1异常的定义
异常就是与我们编译相违背在过程中出现的逻辑或忘记一些赋值等等
分为编译时错误和运行时错误
运行时异常

我们一般处理的时Exception异常;
异常处理
异常处理可以通过关键字try,catch,finally,throw,throws;
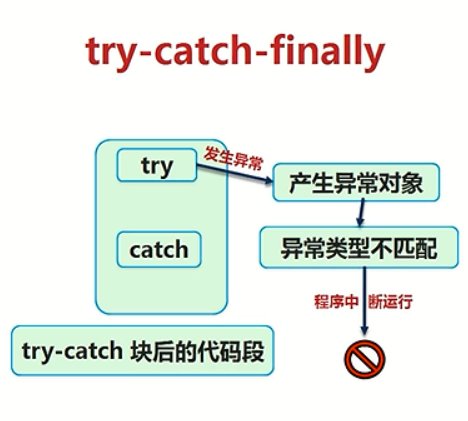
try,catch,finally处理 捕获异常
try捕获异常,通常把try放在我们觉得出错的位置;
catch 捕获异常,当异常出现时,被catch捕获通过Exception方法来提示异常(通常从异常最后一行开始处理异常);
finally
无论前面出现什么都会直接下面语句;
package com.jiedada.exception; import java.util.Scanner; public class Frist { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int x=0,y=0; System.out.println("=============运行开始========="); Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); try { System.out.println("请输入分子"); x=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入分母"); y=sc.nextInt(); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("================程序结束========="); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("该算术表达式结果为"+(x/y)); } } }
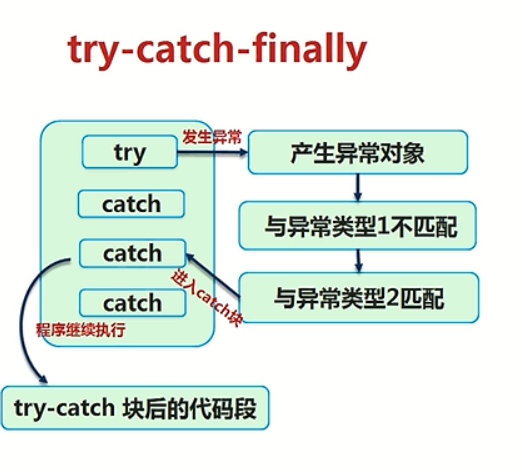
catch可以使用多个子类的方法来判断属于那种类型的错误如ArithmeticException(算术表达式的错误)
在多个cat表达式中最后一个catch中最好或者一定要包含一个Exception的子方法表达式这样才能检查所有错误;
InputMismatchException(判断输入的类型不是不错的

package com.jiedada.exception; import java.util.InputMismatchException; import java.util.Scanner; public class Frist { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int x=0,y=0; System.out.println("=============运行开始========="); Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); try { System.out.println("请输入分子"); x=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入分母"); y=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("该算术表达式结果为"+(x/y)); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("除数不能为0,请重新输入"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch(InputMismatchException e) { System.out.println("请输入整数"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("出错啦---"); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("================程序结束========="); } } }
Sysout.exit(非0数)终止程序运行
return在这个结构中的使用:因为finally的存在,不管怎么都会执行finally中的语句所以
return写在finally中都只会返回finally中的return;
throws声明异常
是抛出异常,通过在方法后面添加throws和 错误信息提示如Exception,ArithmeticException;

是通过调用该方法的实列通过try catch finally来执行
可以通过文档注释对异常进行说明;

package com.jiedada.exception; import java.util.Scanner; public class Three { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { int result=test(); System.out.println(result); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block System.out.println("除数不能为0"); e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 该方法是除法的运算 * @return 该算术的商 * @throws ArithmeticException */ public static int test()throws ArithmeticException{ int x=0,y=0; System.out.println("=============运行开始========="); Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入分子"); x=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入分母"); y=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("================程序结束========="); return x/y; } }
throw处理抛出异常;
第一种方法:throw也是一种抛出异常结构为通过try catch在try中写入throw new 异常类型();
第二种方法:和throws差不太多,通过在代码中写入throw new 异常类型()[建议不要抛出非检查异常如,ArithmeticException]
通过在方法后面添加throws和 错误信息提示如Exception;谁调用谁就通过try catch异常处理;
在Exception中有输入字符串的方法如下:
在第二种中throw new 异常类型()通过在方法后面添加throws后面的异常处理必须要比throw中的大,如


package com.jiedada.exception; import java.util.Scanner; public class Four { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { testAge(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } /*public static void testAge() { System.out.println("请输入入住者的年龄"); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); int age=input.nextInt(); if(age<18||age>80) { try { throw new Exception("18岁以下,80岁以上的人需要家人的陪同入住"); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }else { System.out.println("欢迎入住"); }*/ public static void testAge() throws Exception { System.out.println("请输入入住者的年龄"); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); int age=input.nextInt(); if(age<18||age>80) { throw new Exception("18岁以下,80岁以上的人需要家人的陪同入住"); }else { System.out.println("欢迎入住"); } } }
自定义异常
当需要反复使用一些异常时我们可以自己定义:先创建一个异常继承Eception类,然后和Exception的方法相同。
在创建类的时候我们和其他的类一样需要创建构造类;
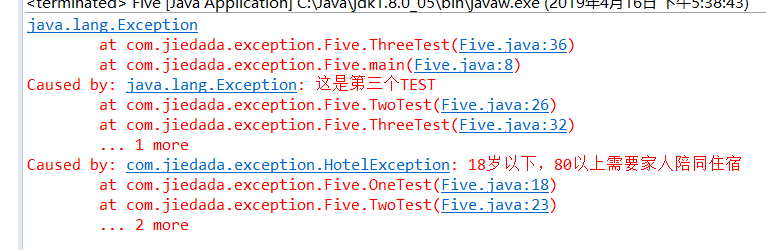
异常链
多个throw的向上抛出产生的异常问腿


package com.jiedada.exception; public class Five { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { ThreeTest(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void OneTest() throws HotelException { throw new HotelException(); } public static void TwoTest() throws Exception { try { OneTest(); }catch(HotelException e) { throw new Exception("这是第三个TEST",e); } } public static void ThreeTest() throws Exception { try { TwoTest(); }catch(Exception e2) { //throw new Exception("这是第三个TEST"); Exception e1=new Exception(); e1.initCause(e2); throw e1; } } }
总结

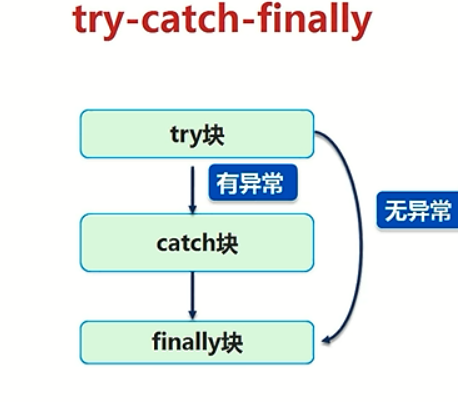
保证能够正常执行当加入System.exit(非0数字)会终端;在该语句中return只会在执行了finally后才会返回值;


当子类继承父类的抛出方法是,子类只能抛出父类抛出方法的子类或者同类
