目录:
1、驱动模块开发
编写驱动hello.c
编写Makefile
insmod加载KO模块
lsmod查看系统加载的模块
rmmod卸载模块
2、模块ko参数传递
3、ko模块符号导出
新建math.c math.h
修改Makefile
hello.c
调用模块符号
1、驱动模块开发
驱动代码需要有四个部分 1.头文件 2.驱动模块装载和卸载函数入口声明 3.实现模块装载和卸载函数入口 4.GPL声明
1) 编写hello.c
/* 驱动代码需要有四个部分 1.头文件 2.驱动模块装载和卸载函数入口声明 3.实现模块装载和卸载函数入口 4.GPL声明 */ //头文件 #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> //实现模块装载和卸载函数入口 static int __init hello_drv_init(void) { //向系统申请资源 printk("-----------%s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); return 0; } static void __exit hello_drv_exit(void) { //释放资源 printk("-----------%s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); } //驱动模块装载和卸载函数入口声明 module_init(hello_drv_init); module_exit(hello_drv_exit); //GPL声明 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
2)编写Makefile
1 ROOTFS_DIR = /home/linux/source/rootfs#根文件系统路径 2 3 ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) 4 5 KERNEL_DIR = /home/linux/kernel/linux-3.14-fs4412 #编译过的内核源码的路径 6 CUR_DIR = $(shell pwd) #当前路径 7 8 all: 9 make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) modules #把当前路径编成modules 10 @#make -C 进入到内核路径 11 @#M 指定当前路径(模块位置) 12 13 clean: 14 make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) clean 15 16 install: 17 sudo cp -raf *.ko $(ROOTFS_DIR)/drv_module #把当前的所有.ko文件考到根文件系统的drv_module目录 18 19 else 20 21 obj-m += hello.o #指定内核要把哪个文件编译成ko 22 23 endif
看一下Makefile:
当我们make的时候会进入Makefile。
第1行,指定ROOTFS_DIR的路径
第3行,判断语句,判断后面括号里逗号两侧的目标是否相等,$(KERNELRELEASE)是内核目录下Makefile定义的一个宏,无实际意义,由于还没进入内核,故这个宏为空,故条件为真。执行下面的语句,执行到all:规则时,又进行了一次make,这一次进入了内核目录下的Makefile,同时给$(KERNELRELEASE)赋值,还指定了要去那个目录下编译模块,但是万一这个目录下有很多c文件,内核怎么知道把哪个文件编译成内核呢?由此内核会根据路径由回到当下的这个Makefile,读取信息,从第一行开始,此时条件语句不成立,执行else后的语句obj-m += hello.o,得知是把当前路径下的对应hello.o的C文件编译成ko文件
all: make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CPU_DIR) modules --> make -C /home/linux/kernel/linux-3.14-fs4412 M=pwq modules //进入到内核目录下的Makefile 将当前目录下的驱动编译为模块 //但是内核又怎么知道编译哪个c文件呢?
由此可知Makefile会被读两次
- 第一次是make的时候,这时候主要读取的路径
- 第二次是内核源码编译的时候,这时候,内核源码要知道要把该路径下哪个文件编译成ko
以后使用Makefile时,修改相应的内核路径和源码路径即可。
(注:内核源码要先编译)
make之后,可以看到生成的相应ko文件,在make install,将ko文件复制到根文件系统下;
3)insmod 加载ko模块
加载模块后可以看到模块转载函数打印出相关信息:
[root@farsight drv_module]# insmod hello.ko
[ 34.280000] -----------hello_drv_init-----------
4)lsmod 查看当前模块
[root@farsight drv_module]# lsmod
hello 809 0 - Live 0xbf000000 (O)
5)rmmod卸载驱动(不要加ko)
[root@farsight drv_module]# rmmod hello
[ 228.895000] -----------hello_drv_exit-----------
2、模块ko参数传递
1)加载模块时insmod hello.ko myname="guoguo" myvalue=22 ,参数会传递给模块内部
实例:
wifi驱动: wifi硬件中内部也运行内部代码,原厂开发,这些代码叫做固件--firmware.bin 装载wifi驱动时,必须告诉固件文件在哪里 insmod rtxxx.ko path=/lib/modules/firmware/xxx.bin
2)在代码中如何处理参数
module_param(name, type, perm) //参数1:表示参数到名字,比如myname, myvalue //参数2:参数到类型, charp, int //参数3: /sys/modules/表示文件到权限: 0666
3)用法
module_param(myvalue, int, 0666); module_param(myname, charp, S_IRUGO|S_IWUGO|S_IXUGO);
传参(当驱动内部已经定义了参数后,优先使用外部传入的参数)
4)测试
修改代码:
1 /* 2 驱动代码需要有四个部分 3 1.头文件 4 2.驱动模块装载和卸载函数入口声明 5 3.实现模块装载和卸载函数入口 6 4.GPL声明 7 */ 8 #include <linux/init.h> 9 #include <linux/module.h> 10 11 static int myvalue = 56; 12 static char *myname = "jack"; 13 14 //实现模块装载和卸载函数入口 15 static int __init hello_drv_init(void) 16 { 17 //一般做系统申请资源 18 printk("-----------%s----------- ", __FUNCTION__); //打印函数名 19 printk("name = %s, value = %d ", myname, myvalue); 20 return 0; 21 } 22 23 static void __exit hello_drv_exit(void) 24 { 25 //一般做系统释放资源 26 printk("-----------%s----------- ", __FUNCTION__); 27 } 28 29 //驱动模块装载和卸载函数入口声明 30 module_init(hello_drv_init); 31 module_exit(hello_drv_exit); 32 33 module_param(myvalue, int, 0644); 34 module_param(myname, charp, S_IRUGO|S_IWUSR); 35 36 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
板上运行:
使用默认参数:

传入参数:

3、module符号导出
(部分参考:linux驱动开发之module导出符号)
驱动开发中,module 是基本的组成,在一个模块中定义的函数,如果想在另一个模块中进行调用,这个时候,就需要进行导出,称为导出符号。
用法:
所要导出的符号,是在一个模块中,也需要使用 modlue_init 和 module_exit 进行修饰这模块的入口函数。在需要导出符号的地方,使用 EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL() 或EXPORT_SYMBOL() 将函数导出。在需要调用的地方,使用 extern 进行声明需要的函数。
下面以实例分析:hello模块调用math模块中的运算函数

1 /* 2 驱动代码需要有四个部分 3 1.头文件 4 2.驱动模块装载和卸载函数入口声明 5 3.实现模块装载和卸载函数入口 6 4.GPL声明 7 */ 8 9 #include <linux/init.h> 10 #include <linux/module.h> 11 #include <linux/stat.h> 12 13 #include "math.h" 14 15 static int myvalue = 56; 16 static char *myname = "jack"; 17 18 //实现模块装载和卸载函数入口 19 static int __init hello_drv_init(void) 20 { 21 //一般做系统申请资源 22 printk("-----------%s----------- ", __FUNCTION__); //打印函数名 23 printk("name = %s, value = %d ", myname, myvalue); 24 printk("a+b = %d, a-b = %d ", my_add(8,2), my_sub(1,10)); //调用math.c中的函数 25 26 return 0; 27 } 28 29 static void __exit hello_drv_exit(void) 30 { 31 //一般做系统释放资源 32 printk("-----------%s----------- ", __FUNCTION__); 33 } 34 35 //驱动模块装载和卸载函数入口声明 36 module_init(hello_drv_init); 37 module_exit(hello_drv_exit); 38 39 module_param(myvalue, int, 0644); 40 module_param(myname, charp, S_IRUGO|S_IWUSR); 41 42 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");

1 #include <linux/module.h> 2 #include <linux/init.h> 3 4 //不需要模块的装载与卸载的入口声明 5 //直接定义好封装的函数 6 7 int my_add(int a, int b) 8 { 9 return a+b; 10 } 11 12 EXPORT_SYMBOL(my_add); 13 14 int my_sub(int a, int b) 15 { 16 return a-b; 17 } 18 19 EXPORT_SYMBOL(my_sub); 20 21 22 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");

1 #ifndef __MATH_H__ 2 #define __MAHT_H__ 3 4 int my_add(int a, int b); 5 int my_sub(int a, int b); 6 7 #endif

1 ROOTFS_DIR = /home/linux/source/rootfs#根文件系统路径 2 3 ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) 4 5 KERNEL_DIR = /home/linux/kernel/linux-3.14-fs4412 #编译过的内核源码的路径 6 CUR_DIR = $(shell pwd) #当前路径 7 8 all: 9 make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) modules #把当前路径编成modules 10 @#make -C 进入到内核路径 11 @#M 指定当前路径(模块位置) 12 13 clean: 14 make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) clean 15 16 install: 17 sudo cp -raf *.ko $(ROOTFS_DIR)/drv_module #把当前的所有.ko文件考到根文件系统的drv_module目录 18 19 else 20 21 obj-m += hello.o #指定内核要把哪个文件编译成ko 22 obj-m += math.o 23 24 endif
math.c也要作为模块编译,在Makefile也要添加math。
注意:
在编译时,导出模块先编译,使用者后编译;
在加载时,导出模块先加载,使用者后加载;
在卸载时,使用者先卸载,导出模块后卸载;
若先装载使用模块,则报错:
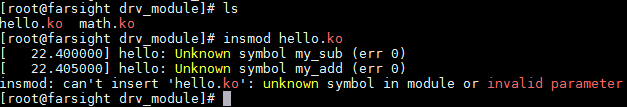
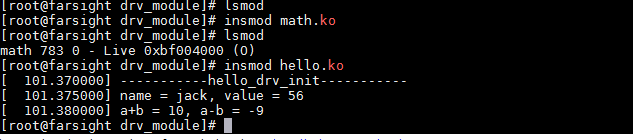
应先加载导出模块:
若先卸载导出模块,报错如下:

