JDK并发包
1. ReentrantLock(重入锁)
public class ReenterLock implements Runnable { public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static int i = 0; @Override public void run(){ for(int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++){ lock.lock(); try{ i++; }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } } public static void main(String[] args){ ReenterLock t1 = new ReenterLock(); Thread t1 = new Thread(t1); Thread t2 = new Thread(t1); t1.start();t2.start(); t1.join();t2.join();
//i=20000000,说明i++被加锁,不能被同一线程同时访问 System.out.println(i); } }
特性:
1.1 中断响应
package com.tianmaying.crawler.impl; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class IntLock implements Runnable{ public static ReentrantLock lock1 = new ReentrantLock(); public static ReentrantLock lock2 = new ReentrantLock(); int lock; public IntLock(int lock){ this.lock = lock; } @Override public void run() { try { if (lock == 1) { lock1.lockInterruptibly(); Thread.sleep(500); lock2.lockInterruptibly(); }else { lock2.lockInterruptibly(); Thread.sleep(500); lock1.lockInterruptibly(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(lock1.isHeldByCurrentThread()){ lock1.unlock(); } if(lock2.isHeldByCurrentThread()){ lock2.unlock(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId()+":线程退出。"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { IntLock r1 = new IntLock(1); IntLock r2 = new IntLock(2); Thread t1 = new Thread(r1); Thread t2 = new Thread(r2); t1.start(); t2.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); t2.interrupt(); } }
1.2 可以为锁设置等待时间
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class TimeLock implements Runnable{ public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run() { try { if(lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)){ System.out.println("get lock success"); Thread.sleep(6000); }else{ System.out.println("get lock failed"); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()){ lock.unlock(); } } } public static void main(String[] args){ TimeLock t1 = new TimeLock(); Thread t11 = new Thread(t1); Thread t12 = new Thread(t1); t11.start(); t12.start(); } }
第一个线程获得了锁,然后休眠6s,然后第二个线程申请锁,等待5s,锁仍然在第一个线程手上,然后第二线程会输出获取锁失败。
使用tryLock()锁,会不断尝试,总会拿到自己的资源
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class TryLock implements Runnable{ public static ReentrantLock lock1 = new ReentrantLock(); public static ReentrantLock lock2 = new ReentrantLock(); int lock; public TryLock(int lock){ this.lock = lock; } @Override public void run() { if(lock == 1){ while(true){ if(lock1.tryLock()){ try { try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (lock2.tryLock()) { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + ":My Job done"); return; } finally { lock2.unlock(); } } }finally { lock1.unlock(); } } } }else{ while(true){ if(lock2.tryLock()){ try { try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (lock1.tryLock()) { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + ":My Job done"); return; } finally { lock1.unlock(); } } }finally { lock2.unlock(); } } } } } public static void main(String[] args){ TryLock r1 = new TryLock(1); TryLock r2 = new TryLock(2); Thread t1 = new Thread(r1); Thread t2 = new Thread(r2); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
可以设置ReentrantLock为公平锁,ReentrantLock fairLock = new ReentrantLock(true);
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class FairLock implements Runnable{ public static ReentrantLock fairLock = new ReentrantLock(true); @Override public void run() { while(true){ try { fairLock.lock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得锁"); }finally { fairLock.unlock(); } } } public static void main(String[] args){ FairLock r1 = new FairLock(); Thread t1 = new Thread(r1,"Thread_t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(r1,"Thread_t2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
输出的结果:
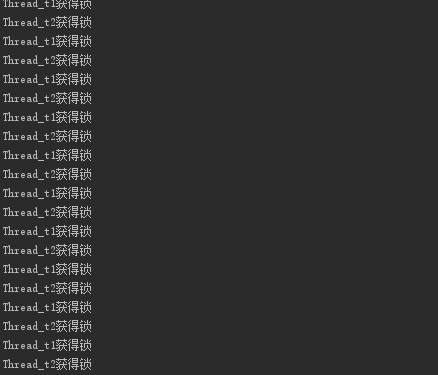
可以看出来线程1和线程2交替获得锁,很公平
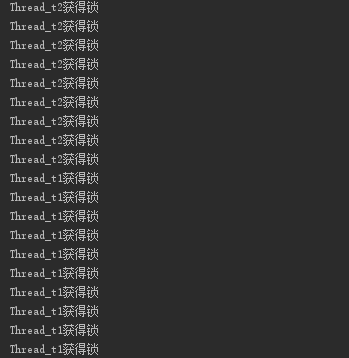
可以看出来线程1和线程2并不是很公平的获得锁
public class ReentrantLockCondition implements Runnable{ public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); @Override public void run() { try { lock.lock(); condition.await(); System.out.println("Thread is going on"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ReentrantLockCondition r1 = new ReentrantLockCondition(); Thread t1 = new Thread(r1); t1.start(); Thread.sleep(2000); lock.lock(); condition.signal(); lock.unlock(); } }