shell脚本中也可以实现逻辑判断。
案例4:shell脚本中的逻辑判断
如果你学过C或者其他语言,相信你不会对if 陌生,在shell脚本中我们同样可以使用if逻辑判断。在shell中if判断的基本语法为:
1)不带else
if 判断语句; then
command
fi
#! /bin/bash
## author:Xiong Xuehao
## Use if in this script.
read -p "Please input a number: " a
if ((a<60));then
echo "you didn't pass this test"
fi
在if1.sh中出现了 ((a<60))这样的形式,这是shell脚本中特有的格式,用一个小括号或者不用都会报错,请记住这个格式,即可。执行结果为:
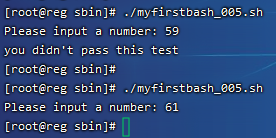
2)带有else
if 判断语句 ; then
command
else
command
fi
#! /bin/bash
## author:Xiong Xuehao
## Use if in this script.
read -p "Please input a number: " a
if ((a<60));then
echo "you didn't pass this test"
else
echo "you pass this test"
fi
执行结果为:
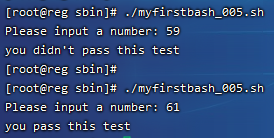
3)带有elif
if 判断语句一 ; then
command
elif 判断语句二; then
command
else
command
fi
#! /bin/bash
## author:Xiong Xuehao
## Use if in this script.
read -p "Please input a number: " a
if ((a<60));then
echo "you didn't pass this test"
elif ((a>=60)) && ((a<85));then
echo "you pass this test"
else
echo "Verry Good!"
fi
这里的 && 表示“并且”的意思,当然你也可以使用 || 表示“或者”,执行结果:
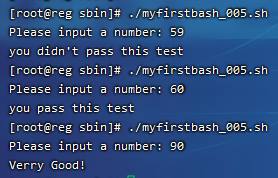
以上只是简单的介绍了if语句的结构。在判断数值大小除了可以用”(( ))”的形式外,还可以使用”[ ]” 注意方括号里面需要有空格。但是就不能使用>, < , = 这样的符号了,要使用 -lt (小于),-gt (大于),-le (小于等于),-ge (大于等于),-eq (等于),-ne (不等于)。
#! /bin/bash
## author:Xiong Xuehao
## Use if in this script.
read -p "Please input a number: " a
if [ $a -lt 60 ];then
echo "$a lt than 60";
elif [ $a -ge 60 ] && [ $a -lt 85 ];then
echo "you pass this test"
elif [ $a -eq 100 ];then
echo "$a eq than 100. Very Good!"
elif [ $a -ne 0 ];then
echo "$a ne than 100. Your Input error!"
elif [ $a -gt 100 ];then
echo "$a gt than 100. Your Input error!"
else
echo "Your Input error!"
fi
运行结果如图:

案例5:shell脚本中判断档案属性
shell 脚本中if还经常判断关于档案属性,比如判断是普通文件还是目录,判断文件是否有读写执行权限等。常用的也就几个选项:
-e :判断文件或目录是否存在
-d :判断是不是目录,并是否存在
-f :判断是否是普通文件,并存在
-r :判断文档是否有读权限
-w :判断是否有写权限
-x :判断是否可执行
使用if判断时,具体格式为: if [ -e filename ] ; then
#! /bin/bash
## author:Xiong Xuehao
## File properties.
read -p "Please input a file or directory: " a
###判断文件或目录是否存在
if [ -e $a ];then
echo "$a The file or directory already exists."
else
echo "$a The file or directory does not exist!"
fi
###判断文件或目录
if [ -d $a ];then
echo "$a The path is a directory and already exists."
elif [ -f $a ];then
echo "$a The path is a file and already exists."
else
echo "$a I don't know!"
fi
###判断权限
if [ -r $a ];then
echo "$a The document has read permission."
else
echo "$a The document does not have read permission!"
fi
if [ -w $a ];then
echo "$a The document has write permission."
else
echo "$a The document does not have write permission!"
fi
if [ -x $a ];then
echo "$a The document has execution permission."
else
echo "$a The document does not have execution permission!"
fi
执行如图:

案例6:shell脚本中用case逻辑判断
在shell 脚本中,除了用if来判断逻辑外,还有一种常用的方式,那就是case了。具体格式为:
case 变量 in
value1)
command
;;
value2)
command
;;
value3)
command
;;
*)
command
;;
esac
上面的结构中,不限制value的个数,*则代表除了上面的value外的其他值。下面笔者写一个判断输入数值是奇数或者偶数的脚本。
#! /bin/bash
## author:Xiong Xuehao
## Use case in this script.
read -p "Please input a number: " n
###判断奇数或者偶数
a=$[$n % 2]
case $a in
1)
echo "The remainder is $a. $n The num is odd."
;;
0)
echo "The remainder is $a. $n The num is even."
;;
esac
输入任意一个自然数,除以2得余数 $a 的值或为1或为0,执行结果为:

case脚本常用于编写系统服务的启动脚本,例如/etc/init.d/iptables中就用到了,不妨去查看一下。