1017. StaircasesTime limit: 1.0 second
Memory limit: 64 MB One curious child has a set of N little bricks (5 ≤ N ≤ 500). From these bricks he builds different staircases. Staircase consists of steps of different sizes in a strictly descending order. It is not allowed for staircase to have steps equal sizes. Every staircase consists of at least two steps and each step contains at least one brick. Picture gives examples of staircase for N=11 andN=5:
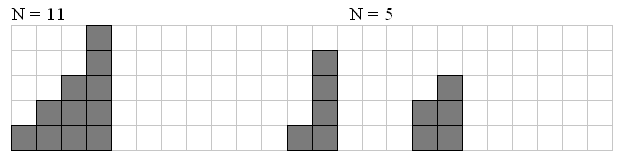 Your task is to write a program that reads the number N and writes the only number Q — amount of different staircases that can be built from exactly N bricks.
InputNumber N
OutputNumber Q
Sample
|
题目的意思就是给你N块砖,如何构造布同的摆放方式。(动态规划)
决策变量: dp[N][k] 表示N块砖,最后一个楼梯的高度为k
状态转移方程:dp[N][k] = dp[N-1][k-1] + dp[N-k][k-1];
为什么会构造如此的状态转移方程??可以递推的去想象dp[N][k]这个状态是怎么从前一个状态来的,
最后一个楼梯的高度为k,有两种来源:在原有楼梯上加和增加新楼梯
1). 直接在上次最后一个楼梯上面加一块(有人可能会疑问为什么不能再最后一个楼梯上加2,3,.....块,如果在最后一个楼梯加两块变成k,这就变成了在N-K块砖组成的楼梯后面加一个高度为k的楼梯,与下面重复)
2).直接在最后一个楼梯后面加一个高度为k的楼梯
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAX 502
using namespace std;
long long dp[MAX][MAX]={0};
int main(){
int N;
cin >>N;
dp[1][1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= N; i ++ ){
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j ++){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-j][j-1];
}
}
long long ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i != N; i ++ ) ans += dp[N][i];
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}