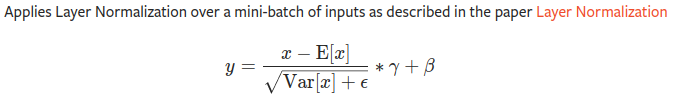Layer Normalization
总览
- 针对同一通道数的图片的H*W进行层正则化,后面的γ和β是可以学习的参数,其中这两个的维度和最后一个的维度相同
- 例如特征图矩阵维度为[3, 577, 768], 那么γ和β的维度均为Tensor(768,)
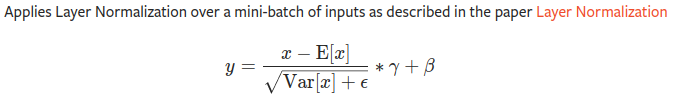

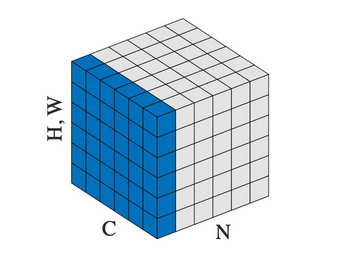
step1:代码示例1
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
input = torch.tensor(
[
[
[
[2., 2.],
[3., 3.]
],
[
[3., 3.],
[2., 2.]
]
],
[
[
[2., 2.],
[3., 3.]
],
[
[3., 3.],
[2., 2.]
]
]
]
)
print(input)
print(input.shape) # torch.Size([2, 2, 2, 2])
layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm([2, 2, 2, 2], elementwise_affine=True)
output = layer_norm(input)
print(output)
"""
tensor([[[[-1.0000, -1.0000],
[ 1.0000, 1.0000]],
[[ 1.0000, 1.0000],
[-1.0000, -1.0000]]],
[[[-1.0000, -1.0000],
[ 1.0000, 1.0000]],
[[ 1.0000, 1.0000],
[-1.0000, -1.0000]]]], grad_fn=<NativeLayerNormBackward>)
"""
# 总结
"""
根据公式
E(x) = ((2+2+3+3)*4)/16 = 2.5
Var(x) = {(2-2.5)**2 * 8 + (3-2.5)**2 * 8} / 16 = 0.5**2
带入公式可以得到:
y = (x - E(x)) / (var(x)**0.5)
可以得到output
"""
step2更改输入观察输出
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
input = torch.tensor(
[
[
[
[3., 2.], # 这里将2 变成 3进行观察输出
[3., 3.]
],
[
[3., 3.],
[2., 2.]
]
],
[
[
[2., 2.],
[3., 3.]
],
[
[3., 3.],
[2., 2.]
]
]
]
)
print(input)
print(input.shape) # torch.Size([2, 2, 2, 2])
layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm([2, 2, 2, 2], elementwise_affine=True)
output = layer_norm(input)
print(output)
"""
tensor([[[[ 0.8819, -1.1339],
[ 0.8819, 0.8819]],
[[ 0.8819, 0.8819],
[-1.1339, -1.1339]]],
[[[-1.1339, -1.1339],
[ 0.8819, 0.8819]],
[[ 0.8819, 0.8819],
[-1.1339, -1.1339]]]], grad_fn=<NativeLayerNormBackward>)
"""
# 总结
"""
由上述的公式可得,输入变化,整个输出都进行了改变
"""
Batch Normalization
- 计算公式同上, 这里他的可学习参数与in_channel同
step1:代码示例1:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# With Learnable Parameters
m = nn.BatchNorm2d(2)
input = torch.tensor(
[
[
[
[2., 2.],
[3., 3.]
],
[
[3., 3.],
[2., 2.]
]
],
[
[
[2., 2.],
[3., 3.]
],
[
[3., 3.],
[2., 2.]
]
]
]
)
print(input)
print(input.shape) # torch.Size([2, 2, 2, 2])
output = m(input)
print(output)
"""
tensor([[[[-1.0000, -1.0000],
[ 1.0000, 1.0000]],
[[ 1.0000, 1.0000],
[-1.0000, -1.0000]]],
[[[-1.0000, -1.0000],
[ 1.0000, 1.0000]],
[[ 1.0000, 1.0000],
[-1.0000, -1.0000]]]], grad_fn=<NativeBatchNormBackward>)
"""
# 总结:
"""
计算的是某个批次的正则
根据公式 以第一个批次为例:
E(x) = {2+2+3+3+2+2+3+3}/8 = 2.5
Var(x) = {(2-2.5)**2 * 4 + (3-2.5)**2 * 4}/8 = 0.5**2
带入公式可以得到:
y = (x - E(x)) / (var(x)**0.5)
可以得到output
"""
进行微小更改观察变化
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# With Learnable Parameters
m = nn.BatchNorm2d(2)
input = torch.tensor(
[
[
[
[3., 2.], # 这里2变成3来观察变化
[3., 3.]
],
[
[3., 3.],
[2., 2.]
]
],
[
[
[2., 2.],
[3., 3.]
],
[
[3., 3.],
[2., 2.]
]
]
]
)
print(input)
print(input.shape) # torch.Size([2, 2, 2, 2])
output = m(input)
print(output)
"""
tensor([[[[ 0.7746, -1.2910],
[ 0.7746, 0.7746]],
[[ 1.0000, 1.0000],
[-1.0000, -1.0000]]],
[[[-1.2910, -1.2910],
[ 0.7746, 0.7746]],
[[ 1.0000, 1.0000],
[-1.0000, -1.0000]]]], grad_fn=<NativeBatchNormBackward>)
"""
# 总结:
"""
进行微小更改观察到,发生变化的是他同一批次里面的
"""
参考
layer_norm
batch_norm