一 题目:合并两个排序的链表
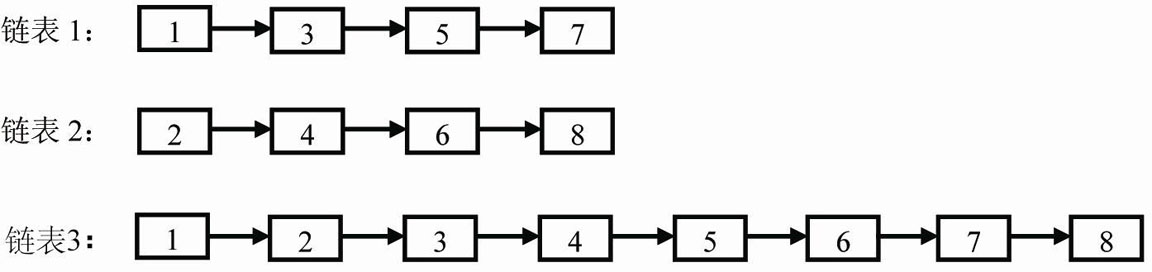
题目:输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的结点仍然是按照递增排序的。例如输入下图中的链表1和链表2,则合并之后的升序链表如链表3所示。
二 代码实现
template <typename T> struct Node { public: T data; Node *pNext; }; template <typename T> class ListEx { private: Node<T> *m_pHead; Node<T> *m_pTail; public: ListEx() { m_pTail = m_pHead = NULL; } ~ListEx() { Node<T> *pTemp = NULL; Node<T> *pNode = m_pHead; while (pNode) { pTemp = pNode; pNode = pNode->pNext; delete pTemp; } m_pHead = m_pTail = NULL; } void add(T data) { Node<T> *pNode = new Node<T>; pNode->data = data; pNode->pNext = NULL; if (m_pHead == NULL) { m_pTail = m_pHead = pNode; } Node<T>* pTemp = m_pTail; pTemp->pNext = pNode; m_pTail = pNode; } Node<T> *GetListHead() { return m_pHead; } }; template <typename T> Node<T>* RebuildArray(Node<T>* pNode1, Node<T>* pNode2) { if (NULL == pNode1) { return pNode2; } else if (NULL == pNode2) { return pNode1; } Node<T>* pNewNode = new Node<T>; pNewNode = NULL; if (pNode1->data <= pNode2->data) { pNewNode = pNode1; pNewNode->pNext = RebuildArray(pNode1->pNext, pNode2); } else { pNewNode = pNode2; pNewNode->pNext = RebuildArray(pNode1, pNode2->pNext); } return pNewNode; } void main() { ListEx<int> *pList1= new ListEx<int>(); pList1->add(1); pList1->add(3); pList1->add(5); pList1->add(7); Node<int> *pHead1 = pList1->GetListHead(); ListEx<int> *pList2= new ListEx<int>(); pList2->add(2); pList2->add(4); pList2->add(6); pList2->add(8); Node<int> *pHead2 = pList2->GetListHead(); Node<int>* p = RebuildArray(pHead1, pHead2); }
将链表换成数组做简单的循环和递归测试
(1)循环实现
void RebuildArray(int *a, int nLen1, int *b, int nLen2, int *pNew) { if (NULL == a || NULL == b || 0 == nLen1 || 0 == nLen2 || NULL == pNew) { return; } int nIndex = 0; int i = 0; int j = 0; while (i < nLen1) { while (j < nLen2) { if (a[i] <= b[j]) { pNew[nIndex++] = a[i++]; break; } else { pNew[nIndex++] = b[j++]; } } } while(i < nLen1) { pNew[nIndex++] = a[i++]; } while(j < nLen2) { pNew[nIndex++] = b[j++]; } }
(2)递归实现
void RebuildArray_2(int *aStart, int *aEnd, int *bStart, int *bEnd, int *pNew) { if (aStart > aEnd) { *pNew = *bStart; return; } else if (bStart > bEnd) { *pNew = *aStart; return; } if (*aStart <= *bStart) { *pNew = *aStart; RebuildArray_2(aStart+1, aEnd, bStart, bEnd, pNew+1); } else { *pNew = *bStart; RebuildArray_2(aStart, aEnd, bStart+1, bEnd, pNew+1); } } void RebuildArray_1(int *a, int nLen1, int *b, int nLen2, int *pNew) { if (NULL == a || NULL == b || 0 == nLen1 || 0 == nLen2 || NULL == pNew) { return; } int *aStart = a; int *aEnd = &a[nLen1 - 1]; int *bStart = b; int *bEnd = &b[nLen2 - 1]; RebuildArray_2(aStart, aEnd, bStart, bEnd, pNew); }