顺序查找
查找原理:
从列表中的第一个元素开始,我们按照基本的元素排序,简单的从一个元素移动到另一个元素,直到找到我们要找的元素或是遍历完整个列表.
实例代码:
def search(item,alist): find=False length=len(alist) for i in range(length): if alist[i] == item: find=True return find
对有序列表进行循环会提升查找的效率:
def search(alist,item): find=False length=len(alist) pos=0 stop=False while pos <=length and not stop: if alist[pos] == item find=True break elif alist[pos]>item: stop = True pos+=1 return find
二分法查找(注意 : 二分法查找查找的对象必须是有序的)
概况:
我们在之前在进行有序列表的查找时,发现如果我们查找的对象在列表的最后一个,我们查找一次之后,还有n-1次才能查找到,二分法查找则是将列表的最中间的元素找到,然后跟我们找的值进行比较,如果比这个数大,则将中间这个数前面的所有数排除掉,在将中间这个值作为新列表的起始值.这样极大地提升了我们的查找效率,当然只有在列表的值很大的时候才能发现出效果.
实例代码:
def search(alist,item): first_index=0 last_index=len(alist-1) find_status=False while first_index<=last_index and not find_status: mid_index=(first_index+last_index)//2 if alist[mid_index] > item: last_index =mid_index-1 elif alist[mid_index] < item: first_index=mid_index+1 else: find=True return find
二叉树
结构: 根节点 叶子节点 - 左叶子节点 - 右叶子节点 子树
二叉树中有节点和树模型,这里我们要分别写节点和树模型.
节点:
class Node: def __init__(self,item): self.left=None self.right=None self.item=item
空树模型:
class Tree: def __init__(self): self.root=None #往树中添加数据 def add(self,item): #实例化一个节点 node=Node(item) #如果树是空树,直接将节点添加到树根 if self.root == None: self.root=node return queue=[self.root] #从队列中取值,并且判断直到return或者队列为空为止 while queue: cur=queue.pop(0) if self.left == None: self.left = node return else: queue.append(cur.left) if self.right == None: self.right = node return else: queue.append(cur.right) #广度优先遍历 def guangdu(self): queue=[self.root] while queue: cur = queue.pop(0) if cur.left is not None: queue.append(cur.left) elif cur.right is not None: queue.append(cur.right) #深度优先遍历(分为三种形式,根左右,左根右,左右根) def root_left_right(self,root): if root == None: return print(root.item,end='') root_left_right(root.left) root_left_right(root.right) def left_root_right(self,root): if root ==None: return left_root_right(self.left) print(root.item) left_root_right(self.right) def left_right_root(self,root): if root == None: return left_right_root(root.left) left_right_root(root.right) print(root.item)
遍历二叉树有两种方法: 广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历
广度优先遍历: 从根节点开始一层一层的开始遍历.
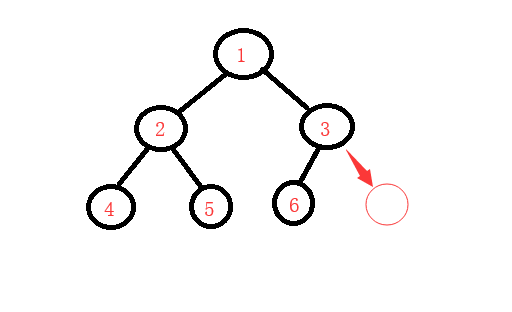
深度优先遍历:从根节点开始,往下找,如果左节点下面还有节点,继续往下找,直到找到最后一个节点为止(这里深度优先遍历分为三种,根左右,左根右,左右根)
根左右(前序)
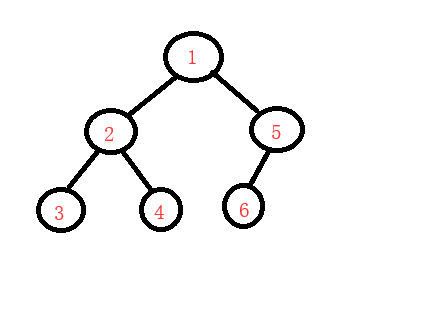
左根右(中序,中序是可以对列表中的元素进行排序的)

左右根(后序)
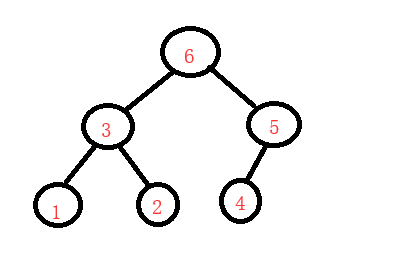
排序二叉树
在插入数据的时候需要一个准则,比如比根节点大的数插入到右边,比根节点小的数插入到左边.
class Node: def __init__(self,item): self.item=item self.left=None self.right=None class Tree: def __init__(self): self.root = None
#以下是广度优先遍历的代码,深度优先遍历跟普通的二叉树一样 def insert(self,item): node=Node(item) if self.root == None: self.root = node return cur = self.root while True: if item > cur.item: if cur.right == None: cur.right = node reutrn cur =cur.right else: if cur.left == None: cur.left =node return cur =cur.left
排序算法
这里我们介绍5中排序规则
- 冒泡排序
- 选择排序
- 插入排序
- 希尔排序
- 快速排序(快排)
冒泡排序(如果前面那个数比后面那个数大,就互换位置)
def maopao(alist): length=len(alist)
#如果不进行这次循环,列表还是无序的,只是将最大值放到了最后的位置 for j in range(length-1):
#这次循环是为了将最大值放到最后 for i in range(length-1-j): if alist[i]>alist[i+1]: alist[i],alist[i+1] = alist[i+1],alist[i] return alist
选择排序(先指定第一个索引位置的数字为最大数字,然后从第二个数开始循环,如果这个数比第一个大,那么将最大索引改为新数的索引,直到循环玩这个列表,在将最大数的索引与列表最后一个索引互换即可)
def xuanze(alist): length=len(alist)
#如果不进行这个for循环,无法将每次循环得到的最大值放到最后一个位置 for j in range(length-1,0,-1): max_index=0 for i in range(1,j+1): if alist[i] > alist[max_index]: max_index = i alist[max_index],alist[j] = alist[j],alist[max_index] return alist
插入排序(假设前面第一个数为一个列表中的第一个元素,从第二个数开始循环,如果比他小,就互换位置,然后再次循环,直到循环到第一个索引为止)
def charu(alist): for i in range(1,len(alist)): while i>0: if alist[i] < alist[i-1]: alist[i],alist[i-1]=alist[i-1],alist[i] i-=1 else: break return alist
希尔排序(其实可以理解成优化版的插入排序,相当于分了个组)
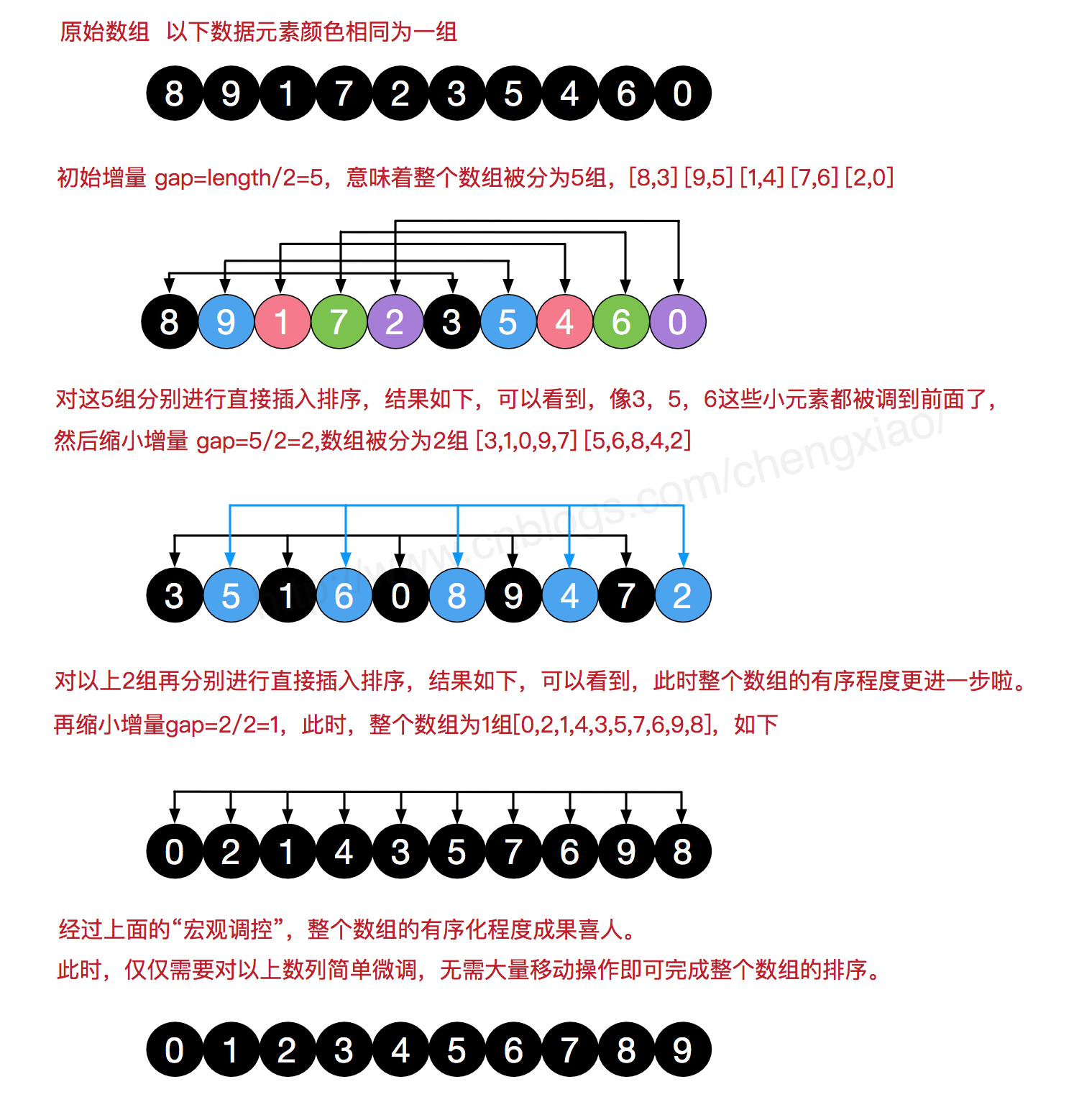
那么有人会问了,为什么我不能直接用插入排序呢,这不是闲的嘛.你想呀,我们这个插入排序是不是要循环好多次呢,如果我们有100万条数据,我们要循环100万次呢,而希尔排序会帮我缩短查找的次数,官方一点就是希尔排序的时间复杂度是O(n),而插入排序的时间复杂度为O(n²).所以希尔排序比直接插入排序要省时.
def sort(alist): gap = len(alist) // 2 while gap >= 1: for j in range(gap,len(alist)): i = j while i>0: if alist[i] < alist[i-gap]: alist[i],alist[i-gap] = alist[i-gap],alist[i] i = i-gap else: break #缩减增量 gap = gap//2 return alist
快速排序
def sort(alist,start,end): low = start high = end mid = alist[low] if low >= high: return while low < high: while low < high: #判断的话要从右往左 if alist[high] > mid: high -= 1 else: alist[low] = alist[high] break while low < high: #判断的话要从左往右 if alist[low] < mid: low += 1 else: alist[high] = alist[low] break alist[low] = mid #mid左侧的子列表 sort(alist,start,low-1) #mid右侧的子列表 sort(alist,low+1,end) return alist