1、重复两次定义
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> int a,b; void fun() { a=100; b=200; printf("%d,%d ",&a,&b); } int main() { int a=5,b=7; fun(); printf("%d,%d ",a,b); printf("%d,%d ",&a,&b); return 0; }
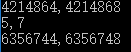
从运行结果中可以看出,如果全局变量定义一次a,b, main函数中定义一次a,b两个地址是不一样的。
改成下面结果就对
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> int a,b; void fun() { a=100; b=200; printf("%d,%d ",&a,&b); } int main() { /*int*/ a=5,b=7; fun(); printf("%d,%d ",a,b); printf("%d,%d ",&a,&b); return 0; }
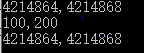
2、强制转换优先级
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> int main() { double a,b; a = 5.5; b = 2.5; printf("%f ",(int)a+b/b); //先强制转换为 int a ,在+double型的b/b printf("%d",(int) (a+b/b)); return 0; }
3、等号的左边只能是变量,不可以是表达式
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int k,a,b=1; unsigned long w=5; k=b+2=w; //错误语句 return 0; }
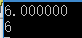
4、逗号运算符的使用(必须在赋值运算符前加括号)
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int a=0, b=0,c=0; c = ( a-=a-5),(a=b,b+3); //赋值运算符的优先级比逗号运算符高,先把5赋值给c; printf("%d %d %d ",a,b,c); c = ( ( a-=a-5),(a=b,b+3) ); //逗号运算符,把最右边的值赋值给c printf("%d %d %d",a,b,c); return 0; }

5、#define 预定义的用法
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define S(x) 4*(x)*x+1 int main() { int k=5,j=2; printf("%d",S(k+j)); // 4*(5+2)*5+2+1 =143 注意define没有括号坚决不加括号,直接写 return 0; }
6、&&符号左边不成立不再执行右边, ||左边成立不再执行右边
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int i=1,j=1,k=2; if( (j++||k++) && i++) //k++将不会被执行 printf("%d %d %d ",i,j,k); //2 2 2 return 0; }
7、scanf中出现*表示跳过指定宽度
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int a,b; double c; scanf("%2d%*2d%2d%2lf",&a,&b,&c); //跳过第3,4个字符 printf("%d %d %f",a,b,c); return 0; }
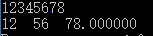
8、字符串长度,遇到转义字符
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include<string.h> int main() { char s1[] = "\141141abc "; printf("\141141abc :%d ",strlen(s1)); /* \ 是一个字符,前一个表示转义 141 三个字符 141 1个字符,注意这里是八进制符,如果超过8那就不是按三个算了 abc 三个字符 一个字符 再加上结束符'�' 共10个字符 而strlen(s)的值为9 */ char s2[] = "\1411111abc "; char s3[] = "\141128abc "; char s4[] = "\141888abc "; printf("\1411111abc :%d ",strlen(s2)); printf("\14189abc :%d ",strlen(s3)); printf("\141888abc :%d ",strlen(s4)); return 0; }
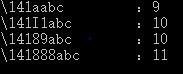 从这里也可以看出 141代表的是字符a,111代表的是字符I,而超过8的就直接输出了
从这里也可以看出 141代表的是字符a,111代表的是字符I,而超过8的就直接输出了
9、自增自减运算符
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include<string.h> int main() { int i=1,s=3; do{ s+= i++; //这里是s为 4 7 11 17而不是5 9 15 if( s%7==0) continue; else ++i; printf("i=%d s=%d ",i,s); }while( s<15); return 0; }