1.导入context约束:spring-context-4.2.xsd
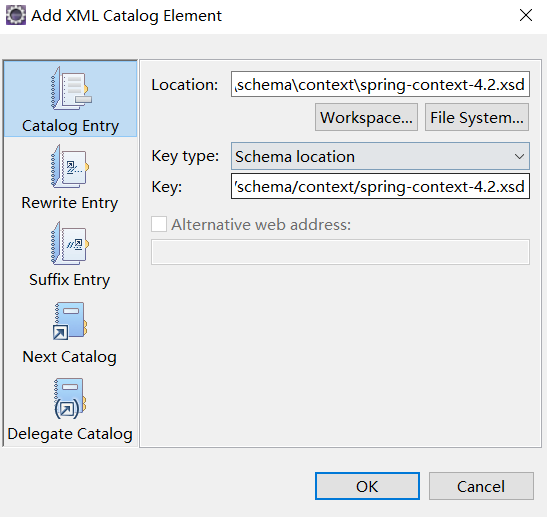
2.design模式打开xml配置文件,右键edit namespaces,点击add添加

完成后应该是这样:
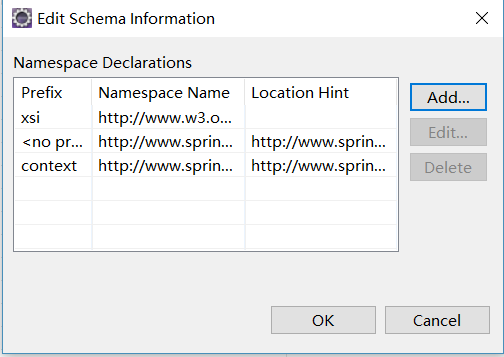
配置文件中这样写即可:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd "> <context:component-scan base-package="bean"></context:component-scan> </beans>
在类中这样使用注解:
package bean; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.junit.validator.PublicClassValidator; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; //代替的配置文件内容<bean name="user" class="bean.User"/> // @Component("user")//四种本质相同,为了方便理解建议使用以下三种 // @Service("user")//service层使用 // @Controller("user")//web层使用 @Repository("user")//dao层使用 //指定对象的作用范围 @Scope(scopeName="singleton") public class User { @Value("Tom")//赋值 private String name; private Integer age; //@Autowired//对象赋值,自动装配 //存在问题:如果是多个类型一致的对象,无法分辨 @Resource(name="car")//这种方式可以明确指定(推荐) private Car car; public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } @Value("20")//也可以在set方法赋值,效果一样,但不破坏封装性 public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", car=" + car + "]"; } @PostConstruct//初始化方法,当相于配置文件中的init-mothod public void init(){ System.out.println("初始化"); } @PreDestroy//销毁方法 public void destory(){ System.out.println("销毁"); } }
Car类:
package bean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("car") public class Car { @Value("car2") private String name; private String color; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car [name=" + name + ", color=" + color + "]"; } }
测试可以写成以前的测试类,如果安装了STS插件,就可以这样:
package annotation; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import bean.User; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="user") private User u; @Test public void fun1(){ System.out.println(u); } }