#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <errno.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <signal.h> void catch_signal(int signo, siginfo_t *info, void *p) { switch (signo) { case SIGINT: printf("accept SIGINT! recv data=%d ",info->si_value.sival_int); break; case 34: //SIGRTMIN似乎不是一个确定的int类型 printf("accept SIGRTMIN! recv data=%d ",info->si_value.sival_int); break; case SIGUSR1: printf("accept SIGUSR1! "); //取消信号阻塞 sigset_t uset; sigemptyset(&uset); sigaddset(&uset, SIGINT); sigaddset(&uset, SIGRTMIN); sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &uset, NULL); printf("阻塞解除了! "); break; } } int main(int arg, char *args[]) { pid_t pid = 0; struct sigaction act; act.sa_sigaction = catch_signal; sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask); act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO; //注册SIGINT信号 if (sigaction(SIGINT, &act, NULL) != 0) { printf("sigaction SIGINT failed ! "); return -1; } //注册SIGTMIN信号 if (sigaction(SIGRTMIN, &act, NULL) != 0) { printf("sigaction SIGINT failed ! "); return -1; } //注册SIGUSR1信号 if (sigaction(SIGUSR1, &act, NULL) != 0) { printf("sigaction SIGINT failed ! "); return -1; } //阻塞SIGINT信号和SIGTMIN信号 sigset_t bset; sigemptyset(&bset); sigaddset(&bset, SIGINT); sigaddset(&bset, SIGRTMIN); //更新进程屏蔽信号状态字 if (sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &bset, NULL) != 0) { printf("sigprocmask() failed ! "); return -1; } pid = fork(); if (pid == -1) { printf("fork() failed ! error message:%s ", strerror(errno)); return -1; } if (pid == 0) { int i = 0, ret = 0; union sigval v1; union sigval v2; for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) { v1.sival_int = 201 + i; ret = sigqueue(getppid(), SIGINT, v1); if (ret != 0) { printf("发送不可靠信号SIGINT失败! error message:%s ", strerror(errno)); } else { printf("发送不可靠信号SIGINT成功! "); } } for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) { v2.sival_int = 301 + i; ret = sigqueue(getppid(), SIGRTMIN, v2); if (ret != 0) { printf("发送可靠信号SIGTMIN失败! error message:%s ", strerror(errno)); } else { printf("发送可靠信号SIGTMIN成功! "); } } //发送SIGUSR1信号 if (kill(getppid(), SIGUSR1) != 0) { printf("kill() failed ! error message;%s ", strerror(errno)); } exit(0); } //父进程 int res = 0, status = 0; while (1) { res = wait(&status); if (res == -1) { if (errno == EINTR) { continue; } break; } } while (1) { sleep(1); } return 0; }

一:SIGINT是不可靠信号。发送了3次父进程只接收到1次,SIGRTMIN是可靠信号,发送了3次父进程接收到3次信号。
二:对于可靠信号,Linux内核会缓存可靠信号,Linux内核可以缓存8192(各个Linux版本不同)条可靠信号;对于不可靠信号,Linux只能缓存一条不可靠信号。
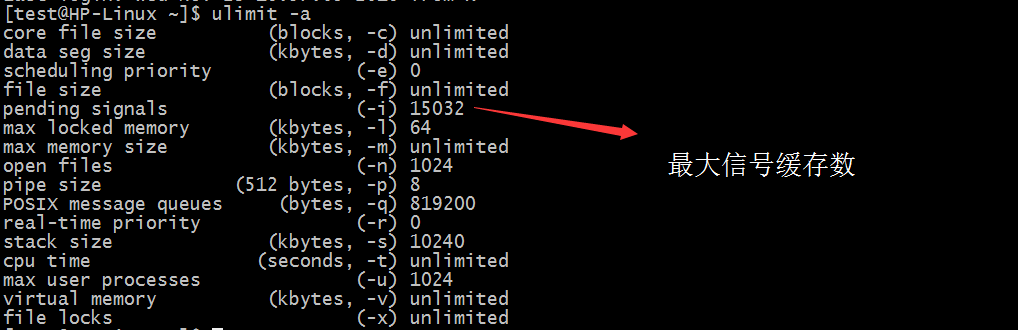
三:执行命令行: ulimit -a
查看Linux支持的信号性能参数
四:发送信号的数量超过系统上限,将会发送失败