1.关于注释:写好注释,每个方法以及方法中重要的步骤,还有类的属性也要注释
方法注释使用块注释/ ** ….. */
重要步骤和属性使用行注释 //
/** * <p> * 方法名称: getItemList * </p> * <p> * 方法功能描述: 得到实验项目列表。 * </p> * <p> * 输入参数描述: String where:输入的查询条件。 * </p> * <p> * 输出参数描述: ArrayList<ItemPojo> * </p> */ public ArrayList<ItemPojo> getItemList(String where) throws Exception { ArrayList<ItemPojo> itemList = new ArrayList<ItemPojo>(); StringBuffer strSQL = _getItemSelectSQL(where); CachedRowSet rs = this.sqlHelper.queryCachedBySql(strSQL.toString()); if (rs != null) { while (rs.next()) { itemList.add(this._setOneItemPojo(rs));//注意:re是游标,刚开始它是指向第一条数据的前面! } rs.close(); } return itemList; }
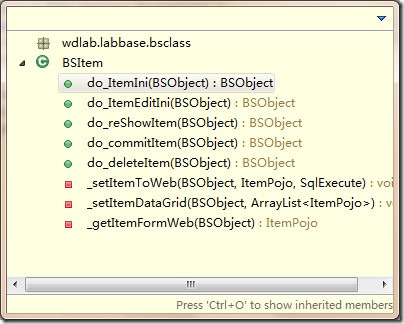
2.关于方法:任何一个类的私有方法声明为private,命名时以下划线开头,并且将私有的方法放在类的最下面,其他的可以供外部调用的方法放在前面
对于前台JS调用的方法用do_开头,并且最开始的页面初始化方法首字母要大写
3.类的属性最好都要进行初始化,例如 String name=””;
private String itemId="";//实验项目编号 private String itemName="";//实验项目名称 private String itemDesc="";//实验项目描述 private int itemState=0;//实验项目状态,注意实验项目状态是int型,默认是0,即有效 private String itemType="";//实验项目类别
4.在编写sql语句时,如果是拼接形成的,即使不是多表操作,习惯上还是用一个字母代替原表,并且在拼接时加上空格
// 取得应用信息的SQL语句
private StringBuffer _getItemSelectSQL(String where) {
StringBuffer strSQL = new StringBuffer();
//String sql="select t.item_id,t.item_name,t.item_state,t.item_type,t.item_desc from T_EXP_ITEM t order by t.item_id";
strSQL.append("select ");
strSQL.append("t.item_id");
strSQL.append(",t.item_name");
strSQL.append(",t.item_state");
strSQL.append(",t.item_type");
strSQL.append(",t.item_desc");
strSQL.append(" from T_EXP_ITEM t ");
if (!where.trim().equals("")) {
strSQL.append(where);
}
strSQL.append(" order by t.item_id");
System.out.println(strSQL.toString());
return strSQL;
}
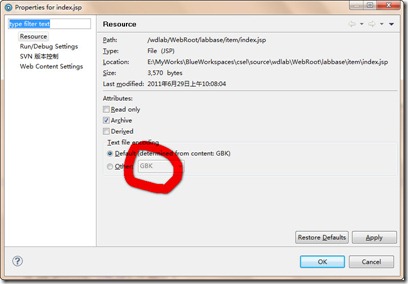
5.关于页面的编码形式,统一使用GBK编码,如果出现了乱码,要注意查看该jsp的property中的默认编码形式
页面的首部一般形式:
<%@page contentType="text/html; charset=gbk"%> <%@taglib uri="http://www.binarystar.com" prefix="BS"%>
property:
6.关于模式窗口:模式窗口是指该窗口打开着的时候还可以打开其他的窗口
7.关于搜索的实现:like只适用于搜索单个字段,但是如果是搜索多个字段,就要使用到concat
concat(lab_name,lab_desc) like
8.状态或者类别一般都是特定的几种,那么就可以在相应的Pojo(JavaBean)中定义一个静态的字符串数组
public static String[] ITEMSTATES={"有效","无效"};//实验项目状态是int,对应于这里的数组下标 public static String[] ITEMTYPES={"电路实验","实习项目"};
9.关于数据库操作:凡是涉及到数据库的连接的内容都要注意try-catch,同时注意资源的释放
错误语句:BSItemDBMang itemMang = new BSItemDBMang(new SqlExecute(), m_bs);
这里的 new SqlExecute() 可能抛出异常,并且 资源没有释放,会导致占用的资源越来越多,运行很慢!
详细实例:
BSItemDBMang itemMang = new BSItemDBMang(new SqlExecute(), m_bs); ArrayList<ItemPojo> itemList = itemMang.getItemList(""); this._setItemDataGrid(m_bs, itemList);
改成:
SqlExecute sqlHelper=new SqlExecute(); try { BSItemDBMang itemMang = new BSItemDBMang(sqlHelper, m_bs); ArrayList<ItemPojo> itemList = itemMang.getItemList(""); this._setItemDataGrid(m_bs, itemList); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw e; }finally{ sqlHelper.close(); }
10.关于rs游标:不要误以为rs刚开始时指向第一个记录
ArrayList<ItemPojo> itemList = new ArrayList<ItemPojo>(); StringBuffer strSQL = _getItemSelectSQL(where); CachedRowSet rs = this.sqlHelper.queryCachedBySql(strSQL.toString()); if (rs != null) { while (rs.next()) { itemList.add(this._setOneItemPojo(rs));//注意:re是游标,刚开始它是指向第一条数据的前面! } rs.close(); }