在写一个webservice的时候,方法的返回值是一个复杂类型,处理方法是写一个结果类(Javabean)作为返回值。想着webservice方法返回值为Map的没写过,然后就试着写了一个简单的Demo。出错了...那我就来劲了,总有办法解决吧....

通过百度(你有Google癖好就用Google吧)。。找到方法,通过前辈们的经验找到解决方法。
业内人士都懂!注重版权,奉上原文链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/jspamd/article/details/8914427
贴上自个Demo代码之前,补充个知识点,webservice中发布方法的参数以及返回值可以很好的处理基本类型,POJO类,数组,以及list集合等复杂类型,但是在处理Map,非JavaBean式的类,我们需要自定义一个转换器,负责将webservice中不能处理的类型转换为可以处理的类型
(1)需要使用注解@XmlJavaTypeAdapter修饰返回类型
1 @WebService 2 public interface HelloService { 3 public String sayHello(String name); 4 public String sayGoodBy(String name); 5 public String sayHello2(String name); 6 7 public @XmlJavaTypeAdapter((XmlMapAdapter.class)) Map<String, String> getSpace(String name); 8 }
(2)自定义一个可以替代不可处理参数类型的类(可以理解为模拟Map接口的类,这个类是POJO)
1 public class MyStringMap { 2 private List<Entry> entries; 3 4 /** 5 * @return entries 6 */ 7 public List<Entry> getEntries() { 8 return entries; 9 } 10 11 /** 12 * @param entries the entries to set 13 */ 14 public void setEntries(List<Entry> entries) { 15 this.entries = entries; 16 } 17 18 public static class Entry { 19 private String key; 20 private String value; 21 /** 22 * @return key 23 */ 24 public String getKey() { 25 return key; 26 } 27 /** 28 * @param key the key to set 29 */ 30 public void setKey(String key) { 31 this.key = key; 32 } 33 /** 34 * @return value 35 */ 36 public String getValue() { 37 return value; 38 } 39 /** 40 * @param value the value to set 41 */ 42 public void setValue(String value) { 43 this.value = value; 44 } 45 46 } 47 }
(3)自定义一个转换器(作为@XmlJavaTypeAdapter注解中value)
1 public class XmlMapAdapter extends XmlAdapter<MyStringMap, Map<String, String>>{ 2 @Override 3 //Map(不可处理)转换为可处理的类(自定义的POJO类,就是模拟Map的一个类) 4 public MyStringMap marshal(Map<String, String> v) throws Exception { 5 MyStringMap result = new MyStringMap(); 6 List<pojo.MyStringMap.Entry> entries = new ArrayList<MyStringMap.Entry>(); 7 for(Entry<String, String> e : v.entrySet()){ 8 pojo.MyStringMap.Entry entry = new pojo.MyStringMap.Entry(); 9 entry.setKey(e.getKey()); 10 entry.setValue(e.getValue()); 11 entries.add(entry); 12 } 13 result.setEntries(entries); 14 return result; 15 16 } 17 //自定义可处理类转换为Map(不可处理的类型) 18 @Override 19 public Map<String, String> unmarshal(MyStringMap v) throws Exception { 20 Map<String, String> result = new HashMap<String, String>(); 21 for(pojo.MyStringMap.Entry e : v.getEntries()){ 22 result.put(e.getKey(), e.getValue()); 23 } 24 return result; 25 } 26 }
(4)接口的实现类
1 @WebService(endpointInterface="com.webservice.HelloService",serviceName="MyService",targetNamespace="http://www.baidu.com") 2 public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService { 3 4 @WebMethod(operationName="AliassayHello") 5 @WebResult(name="myReturn") 6 @Override 7 public String sayHello(@WebParam(name="name")String name) { 8 System.out.println("Hello,"+name); 9 return "Hello,"+name; 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 public String sayGoodBy(@WebParam(name="name")String name) { 14 System.out.println("GoodBy,"+name); 15 return "GoodBy,"+name; 16 } 17 18 @WebMethod(exclude=true)//不会被发布出去 19 @Override 20 public String sayHello2(String name) { 21 System.out.println("hello2"+ name); 22 return "Hello2,"+name; 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 public Map<String, String> getSpace(String name) { 27 HashMap<String, String> resultMap = new HashMap<String,String>(); 28 29 resultMap.put("age", "12"); 30 resultMap.put("name", name); 31 resultMap.put("orid", "123123"); 32 resultMap.put("address", "北京"); 33 34 System.out.println(resultMap); 35 return resultMap; 36 } 37 38 public static void main(String[] args) { 39 Endpoint.publish("http://127.0.0.1:8099/hello", new HelloServiceImpl()); 40 System.out.println("服务发布成功!"); 41 } 42 43 }
剩下的就是测试工作,这里就没写客户端程序去测试了,使用SoapUI测试下
soap请求消息:
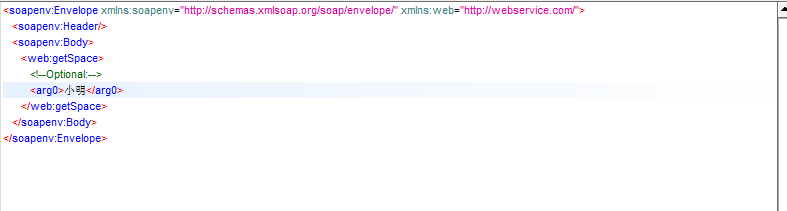
soap响应
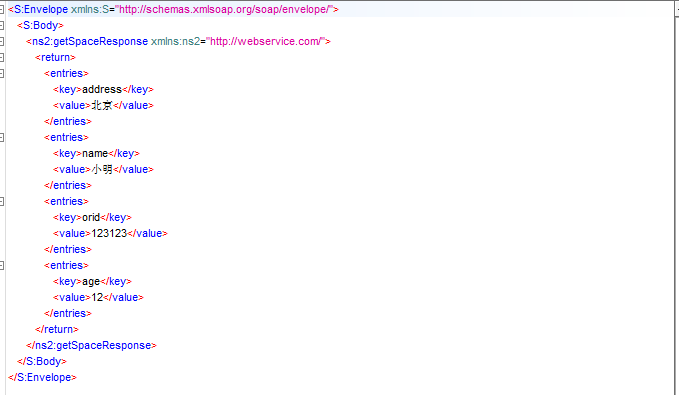
个人理解webservice中的转换器的思想机制和struts2 中的类型转换机制是一个样的。
朋友,看我这么帅,点个赞呗