1.冒泡排序:
注意:2,5 如果当前j是5,j-1是2,5比2大,那5和2就不会交换,并且下一次比较的j是2,就不再是5
void Bubble_Sort(vector<int> input){ int length = input.size(); if(length <= 0) return; bool flag = true; for(int i = 0;i < length && flag;i++){ flag = false; for(int j = length - 1;j > i;j--){ if(input[j] < input[j-1]){ swap(input[j],input[j-1]); flag = true; } } } }
2.直接插入排序

void Insert_Sort(vector<int> input){ int length = input.size(); if(length <= 0) return; int tmp; int i,j; for(i = 1;i < length;i++){ if(input[i] < input[i-1]){ tmp = input[i]; for(j = i-1;j >= 0 && input[j] > input[i];j--){ input[j+1] = input[j]; } input[j] = tmp; } } }
自己的写法:
void Insert_Sort(vector<int> input){ int length = input.size(); if(length <= 1) return; for(int i = 1;i < length;i++){ if(input[i] < input[i-1]){ for(int j = i-1;j >= 0;j--){ if(input[j] <= input[j+1]) break; else swap(input[j],input[j+1]); } } }
3.选择排序
以下面5个无序的数据为例:
56 12 80 91 20
第1趟:12 56 80 91 20
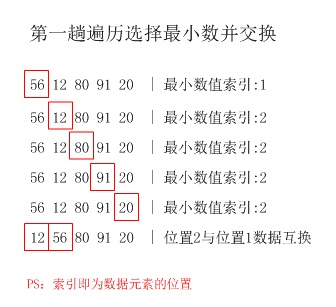
第2趟:12 20 80 91 56
第3趟:12 20 56 91 80
第4趟:12 20 56 80 91
void Select_Sort(vector<int> input){
int length = input.size();
if(length <= 0)
return; for(int i = 0;i < length;i++){
int min = i; for(int j = i+1;j < length;j++){
if(input[j] < input[min]){
min = j; } }
if(min != i){
swap(input[i],input[min]); } }
}
4.希尔排序
http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6668714
void Shell_Sort(vector<int> input){ int length = input.size(); if(length <= 0) return; for(int gap = length/2;gap >= 1;gap /= 2){ for(int i = 0;i < length;i++){ for(int j = i+gap;j < length;j += gap){ if(input[j] < input[j-gap]){ int tmp = input[j]; int k = j-gap; while(k >= 0 && input[k] > tmp){ input[k+gap] = input[k]; k -= gap; } input[k+gap] = tmp; } } } } }
5.堆排序
6.归并排序

void MergeSort(vector<int> input,int start,int mid,int end){ vector<int> front; vector<int> behind; int i,j,k; int len1 = mid - start + 1; int len2 = end - mid; int len3 = end - start + 1; for(i = 0;i < len1;i++){ front.push_back(input[i]); } for(j = 0;i < len2;j++){ behind.push_back(input[j+mid+1]); } for(i = 0,j = 0,k = 0;i < len1 && j < len2 && k < len3;k++){ if(front[i] < behind[j]){ input[k] = front[i]; i++; } else{ input[k] = behind[j]; j++; } } while(i <= len1){ input[k++] = front[i++]; } while(j <= len2){ input[k++] = front[j++]; } } void Merge(vector<int> input,int start,int end){ if(start < end){ int mid = (strat + end)/2; Merge(input,start,mid); Merge(input,mid+1,end); MergeSort(input,start,mid,end); } } void Sort(vector<int> input){ int length = input.size(); if(length <= 0) return; Merge(input,0,length-1); }
7.快排
时间复杂度分析:https://www.cnblogs.com/fengty90/p/3768827.html
最好和平均:
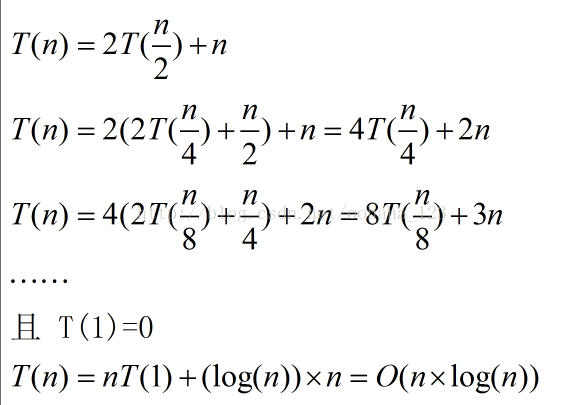
最坏时间复杂度:
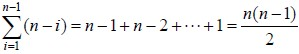
partition函数以end为界将数组分为左侧小于end的数值,右侧大于end的数值,并且同时返回end的数值在新数组的坐标值,方便之后分别在左侧和右侧继续排序。
注意:quick_sort,partition两个函数的vector都需要用引用,不然这个代码就跑不通
partition时间复杂度是logn,快排时间复杂度是nlogn
small记录的是最后一个小于比较的数的位置
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; class solution{ public: void quick_sort(vector<int> &input,int start,int end){ if(input.empty()) return; if(start == end) return; int index = partition(input,start,end); if(start < index) quick_sort(input,start,index-1); if(index < end) quick_sort(input,index+1,end); } int partition(vector<int> &input,int start,int end){ int small = start - 1; for(int i = start;i < end;i++){ if(input[i] < input[end]){ small++; if(small != i) swap(input,small,i); } } small++; swap(input,small,end); return small; } void swap(vector<int> &input,int start,int end){ int tmp = input[start]; input[start] = input[end]; input[end] = tmp; } }; int main(){ vector<int> input(4,1); input[1] = 3; input[2] = 5; input[0] = 2; solution a; a.quick_sort(input,0,3); for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++) cout << input[i] << endl; }
自己又写了一个版本:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; class Solution{ public: void quicksort(vector<int>& nums){ if(nums.empty()) return; int start = 0,end = nums.size() - 1; sort(nums,start,end); } void sort(vector<int>& nums,int start,int end){ if(start == end) return; int index = partition(nums,start,end); if(index > start) sort(nums,start,index-1); if(index < end) sort(nums,index+1,end); } int partition(vector<int>& nums,int start,int end){ int small = start - 1; for(int i = start;i < end;i++){ if(nums[i] < nums[end]){ small++; if(small != i) swap(nums[small],nums[i]); } } small++; swap(nums[small],nums[end]); return small; } }; int main(){ Solution debug; int a[] = {9,2,6,1,5,4,8}; vector<int> nums(a,a+7); debug.quicksort(nums); for(int i = 0;i < nums.size();i++){ cout << nums[i] << " "; } cout << endl; }