一、集合框架
有关LinkedList的集合的,它是一个链表结构的集合
1、链表结构
1.1 单链表的结构
所谓单链表(Linked)在内存中不连续的一端内存空间, 链表的每一个元素是一个节点,每一个结点由数据元素和下一个结点的存储位置组成,链表结构与数组结构最大区别是链接结构的存储内存是不连续的,而数组结构的内存是连续的,链表结构不能与数组结构一样快速查找,
链表结构操作特点是 添加,删除元素效率高,查询效率低;
数组结构操作特点: 添加,删除效率低,查询效率高
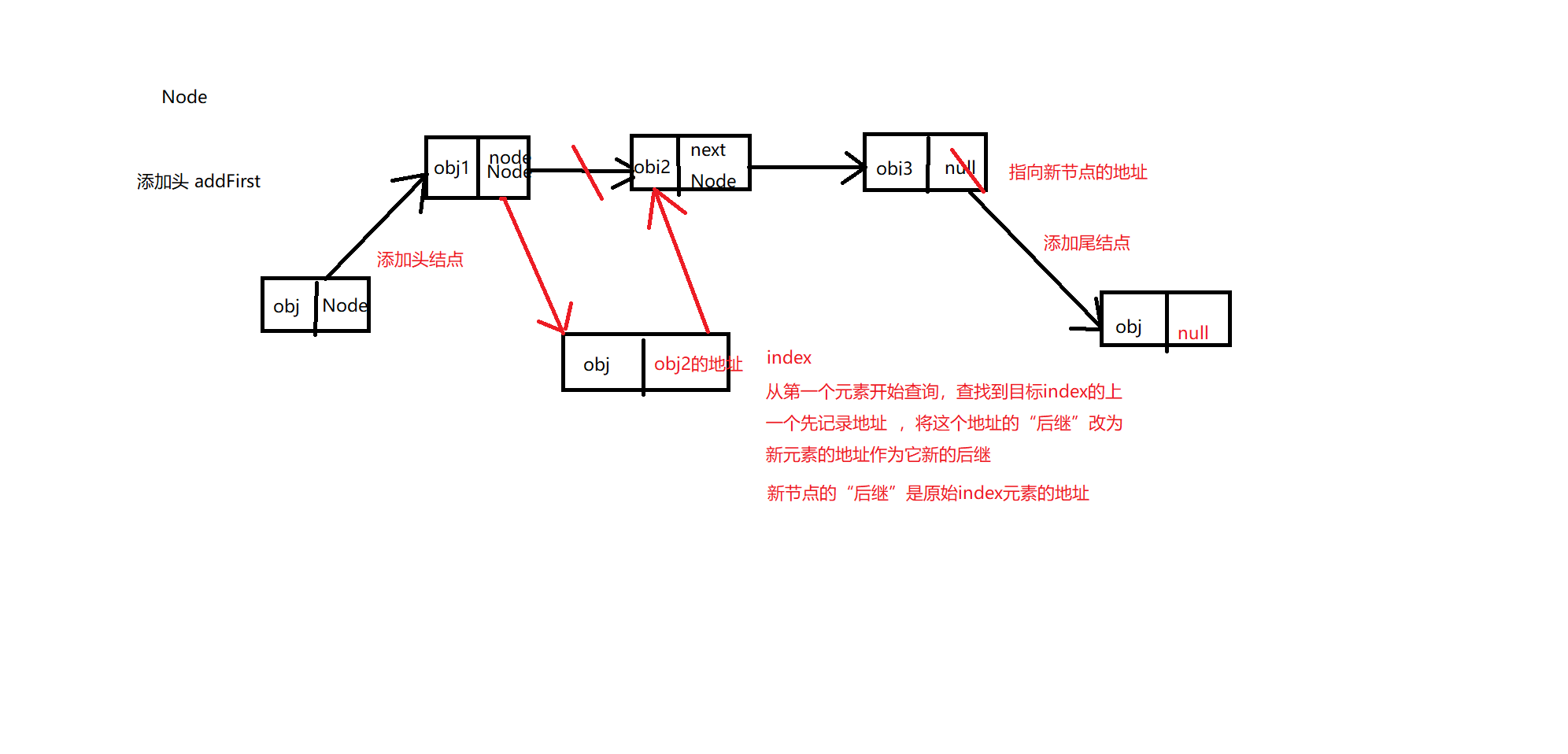
前驱: 该节点的上一个元素的地址
后继: 该节点的下一个元素的地址
链表结构中最后一个元素的”后继“为null
1.2 单链表的实现
链表实现添加元素:
/**
* 添加到最后元素
* @param obj
*/
public void addLast(Object obj){
//将节点添加到最后
//add(obj , this.size);
// 创建节点
// Node node = new Node(obj);
// // 找到最后一个元素的地址
// Node lastNode = this.header;
// for(int i = 0;i<this.size-1 ;i++){
// lastNode = lastNode.next;
// }
//
// lastNode.next=node;
// 找最后一个结点 (由于最后一个结点的next是null)
Node node = new Node(obj);
Node lastNode = this.header;
while(lastNode.next!=null){
lastNode = lastNode.next;
}
lastNode.next = node;
this.size++;
}
/**
* 删除第一个节点
* @param index
* @return
*/
public void removeFirst(){
//删除第一个节点
if(this.size==0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有需要删除的原始");
}
// 获取当前连接的“后继”
Node node = this.header.next;
// 并让后继作为头
this.header = node;
this.size--;
}
/**
* 删除最后节点
*/
public void removeLast(){
//删除是否存在数据
if(this.size==0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有需要删除的原始");
}
// 找最后一个元素的前一个 地址 ,并将该地址的next 改为null
Node cur = this.header;
Node pre = this.header;
while(cur.next!=null){
pre = cur;
// 下一个变为当前
cur = cur.next;
}
// 最后一个元素 就是 当前
pre.next = null;
size--;
}
单链练习:整体
package linked;
import javax.xml.soap.Node;
/**
* @ClassName:JAVA
* @Author:ZhouHongTing
* @pate:2020/10/26 18:47
* @Description;
*/
public class Test<T> {
//创建链表头部
Node header; //如果有节点,那么这就是头节点
int size;//计算链表数量
//创建节点类
class Node<T>{
//节点内容
T data;
Node next;//下一个节点地址
public Node(T data){
this.data=data;
}
//获取data
public T getData(){
return data;
}
//设置data
public void setData(T data){
this.data=data;
}
//获取下一个节点地址
public Node next(){
return next;
}
//设置下一个节点地址
public void setNext(){
this.next=next;
}
}
/**
* 将元素添加到第一个节点
*/
public void addFirst(T n){
//创建节点
Node node=new Node(n);
node.next=this.header;//新节点的后继就是原节点头部
this.header=node;//将头节点变为新要添加的节点
//节点计数器加一
size++;
}
/**
* 添加到最后元素
*/
public void addLast(T n){
//创建新节点
Node node=new Node(n);
Node lastNode=this.header;//创建一个最后节点,赋予头值从头开始算,求出最后节点
while (lastNode.next!=null){
lastNode=lastNode.next;
}
lastNode.next=node;
this.size++;
}
/**
* 插入一个指定下标节点
*/
public void addIndex(T n,int index){
Node node=new Node(n);//创建新节点
Node cle=this.header;//创建 一个前节点获取头节点值作为初始值
Node cur;//创建一个后一个节点,装前一个节点的(下一个节点地址)
for(int i=0;i<index-1;i++){
cle=cle.next;//循环判断到指定下标的前一个节点
}
cur=cle.next;//将前一个节点的下个节点地址存入
cle.next=node;//前一个节点的下一个节点地址就是当前插入元素节点
node.next=cur;//当前节点的下个节点位置就是原先前节点的下个节点地址
this.size++;
}
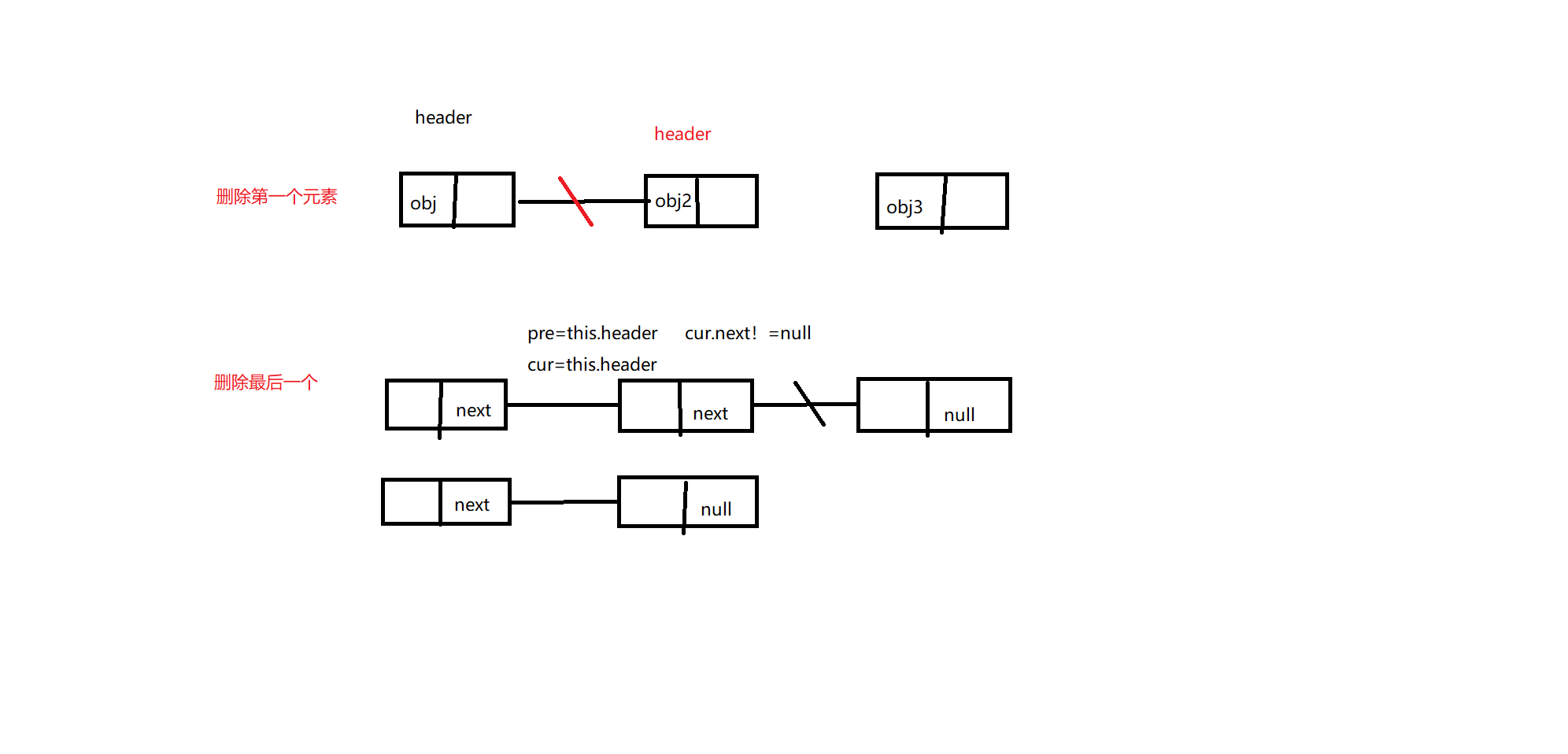
/**
* 删除第一个节点
*/
public void removeFirst(){
//先判断是否存在节点
if(this.size==0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有需要删除的节点");
}
//获取当前节点的"后继"
Node node=this.header.next;//获取当前头节点的后继节点
//让后继节点替换头节点便完成删除头节点
this.header=node;
this.size--;
}
/**
*删除一个指定下标节点
*/
public void removeIndex(int index){
// Node node=new Node(n);
if(this.size<index){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("要删除的节点不存在");
}
Node pre=this.header;
Node cur=this.header;
for(int i=0;i<index;i++){
pre=cur;
cur=pre.next;
}
pre.next=cur.next;
this.size--;
}
/**
* 删除最后节点
*/
public void removeLast(){
//判断是否存在节点
if(this.size==0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有节点");
}
//找到最后一个节点的前一个节点,并将它下个节点地址改为null
Node cur=this.header;
// Node pre=header;
while (cur.next!=null){
// pre=cur; //获取的后继节点就是下一个节点
cur=cur.next;//获取节点后继,直到cur.next=null
}
// pre.next=null;
cur.next=null;
this.size--;
}
/**
* 根据下标获取节点
* @param
*/
public Node getShowInfo(int index){
//判断是否为空节点
if(this.size==0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("这是空节点");
}
if(index==0){
return this.header;
}
//查找指定下标的元素
Node cur=this.header;//从第一个元素开始
int j=0;
while (index!=j&&index<this.size){
cur=cur.next;
j++;
}
return cur;
}
//测试
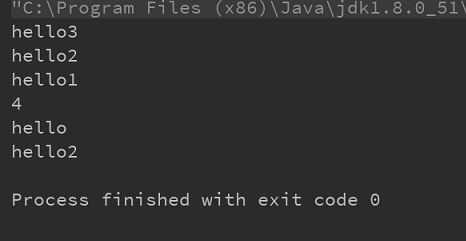
public static void main(String[]args){
Test test=new Test();
test.addFirst("hello1");
test.addFirst("hello2");
test.addFirst("hello3");
for(int i=0;i<test.size;i++){
System.out.println(test.getShowInfo(i).getData());//输出添加的节点元素
}
test.addIndex("hello",1);//在指定位置添加节点元素
System.out.println(test.size); //查看节点数量 //4
test.removeFirst(); //删除第一个节点元素
System.out.println(test.header.getData()); //hellio
test.removeLast(); //删除最后一个节点元素
System.out.println(test.size); //2
System.out.println(test.getShowInfo(test.size-1).getData());//hello2
test.removeIndex(1); //删除指定下标为1 的节点元素
System.out.println(test.size); //1
System.out.println(test.getShowInfo(1).getData()); //hello
}
}
2、队列结构
队列结构(Queue): 在基于链表结构的基础上 ,实现的一种“先进先出”的结构, 常用操作 入队(put),出队(pop) ,设置队列的头结点 和 尾结点

package com.j2008.dataStruct;
public class MyQueue<T> {
// 头结点
private Node front;
// 尾结点
private Node tail;
// 大小
private int size;
public MyQueue(){
// 头,尾为空
this.front= this.tail=null;
}
class Node{
private T obj;
private Node next;
public Node(T obj){
this.obj = obj;
}
public T getObj() {
return obj;
}
public void setObj(T obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 入队 : 将元素添加到队列的尾部
*/
public void put(T obj){
// 创建节点
Node node = new Node(obj);
// 如果元素为空 则头就尾,尾就是头
if(isEmpty()){
this.front = this.tail = node;
return ;
}
// 将新元素的地址 作为尾的next
this.tail.next=node;
//将新元素的结点 作为尾节点
this.tail = node;
this.size++;
}
/**
* 出队: 将元素从队列的头部移除 (保持与队列脱离关系)
* @return
*/
public T pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有可出队的元素");
}
// 移除头部元素
Node popNode = this.front;
// 设置现在的头元素是下一个
this.front = popNode.next;
// 将弹出的元素next 设置null,与队列脱离关系
popNode.next=null;
this.size--;
// 如果没有元素了 则需要 设置头尾都是null
if(this.size<0){
this.front=this.tail=null;
}
return popNode.getObj();
}
/**
* 判断元素是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
if(this.front==null && this.tail==null){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
队列结构整体练习:
package linked;
/**
* @ClassName:JAVA
* @Author:ZhouHongTing
* @pate:2020/10/27 9:08
* @Description;
*/
public class Test2<T> {
//创建头部结点
private Node front;
//创建尾部结点
private Node tail;
//创建结点计数器
int size=0;
public class Node{
//创建结点元素,装纳内容
private T Info;
//创建下一个节点地址对象
Node next;
public Node(T info) {
this.Info = info;
}
public T getInfo() {
return Info;
}
public void setInfo(T info) {
this.Info = info;
}
}
/**
* 入队
*/
public void put(T t){
Node node=new Node(t);
//判断结点是否为空
if(isEmpty()){
front=tail=node; //若都为空,则添加的元素,遵循先进先出,即尾就是头;
}
//若不为空,则新添加的节点元素为尾
tail.next=node;
tail=node;
size++;
}
/**
* 出队
*/
public void out(){
//判断有无结点
if(isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("结点为空");
}
//若不为空,则从头开始出队,即删除头部元素
Node node=front;//获取头结点元素
front=node.next;//将头结点下个结点地址,重新赋值给头结点,即原来的头结点被它的下一个结点覆盖
//将获取的头结点与队列断开联系,即出队,即设置它的下个结点地址为空
node.next=null;
size--;
//当计算器为0时,则头尾皆空
if(this.size<=0){
front=tail=null;
}
}
/**
* 判断结点是否为空
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
if(front==null&&tail==null){
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test2 t=new Test2();
//入队
t.put("hello1");
t.put("hello2");
t.put("hello3");
//输出结点数量
System.out.println(t.size);//3
//输出头结点元素
System.out.println(t.front.Info);//hello
//输出尾结点元素
System.out.println(t.tail.Info);//hello3
//出队
t.out();
System.out.println(t.size);//2
//输出头结点元素
System.out.println(t.front.Info);//hello2
//输出尾结点元素
System.out.println(t.tail.Info);//hello3
}
}
3、栈结构
栈(Stack)结构也是常用数据结构之一,它具有 “后进先出” 的特点

public class MyStack<T> {
// 定义一个数组 ,用于存储元素
private Object[] obj;
private int size;
public MyStack(){
obj = new Object[10];
size=0;
}
/**
* 入栈: 压入栈顶元素
* @param t
*/
public void push(T t){
expandCapacity(size+1);
obj[size]=t;
size++;
}
/**
* 返回栈顶元素:peek
*/
public T peek(){
if(size>0) {
return (T) obj[size - 1];
}
return null;
}
/**
* 出栈: 返回栈顶的元素,并删除该元素
* @return
*/
public T pop(){
T t = peek();
if(size>0) {
// 将最后一个元素 删除
obj[size - 1] = null;
size--;
}
return t;
}
/**
* 是否为空元素
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
/**
* 扩容数组大小 : 扩容1.5倍
*/
public void expandCapacity(int size){
if(obj.length< size){
// 需要扩容
int length = size*3/2 + 1;
this.obj = Arrays.copyOf(this.obj,length);
}
}
}
链表实现栈结构练习:
package linked;
/**
* @ClassName:JAVA
* @Author:ZhouHongTing
* @pate:2020/10/27 9:53
* @Description;
*/
public class Test3<T> {
//创建头部结点
private Node head;
//创建结点计数器
int size;
//创建结点
public class Node{
//创建内容变量
private T Info;
//创建下个结点地址对象
Node next;
public Node(T info) {
Info = info;
}
public T getInfo() {
return Info;
}
public void setInfo(T info) {
Info = info;
}
}
/**
* 入栈
*/
public void put(T t){
//创建新结点元素
Node node=new Node(t);
//每装入一个新结点,都为头结点
//创建一个结点来装纳头结点,然后交换
Node next=head;
head=node; //将新结点设置为头部结点
head.next=next; //将原头结点,设置为现在的头结点的下一个结点地址
size++;
}
/**
* 出栈
*/
public void out(){
//入栈出栈,先进后出
//判断是否为空结点
if(size==0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("结点为空");
}
//创建一个结点来装入头部结点,出栈的第一个元素
Node node=head;
head=node.next; //将头结点的下一个结点地址元素设置为新的头部
//设置原先头结点的下个结点地址为空,切断与栈的练习,出栈
node.next=null;
size--;
}
/**
* 输出指定下标结点元素
*/
public Node showInfo(int index){
//判断是否为空
Node pre=this.head;
if(index<0||index>=size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有结点");
}
for(int i=0;i<index;i++){
pre=pre.next;
}
return pre;
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//入栈
Test3 t=new Test3();
t.put("hello1");
t.put("hello2");
t.put("hello3");
t.put("hello4");
//测试
for (int i=0;i<t.size;i++){
System.out.println(t.showInfo(i).Info);
}
//出栈
t.out();
t.out();
// System.out.println(t.showInfo(2).Info);
System.out.println(t.size);
//测试
for (int i=0;i<t.size;i++){
System.out.println(t.showInfo(i).Info);
}
}
}
结果: