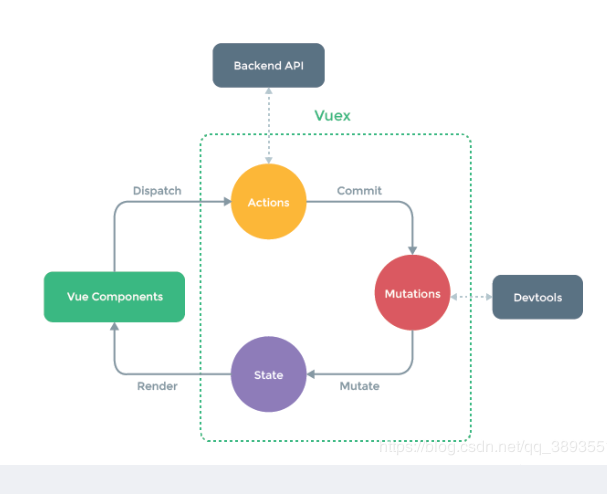
vuex的设计思想:单向数据流的设计思想(数据可控,错误好追踪)
在组件中不能修改state中的数据,只能通过commit mutation来修改数据,或者dispatch action,在action中再commit mutation来修改数据
vuex任务分析:
***.vue----------------------------------------------
<div>{{$store.state.count}}</div>
this.$store.dispatch("asyncIncrement", request2)
main.js中-------------------------------------------
import store from './store'
new Vue({
store,(在此挂载一下的目的就是供上面.vue组件中可以通过$store直接去访问)$store也是通过prototype的方式进行挂载的
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
store.js------------------------------------------------(vuex装进来)
import Vue from "vue"
import Vuex from "vuex"
Vue.use(Vuex);//use方法调用了install方法
export default new Vuex.Store({//创建store实例
state:{count:0}, //存数据的
mutations:{ //改数据的
increment(state){
state.count += 1
}
},
getters:{ //类似计算属性,对state进行加工
left(state){
return 1-state.count
}
},
actions:{ //异步方法可写入,通过commit修改mutation
asyncIncrement({getters,commit}){ //参数能拿到getters,commit等,是因为vuex里封装的方法将Store的实例当参数传出
return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
commit("increment");
resolve();
return;
},1000);
})
}
}
})
任务分析----------------------------------
·实现插件:$store(store的实例)挂载
·实现Store类:解析vuex的配置,持有$state,实现dispatch,commit,getters核心概念:
·借助vue实现数据的响应式
vuex.js---------------------------------------实现代码
let Vue;
class Store { //(通过store.js的vuex实例(Vuex.Store)可知,要创建一个Store类,实例中传了一个参数包含state,mutation,action等,所以Store类重要对其进行解析)
//持有state,并使其响应化
//实现commit和dispatch两个方法
constructor(options){
//解析实例中传入的数据
this.state = new Vue({data:options.state}); //因为state要实现数据响应式, //this.state是Vue实例,访问this.state.count就为响应式的count
this.mutations = options.mutations;
this.actions = options.actions;
//bind this----- commit和dispatch方法中在调用时 this的指向会出现问题(出现函数中调用函数的情况下,this指向会出现问题)
this.commit = this.commit.bind(this);
this.dispatch = thid.dispatch.bind(this);//箭头函数
options.getters && this.handleGetters(options.getters);
}
handleGetters(getters){
this.getters = {};//定义this.getters
//遍历getters选项,为this.getters定义property
//属性名就是选项中的key,只需要定义get函数保证其只读性
Object.keys(getters).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters,key,{
get:() => {
return getters[key](this.state)
}
})
})
}
//实现commit:可修改state中的数据
commit(type,arg){
this.mutations[type](this.state,arg);//从mutations里拿到名字为type的方法,调用他,把state数据以及参数传给他
}
dispatch(type,arg){
return this.actions[type](this,arg); //从actions里拿到名字为type的方法,传入的参数为this为当前实例,所以actions中的方法可以({commit,state})
}
}
//声明插件的install方法(Vue.use()用到install方法,规定)
function install(_Vue){//-----vue的插件必须实现install方法--规定
Vue = _Vue; //_Vue是形参:Vue的构造函数,use会把它传进来的
Vue.mixin({ //混入
beforeCreate(){
//this指的是组件实例
if(this.$options.store){ //vue实例传进去的store,即new Vue({store})
Vue.prototype.$store = this.$options.store;//use先执行,实例后创建,所以必须写入到mixin 不然此实例不存在
}
}
})
}
//导出vuex
export default {Store,install}
vuex里有个类叫store(绿框),能改数据的只有mutation;
vuex里要实现数据的响应式(因为组件中用到的数据,如果数据发生变化,界面要变更,所以数据必须是响应式的)--- 实现:vuex的构造函数初始化时做了响应式,所以与vue紧耦合,只能用在vue中;
