成的长度为m的字符串,且不能包含子串BA。
A有a个,B有b个,C有m - a - b个。
也就是说对于A,它不能放在B字符的后面。
那么我们先考虑B,C两个的排列。
显然是C(m - a,b)。
我们再考虑此时A的能放置的位置。
第一个A:最前面或者所有C的后面,即1 + m - a - b
第二个A:最前面或者所有C的后面,或者前一个A的后面,即1 + m - a - b + 1
那么第i个A:1 + m - a - b + i - 1 = m - a - b + i.
所以a个A能放置的方案数为(m - a - b + 1) * (m - a - b + 2) **** (m - a - b + a).
令m - a - b = n,即为(n + 1) * (n + 2) * .. (n + a) = (n + a)! / n!
因为这里所有a都是等价的,所以需要去重复的方案数,即除以a!
得(n + a)! / (n! * a!).仔细看这个不就是C(n + a,a)吗..
然后就可以做了.C(n + a,a) = C(m - b,a)。//n代换掉
所以最后ans = C(m - a,b) * C(m - b,a).

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int N = 1e6 + 5; const int M = 2e4 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 998244353; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int f = 1,x = 0;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} LL f[N],inv[N]; LL quick_mi(LL a,LL b) { LL re = 1; while(b) { if(b & 1) re = re * a % Mod; b >>= 1; a = a * a % Mod; } return re; } void init() { f[0] = 1; for(int i = 1;i < N;++i) f[i] = f[i - 1] * i % Mod; inv[N - 1] = quick_mi(f[N - 1],Mod - 2); for(int i = N - 2;i >= 0;--i) inv[i] = inv[i + 1] * (i + 1) % Mod; } LL C(LL n,LL m) { return f[n] * inv[m] % Mod * inv[n - m] % Mod; } void solve() { int m,a,b;m = read(),a = read(),b = read(); LL ans = C(m - a,b) * C(m - b,a) % Mod; printf("%lld ",ans); } int main() { init(); int ca;ca = read(); while(ca--) { solve(); } return 0; }
P3455 [POI2007]ZAP-Queries:
回顾一下.
$sum_{i = 1}^{a}sum_{j = 1}^{b}[gcd(i,j) = d] -> sum_{i = 1}^{[frac{a}{d}]}sum_{j = 1}^{[frac{b}{d}]}[gcd(i,j) = 1]$
改为枚举约数即可,这里有一点,就是因为有两段的分块,我们是一起分块的,所以每次取右界,要取近的,这样保证两段都是满足n / L,m / L都是对于他们自己的那段一样的。

// Author: levil #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsigned long long ULL; typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int N = 5e4 + 5; const int M = 2e4 + 5; const double eps = 1e-10; const LL Mod = 998244353; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e9 #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int f = 1,x = 0;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } inline long long ADD(long long x,long long y) {return (x + y) % Mod;} inline long long DEC(long long x,long long y) {return (x - y + Mod) % Mod;} inline long long MUL(long long x,long long y) {return x * y % Mod;} int mu[N],prime[N],tot = 0; bool vis[N]; void init() { mu[1] = 1; for(int i = 2;i < N;++i) { if(!vis[i]) { prime[++tot] = i; mu[i] = -1; } for(int j = 1;j <= tot && prime[j] * i < N;++j) { vis[prime[j] * i] = 1; if(i % prime[j] == 0) { break; } else mu[prime[j] * i] = -mu[i]; } } for(int i = 1;i < N;++i) mu[i] += mu[i - 1]; } void solve() { int a,b,d;a = read(),b = read(),d = read(); int n = a / d,m = b / d; int up = min(n,m); LL ans = 0; for(int L = 1,r = 0;L <= up;L = r + 1) { r = min(n / (n / L),m / (m / L)); ans += 1LL * (mu[r] - mu[L - 1]) * (n / L) * (m / L); } printf("%lld ",ans); } int main() { init(); int ca;ca = read(); while(ca--) { solve(); } return 0; }
