Spring AOP 的使用过程理解
首先,aop的使用场景介绍:
1、处理一些通用的非功能性的需求,不影响业务流程,比如说打印日志、性能统计、推送消息等;
2、aop无法拦截static、final方法、private方法
3、无法拦截内部方法调用

如果只要访问目标方法的参数,Spring还提供了一种更简单的方法:我们可以在程序中使用args来绑定目标方法的参数。如果在一个args表达式中指定了一个或多个参数,则该切入点将只匹配具有对应形参的方法,且目标方法的参数值将被传入增强处理方法。
Person.java :
public interface Person { public String sayHello(String name); public void eat(String food,Date time); }
Chinese.java :
@Component public class Chinese implements Person { @Override public void eat(String food, Date time) { System.out.println("我正在吃"+food+",现在时间是:"+time); } @Override public String sayHello(String name) { return name+" Hello,Spring AOP"; } }
AccessArgAspect.java :
@Aspect public class AccessArgAspect { @AfterReturning(returning="retVal", pointcut="execution(* com.bean.*.*(..)) && args(food,time)") public void access(String food,Date time,Object retVal){ System.out.println("目标方法中Strig参数为:"+food); System.out.println("目标方法中Date参数为:"+time); System.out.println("模拟记录日志..."); } }
bean.xml :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.bean"> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect"/> </context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> </beans>
Test.java
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); Person p=(Person) ctx.getBean("chinese"); System.out.println(p.sayHello("张三")); p.eat("西瓜",new Date()); } }
运行程序,控制台输出:

切入点表达式部分增加了&&args(food,time)部分,意味着可以在增强处理方法中定义food和time两个形参------定义这两个形参时,形参类型可以随意指定,但是一旦指定,譬如这里分别是String类型和Date类型,这两个形参类型将用于限制该切入点只匹配第一个参数类型为String,第二个参数类型为Date的方法。
我们如果修改access方法的形参列表为:
public void access(int food,Date time,Object retVal)
那么该切入点表达式只能匹配第一个形参类型为int,第二个形参类型为Date的方法,此例子中没有这样的方法,也就匹配不上。此时运行程序,看控制台输出:
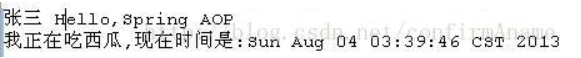
可以看到没有方法匹配上,程序里的增强处理没起作用。
至此可以看出,使用 args表达式 有如下两个作用:
① 提供了一种简单的方式来访问目标方法的参数。
② 可用于对切入表达式增加额外的限制。
除此之外,使用args表达式时还可使用如下形式:args(name,age,..),这表明增强处理方法中可以通过name,age来访问目标方法的参数。注意上面args表达式括号中的2点,它表示可以匹配更多参数。