Android消息处理的大致的原理如下:
1.有一个消息队列,可以往队列中添加消息
2.有一个消息循环,可以从消息队列中取出消息
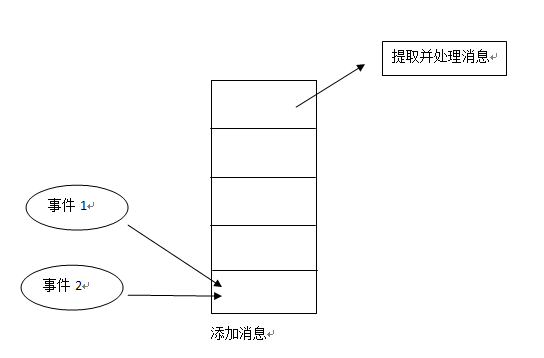
Android系统中这些工作主要由Looper和Handler两个类来实现:
Looper类: 有一个消息队列,封装消息循环
Handler类: 消息的投递、消息的处理
Looper类:
Looper的使用需先调用 Looper.prepare(),然后调用Looper.loop()开启消息循环。
1 public static void prepare() { 2 prepare(true); 3 } 4 5 private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { 6 if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { 7 throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); 8 } 9 sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); 10 }
static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();
prepare会在调用线程的局部变量中设置一个Looper对象;
ThreadLocal是java中线程局部变量类,有两个关键函数:
set: 设置调用线程的局部变量
get: 获取调用线程的局部变量
Looper的构造函数:
1 private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) { 2 mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed); 3 mThread = Thread.currentThread(); 4 }
创建了一个消息队列,用于存放消息。
Looper.loop(), myLooper()通过ThreadLocal对象获取了prepare时创建的Looper对象。loop里面是一个循环,循环从MessageQueue中取消息,然后通过Handler去处理。
(msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); target是一个Handler对象,后面会提到)
1 public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() { 2 return sThreadLocal.get(); 3 } 4 5 public static void loop() { 6 final Looper me = myLooper(); 7 if (me == null) { 8 throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread."); 9 } 10 final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; 11 12 // Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process, 13 // and keep track of what that identity token actually is. 14 Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); 15 final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); 16 17 for (;;) { 18 Message msg = queue.next(); // might block 可能会阻塞 19 if (msg == null) { 20 // No message indicates that the message queue is quitting. 21 return; 22 } 23 24 // This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger 25 Printer logging = me.mLogging; 26 if (logging != null) { 27 logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " + 28 msg.callback + ": " + msg.what); 29 } 30 31 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); 32 33 if (logging != null) { 34 logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback); 35 } 36 37 // Make sure that during the course of dispatching the 38 // identity of the thread wasn't corrupted. 39 final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); 40 if (ident != newIdent) { 41 Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x" 42 + Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x" 43 + Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to " 44 + msg.target.getClass().getName() + " " 45 + msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what); 46 } 47 48 msg.recycleUnchecked(); 49 } 50 }
Looper的作用:
-
封装一个消息队列
-
prepare()方法把Looper对象和调用的线程绑定起来
-
通过loop()方法处理消息队列中的消息
Hander类:
Handler有多个构造函数,常用的就下面几个:
1 public Handler() { 2 this(null, false); 3 } 4 5 public Handler(Looper looper) { 6 this(looper, null, false); 7 } 8 9 public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) { 10 mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); 11 if (mLooper == null) { 12 throw new RuntimeException( 13 "Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()"); 14 } 15 mQueue = mLooper.mQueue; 16 mCallback = callback; 17 mAsynchronous = async; 18 } 19 20 public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) { 21 mLooper = looper; 22 mQueue = looper.mQueue; 23 mCallback = callback; 24 mAsynchronous = async; 25 }
无参构造函数,通过Looper.myLooper()获取调用线程的Looper对象; Handler提供了一个Callback的接口,参数里面的Callback在处理消息的时候会用到,如果设置了全局Callback,消息会通过这个Callback处理,如果未设置,则需重重载handlerMessage()方法来处理消息。
1 public interface Callback { 2 public boolean handleMessage(Message msg); 3 }
(1) Handler和Message ----> Handler把Message插入Looper的消息队列。
Handler有一系列的处理消息的函数,比如:
1 public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg) 2 { 3 return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0); 4 } 5 6 public final boolean sendEmptyMessage(int what) 7 { 8 return sendEmptyMessageDelayed(what, 0); 9 } 10 11 public final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) { 12 Message msg = Message.obtain(); 13 msg.what = what; 14 return sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis); 15 } 16 17 public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis) 18 { 19 if (delayMillis < 0) { 20 delayMillis = 0; 21 } 22 return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis); 23 } 24 25 public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { 26 MessageQueue queue = mQueue; 27 if (queue == null) { 28 RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( 29 this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); 30 Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); 31 return false; 32 } 33 return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis); 34 } 35 36 public final boolean sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(Message msg) { 37 MessageQueue queue = mQueue; 38 if (queue == null) { 39 RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( 40 this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); 41 Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); 42 return false; 43 } 44 return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, 0); 45 }
这些都是将消息插入到Looper的消息队列,sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue()是将消息插入到消息队列的队列头,所以优先级很高。所有方法最后都是通过enqueueMessage()方法插入消息。
1 private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { 2 msg.target = this; 3 if (mAsynchronous) { 4 msg.setAsynchronous(true); 5 } 6 return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis); 7 }
msg.target = this,前面有提到,target是Handler对象,消息的处理最后都需通过这个。
(2)Handler的消息处理
上面的Looper.loop()方法中,不断从消息队列中提取消息,然后通过Handler的dispatchMessage()方法处理消息。
1 public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) { 2 if (msg.callback != null) { 3 handleCallback(msg); 4 } else { 5 if (mCallback != null) { 6 if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) { 7 return; 8 } 9 } 10 handleMessage(msg); 11 } 12 }
如果Message设置了callback,则通过这个callback处理,如果Message没设置callback则先通过全局callback来处理,如果都没设置,则通过handlerMessage()方法来处理。
简单总结一下:
Looper中有一个MessageQueue,里面存储一个个待处理的Message。
Message中有一个Handler,这个Handler处理Message。
转载还望注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaojianli/p/5642380.html