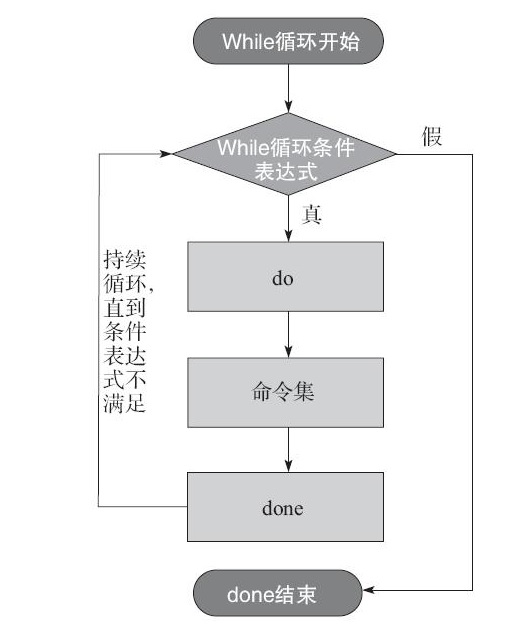
一、while语句介绍
while循环语句主要用来重复执行一组命令或语句,一直到条件不在满足为止,常用于守护进程或持续运行的程序。
二、while语句的语法格式
1、一般格式 while <条件表达式> #条件表达式为真则执行下面的命令集 do 命令集 done 2、死循环格式 while true do 命令集 done 3、按行读取相应的文件内容并处理 while read line do 命令集 done < path to file
四、until语句
until语句与while语句的用法相反,until是条件表达式为假及不成立则执行下面的命令集
until <条件表达式> #条件表达式不成立就这执行下面的命令集 do 命令集 done until循环语句的用法与while循环语句的用法类似,区别是until会在条件表达式不成立时,进入循环执行指令;条件表达式成立时,终止循环。
1、每2秒输出一个系统的负载
#! /bin/bash while true #每2秒输出1次,这里需要while的死循环 do uptime #系统的负载信息 sleep 2 #系统睡眠2秒 done
脚本测试
[root@node1 scripts]# bash while1.sh 04:46:30 up 20 days, 7:35, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 04:46:32 up 20 days, 7:35, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 04:46:34 up 20 days, 7:35, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 04:46:36 up 20 days, 7:35, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 ^C #每2秒输出一次系统负载,ctrl+c退出脚本
#! /bin/bash i=1 while ((i < 6)) #while [ $i -lt 6 ] do echo $i ((i++)) #每次打印完后,i自加1 done
[root@node1 scripts]# bash while2.sh 1 2 3 4 5
until语句
#! /bin/bash i=1 until ((i > 6)) #i < 6则执行下面的命令 do echo $i ((i++)) done
#! /bin/bash sum=0 i=1 while ((i < 101)) do ((sum=sum+i)) ((i++)) done echo sum=$sum
until语句
#! /bin/bash sum=0 i=1 until ((i > 101)) do ((sum=sum+i)) ((i++)) done echo sum=$sum
首先让系统随机生成一个数字,给这个数字设定一个范围(1~60),让用户输入所猜的数字。游戏规则是:对输入进行判断,如果不符合要求,就给予高或低的提示,猜对后则给出猜对所用的次数,请用while语句实现。
#! /bin/bash NUM1=$((RANDOM%61)) #对61取模,生成1~60的随机数 SUM=1 while true do read -p "Please input your number:" NUM2 expr $NUM2 + 1 &> /dev/null #判断输入的数字必须为正整数 if [ $? -ne 0 ];then echo "Plesae input your number (1~60)" continue fi if [ $NUM2 -lt 1 -o $NUM2 -gt 60 ];then #判断输入的必须是1~60的数字 echo "Plesae input your number (1~60)" continue fi if [ $NUM1 -lt $NUM2 ];then echo "Your number is bigger, please guess again" ((SUM++)) continue elif [ $NUM1 -gt $NUM2 ];then echo "Your number is smaller, please guess again" ((SUM++)) continue else echo "Congratulations on your guess" echo "your guess number is $NUM1,you total $SUM" exit 1 fi done
测试脚本
[root@node1 scripts]# sh while4.sh Please input your number:30 Your number is smaller, please guess again Please input your number:40 Your number is smaller, please guess again Please input your number:50 Your number is bigger, please guess again Please input your number:45 Your number is smaller, please guess again Please input your number:47 Your number is smaller, please guess again Please input your number:48 Congratulations on your guess your guess number is 48,you total 6
手机充值10元,每发一次短信(输出当前余额)花费1角5分钱,当余额低于1角5分钱时就不能再发短信了,提示“余额不足,请充值”(允许用户充值后继续发短信),请用while语句实现。 在解答之前,先进行单位换算,统一单位,让数字变成整数,即: 10元=1000分,1角5分=15分
#!/bin/sh export LANG="zh_CN.UTF-8" #<==指定中文字符集以防止乱码。 sum=15 #<==初始总费用为15。 msg_fee=15 #<==发一条短信需要15。 msg_count=0 #<==初始发送次数为0。 menu(){ #<==定义和用户交互的菜单。 echo "当前余额为$sum分,每条短信需要${msg_fee}分" cat <<END ========================== 1.充值 2.发消息 3.退出 ========================== END } recharge(){ #<==付费函数 read -p "请输入金额充值:" money #<==提示用户输入金额。 expr $money + 1 &>/dev/null #<==判断金额是否为整数。 if [ $? -ne 0 ] #<==如果返回值不为0,即不是整数,则打印提示输入整数。 then echo "then money your input is error,must be int." else #<==如果返回值为0,即表示金额为整数,则进行充值操作。 sum=$(($sum+$money)) #<==将金额加到总费用里。 echo "当前余额为:$sum" #<==打印充值后的金额。 fi } sendInfo(){ #<==定义发送短信的函数。 if [ $sum -lt ${msg_fee} ] #<==如果总费用小于15(单条短信的费用),则打印then后面的提示。 then printf "余额不足:$sum ,请充值。 " else #<==如果总费用大于15(单条短信的费用),则进入while循环。 while true #<==注意这里的条件为真。 do read -p "请输入短信内容(不能有空格):" msg #<==提示用户输入要发送的信息。 sum=$(($sum-${msg_fee})) #<==减掉短信的费用。 printf "Send "$msg" successfully! " #<==打印成功发送短信的提示。 printf "当前余额为:$sum " #<==打印当前余额。 if [ $sum -lt $msg_fee ] #<==如果总费用小于单条费用。 then printf "余额不足,剩余$sum分 " #<==则打印余额不足。 return 1 #<==跳出循环和函数。 fi done fi } main(){ #<==定义主函数。 while true #<==开始执行持续循环,条件始终为真,注意当条件始终为真时,就要想办法在循环里加入跳出循环的命令。 do menu #<==执行菜单函数。 read -p "请输入数字选择:" men #<==接收用户输入。 case "$men" in 1) #<==当用户的输入为1,表示想充值了,则加载recharge充值函数。 recharge ;; 2) #<==当用户的输入为2,表示想发消息了,则加载sendInfo函数。 sendInfo ;; 3) #<==当用户的输入为3,则表示想退出了。 exit 1 ;; *) #<==当用户的输入为其他值,给出正确的输入提示。 printf "选择错误,必须是{1|2|3} " esac done } main #<==最后执行主函数main。
#! /bin/bash #当脚本在执行过程中尝试使用未定义过的变量时,报错并退出运行整个脚本 set -u #当脚本中任何以一个命令执行返回的状态码不为0时就退出整个脚本 set -e #加载库文件 . /etc/init.d/functions #指定中文字符集以防止乱码。 export LANG="zh_CN.UTF-8" #使用root用户 if [ $(echo $UID) -ne 0 ];then echo "Please execute using root!!!" exit 1 fi #判断url个数 if [ $# -ne 1 ];then echo "Usage $0 url" exit 1 fi #使用while死循环来每10秒判断一次url是否正常 while true do wget -o /dev/null -T 3 --tries=1 --spider $1 if [ $? -ne 0 ];then action "URL:$1 is error!!! " /bin/false else action "URL:$1 is running!!!" /bin/true fi sleep 10 done
脚本测试
[root@node1 scripts]# sh while5.sh www.baidu.com URL:www.baidu.com is running!!! [ OK ] URL:www.baidu.com is running!!! [ OK ] URL:www.baidu.com is running!!! [ OK ] URL:www.baidu.com is running!!! [ OK ] URL:www.baidu.com is running!!! [ OK ] URL:www.baidu.com is running!!! [ OK ] ^C [root@node1 scripts]# sh while5.sh www.dfafasdfa.comasdf URL:www.dfafasdfa.comasdf is error!!! [FAILED] URL:www.dfafasdfa.comasdf is error!!! [FAILED]
#! /bin/bash if [ $(echo $UID) -ne 0 ];then echo "Please execute using root!!!" exit 1 fi if [ $# -ne 1 ];then echo "Usage $0 path_filename!!!" exit 1 fi if [ ! -f $1 ];then echo "file $1 is not exist!!!" exit 1 fi while read line do echo $line done<$1
脚本测试
[root@node1 scripts]# sh while7.sh Usage while7.sh path_filename!!! [root@node1 scripts]# sh while7.sh jasd file jasd is not exist!!! [root@node1 scripts]# sh while7.sh /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 [root@node1 scripts]# sh while7.sh /etc file /etc is not exist!!!
六、while总结
(1)While循环结构及相关语句总结
1、while循环的特长是执行守护进程,以及实现我们希望循环持续执行不退出的应用,适合用于频率小于1分钟的循环处理,其他的while循环几乎都可以被后面即将要讲到的for循环及定时任务crond功能所替代。 2、case语句可以用if语句来替换,而在系统启动脚本时传入少量固定规则字符串的情况下,多用case语句,其他普通判断多用if语句。 3、一句话场景下,if语句、for语句最常用,其次是while(守护进程)、case(服务启动脚本)。
(2)Shell脚本中各个语句的使用场景
1、条件表达式,用于简短的条件判断及输出(文件是否存在,字符串是否为空等) 2、if取值判断,多用于不同值数量较少的情况。 3、for最常用于正常的循环处理中。 4、while多用于守护进程、无限循环(要加sleep和usleep控制频率)场景。 5、case多用于服务启动脚本中,打印菜单可用select语句,不过很少见,一般用cat的here文档方法来替代。